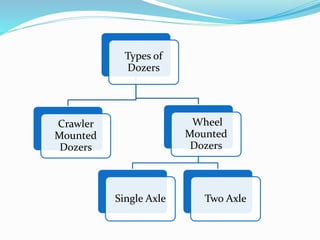
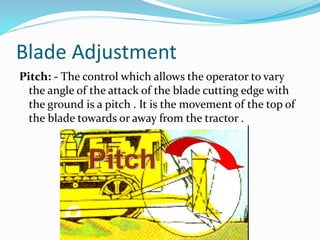
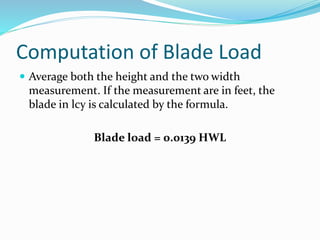
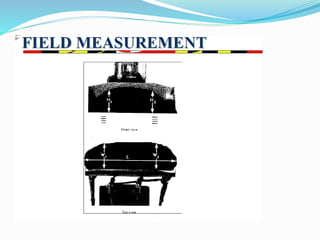
This document discusses dozers and their uses in construction. It describes different types of dozers, including crawler dozers and wheel dozers. It explains that dozers are used for tasks like land clearing, dozing, ripping, and towing equipment. The document discusses how a dozer's blade can be adjusted through tilt, pitch, and angling. It also provides methods for estimating a dozer's production rate based on blade type, material conditions, and cycle time, including measuring blade loads in the field.