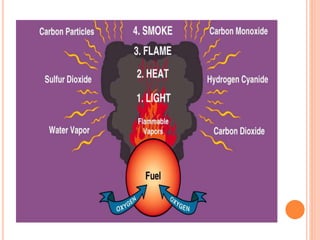
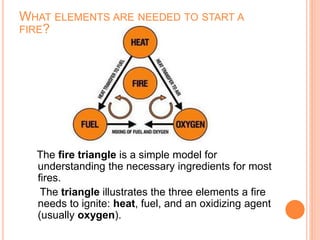
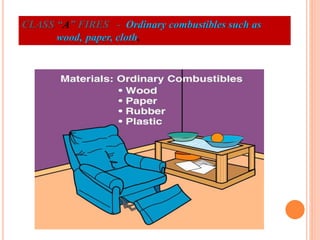
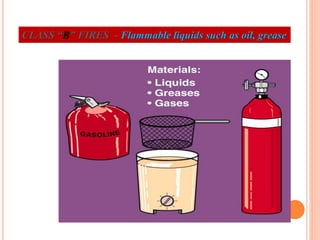
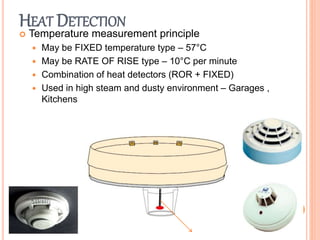
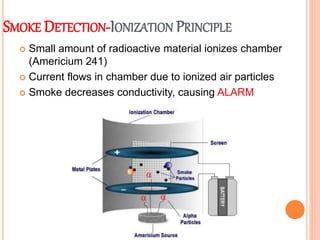
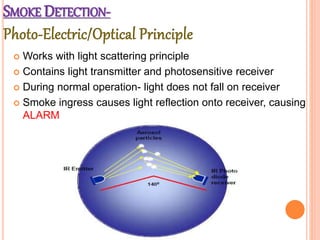
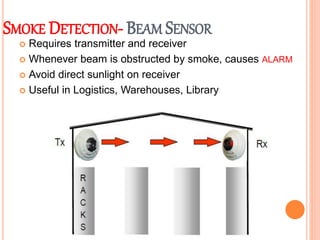
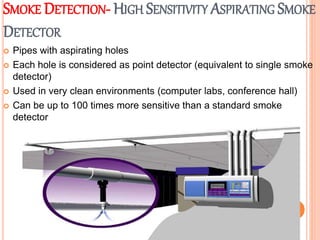
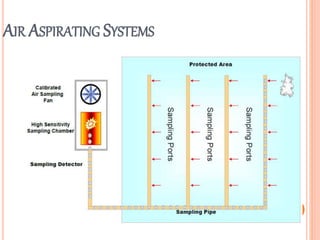
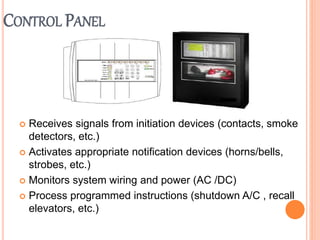
Fire is a chemical reaction that requires heat, fuel, and oxygen. There are four main classes of fire based on the type of fuel involved - Class A involves ordinary combustibles like wood and paper, Class B involves flammable liquids, Class C involves flammable gases, and Class D involves flammable metals. A fire alarm system uses detection devices like heat detectors and smoke detectors to detect fires, and alarm devices like sounders to alert people. It also requires control panels to receive signals and activate notifications. Common fire extinguishers are rated based on the types of materials they can extinguish. Buildings also use sprinkler systems, which activate individual sprinkler heads as they heat up from a fire. Regular maintenance