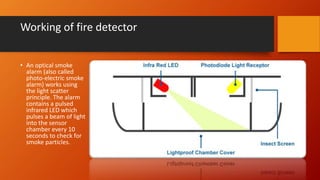
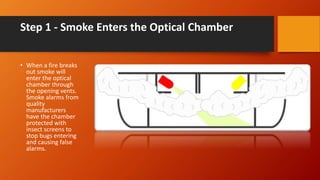
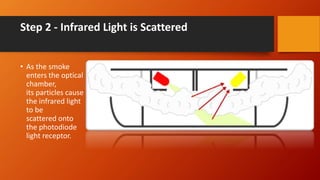
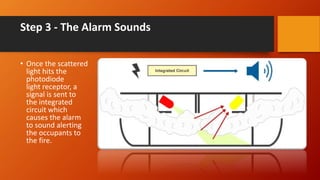
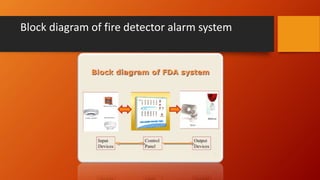
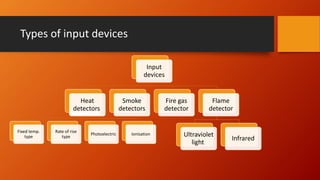
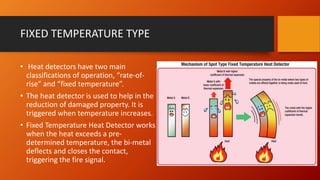
The document discusses fire detection and alarm systems. It defines intelligent buildings and outlines key features of fire detection systems such as detecting fires early and notifying occupants. It describes the working of optical smoke alarms and different types of input devices like heat, smoke and flame detectors. The document also explains how fire alarm systems function, including output devices like sounders and beacons. Finally, it discusses factors that influence the layout and cost of commercial fire detection and alarm systems.