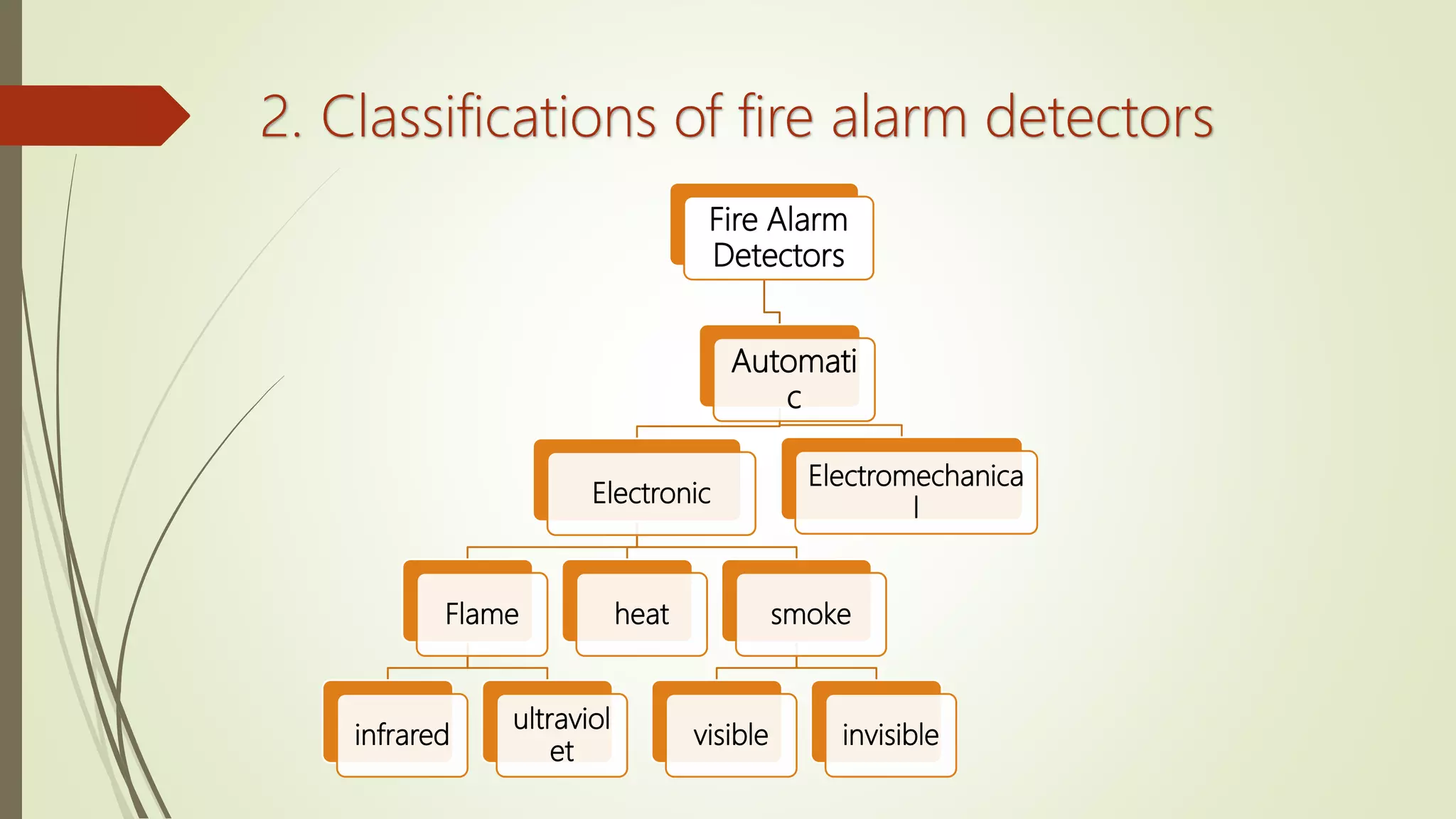
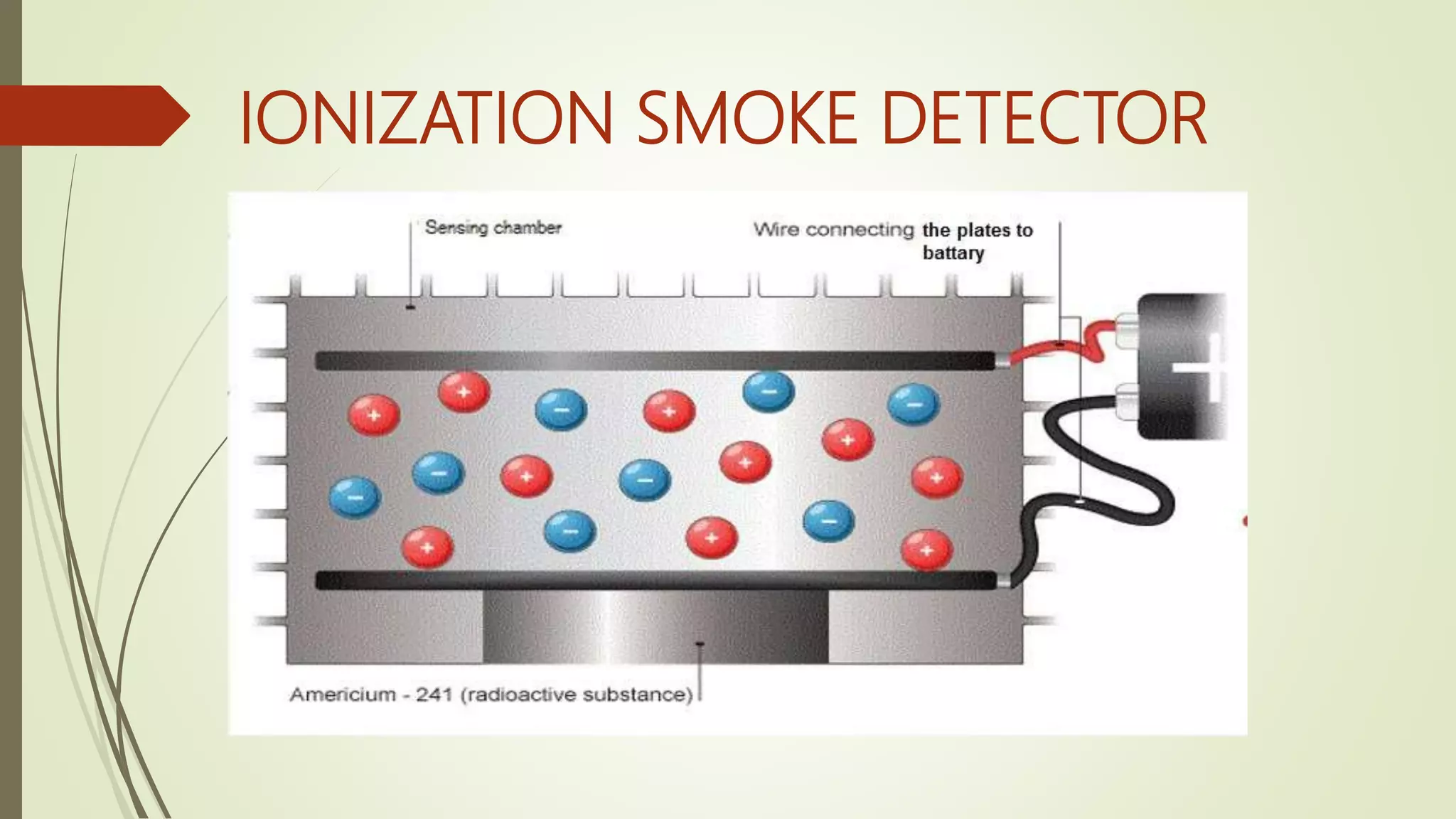
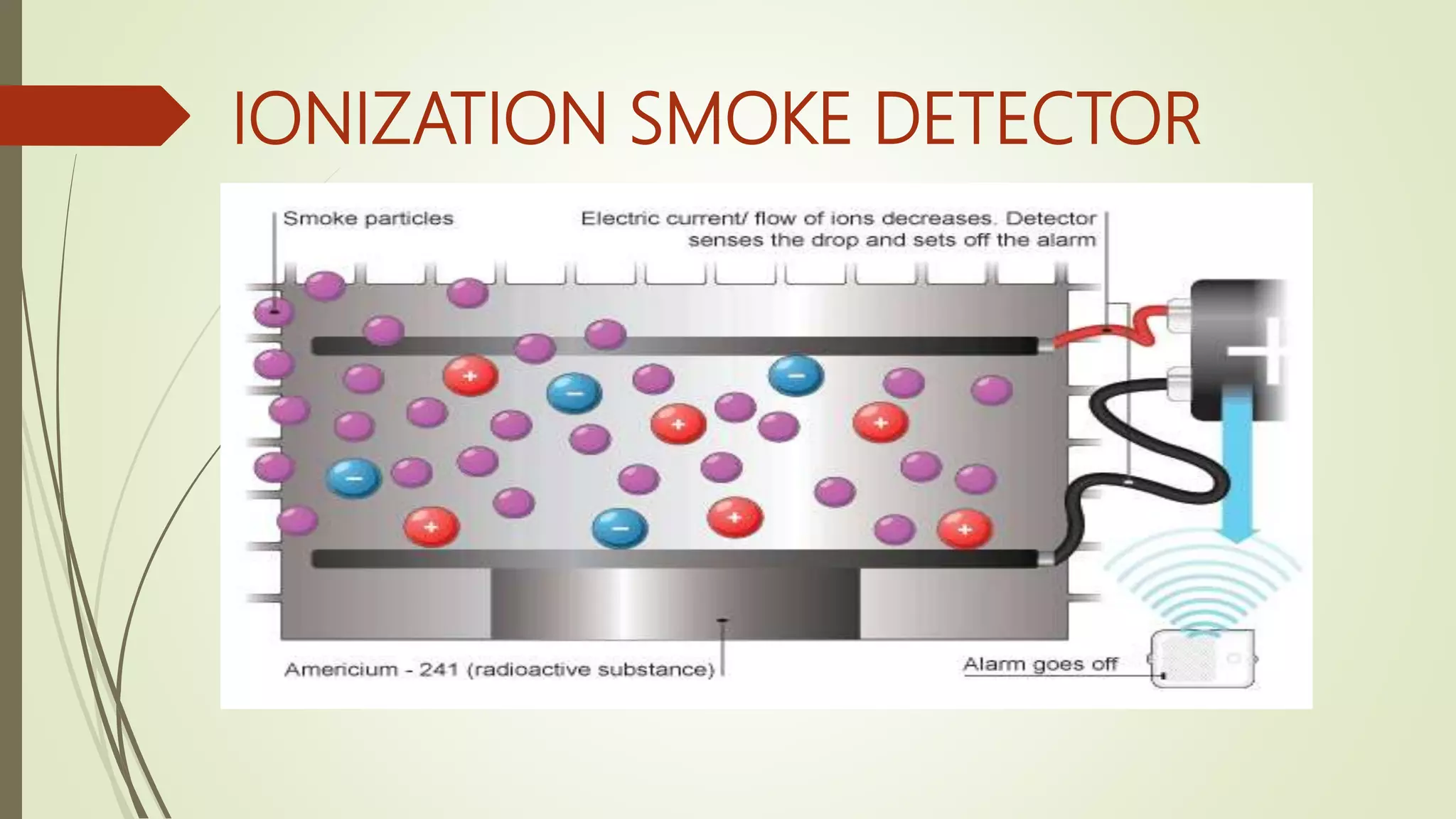
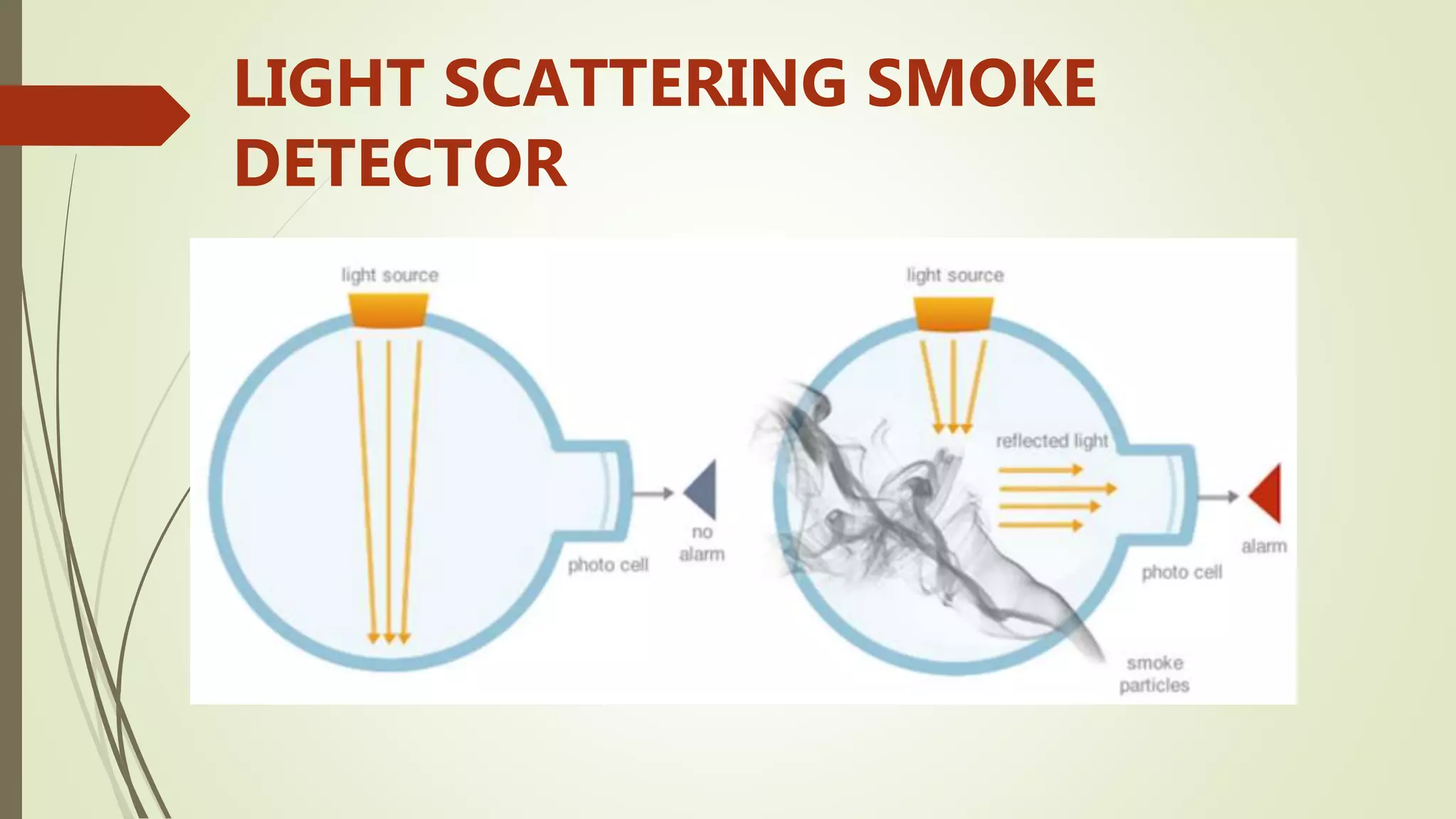
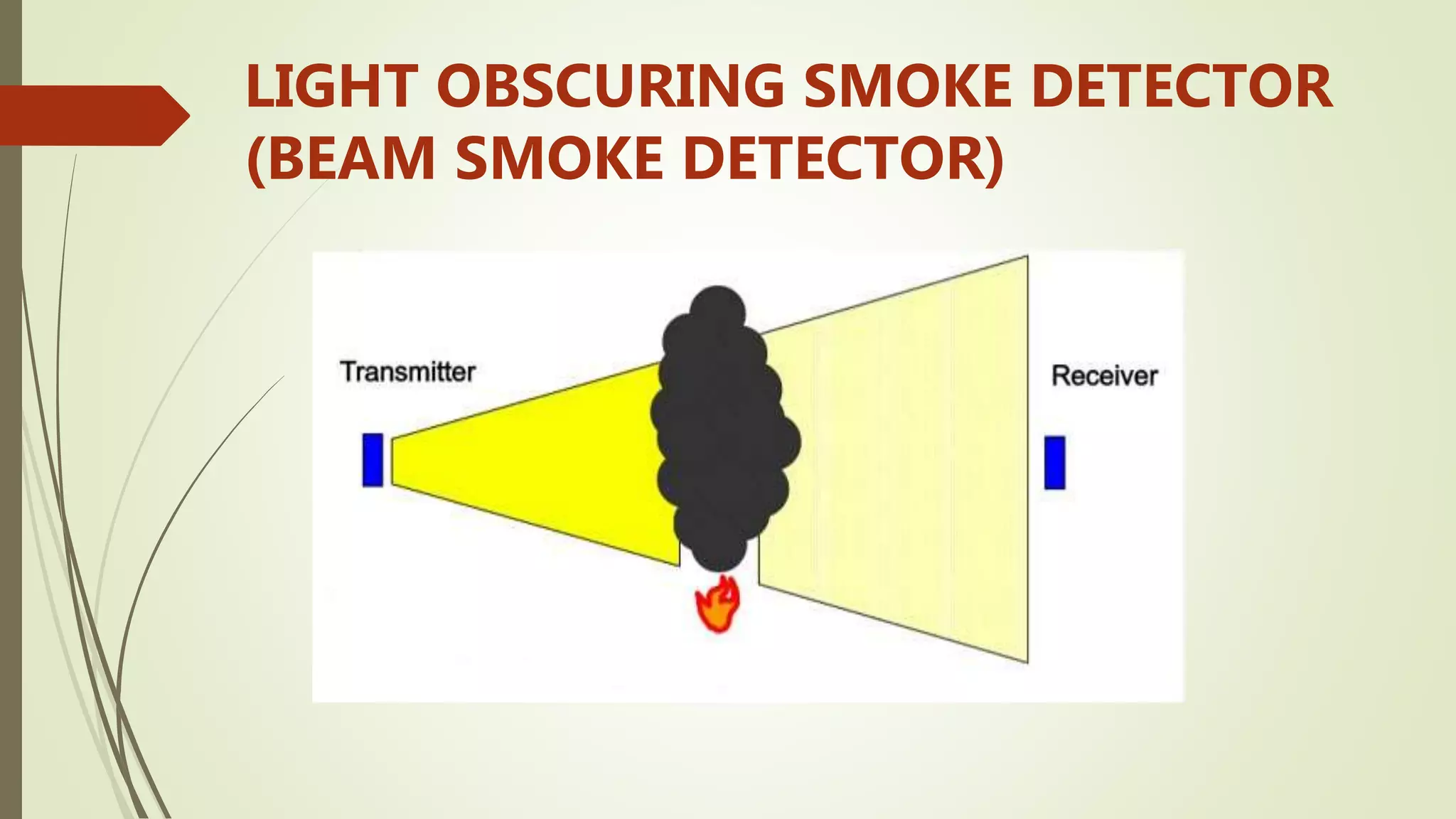
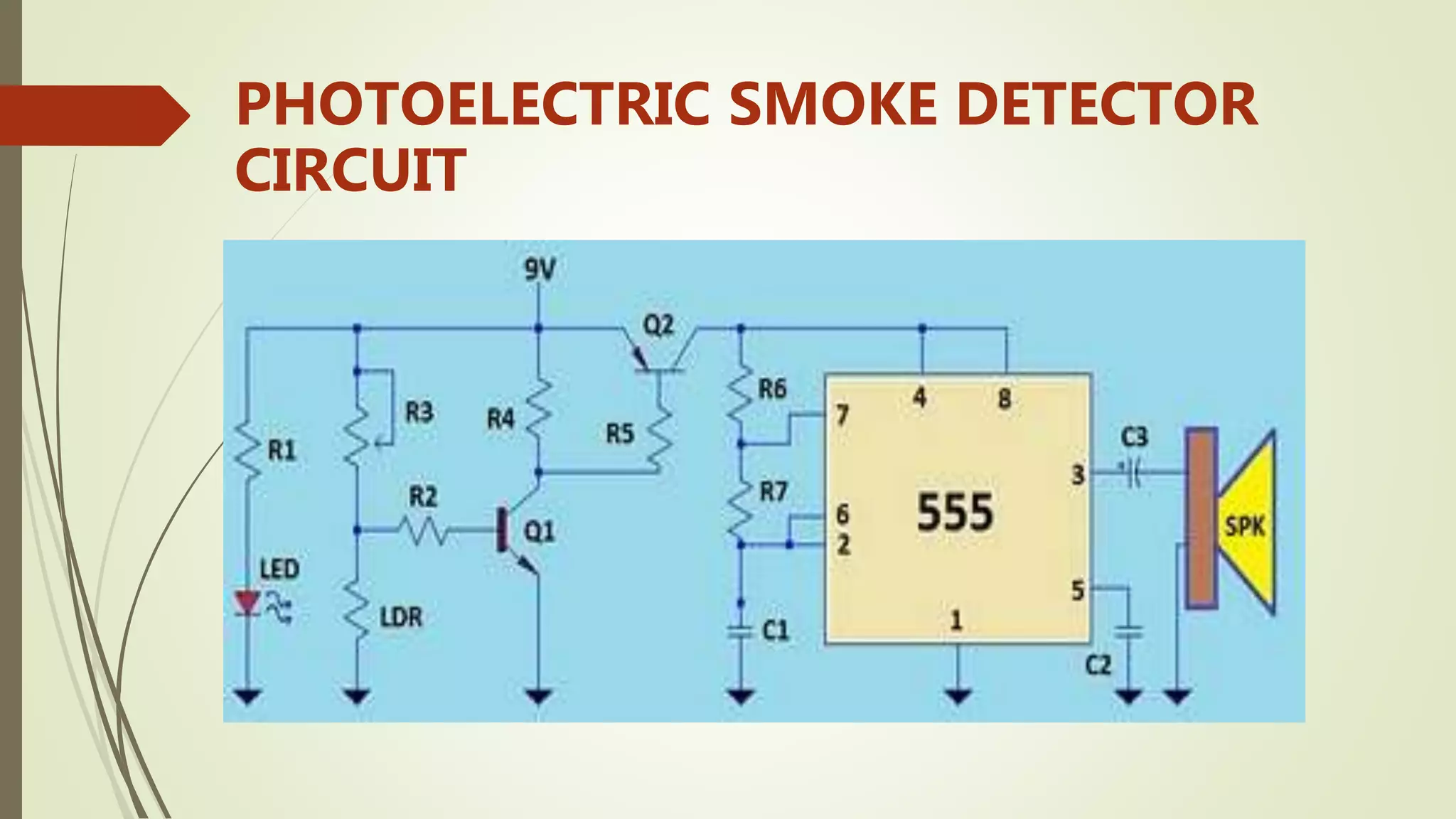
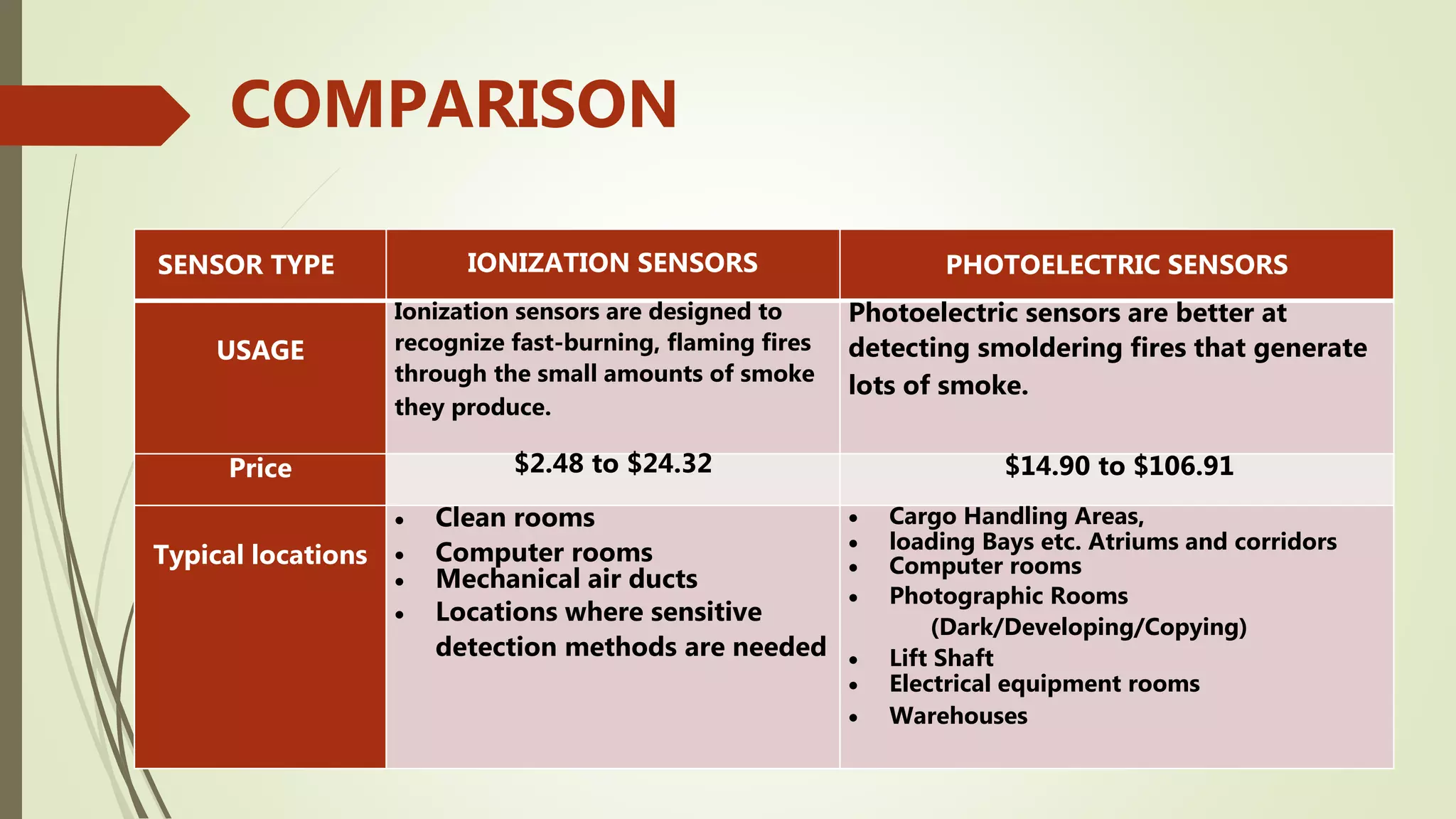
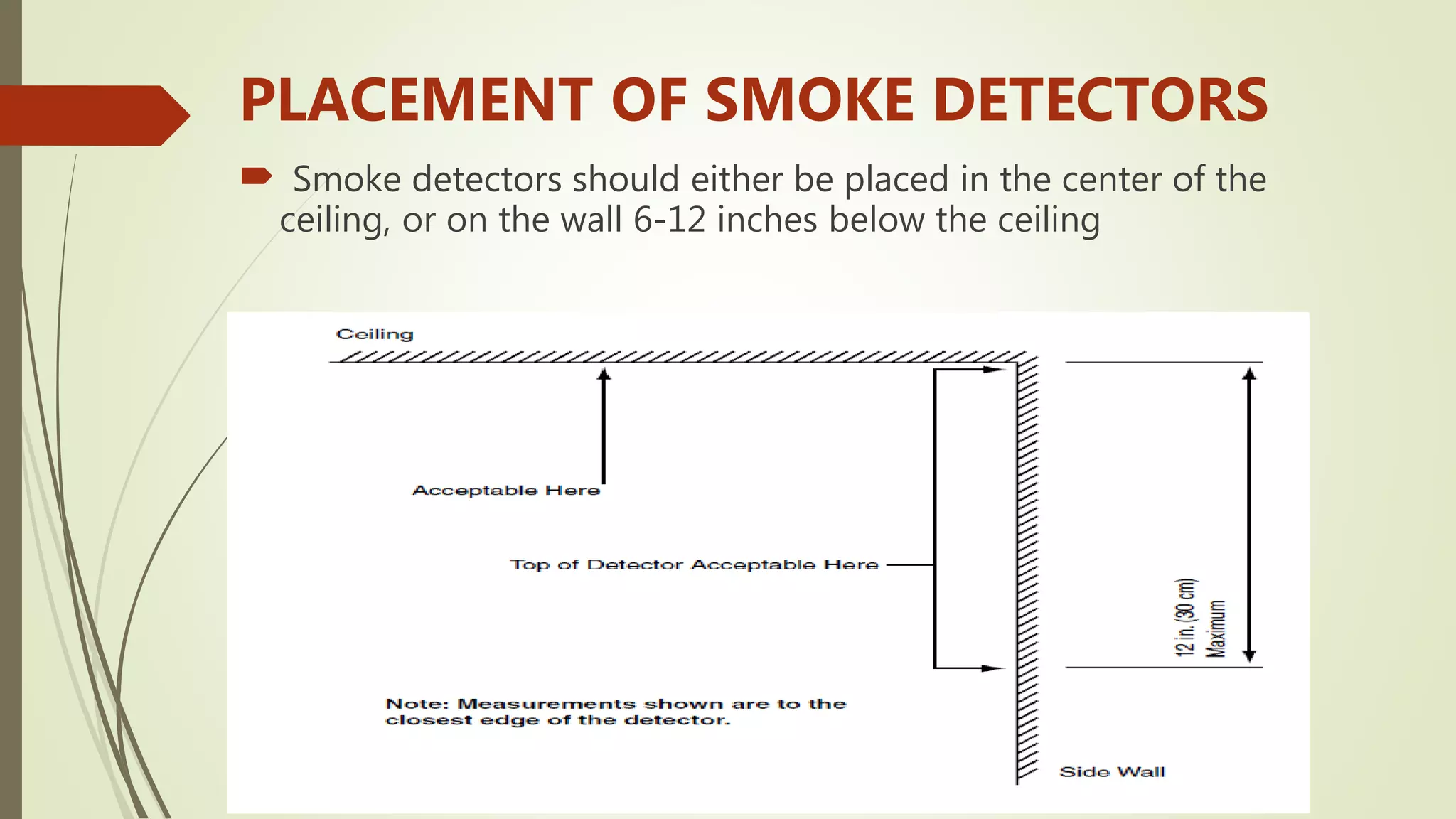
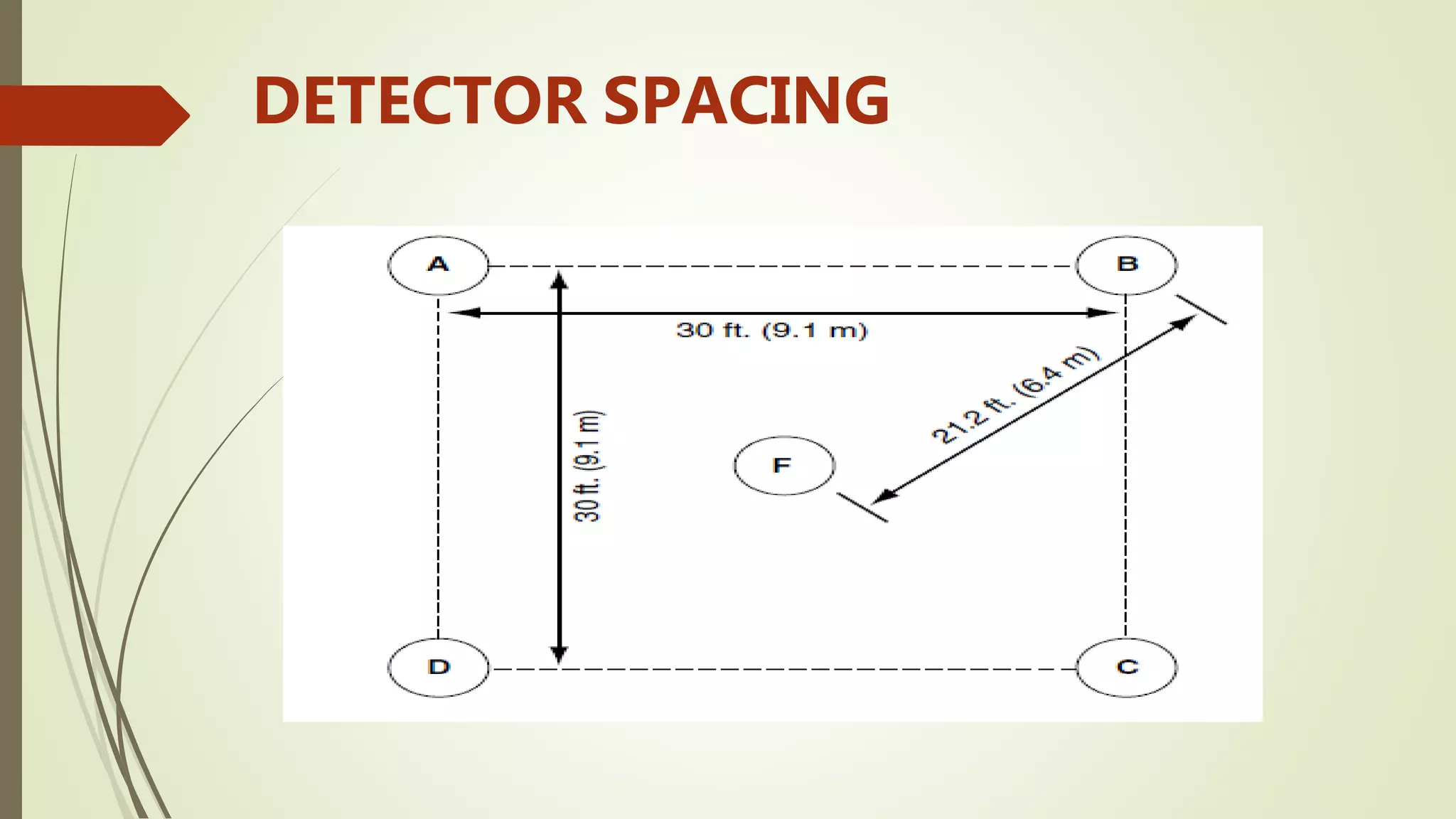
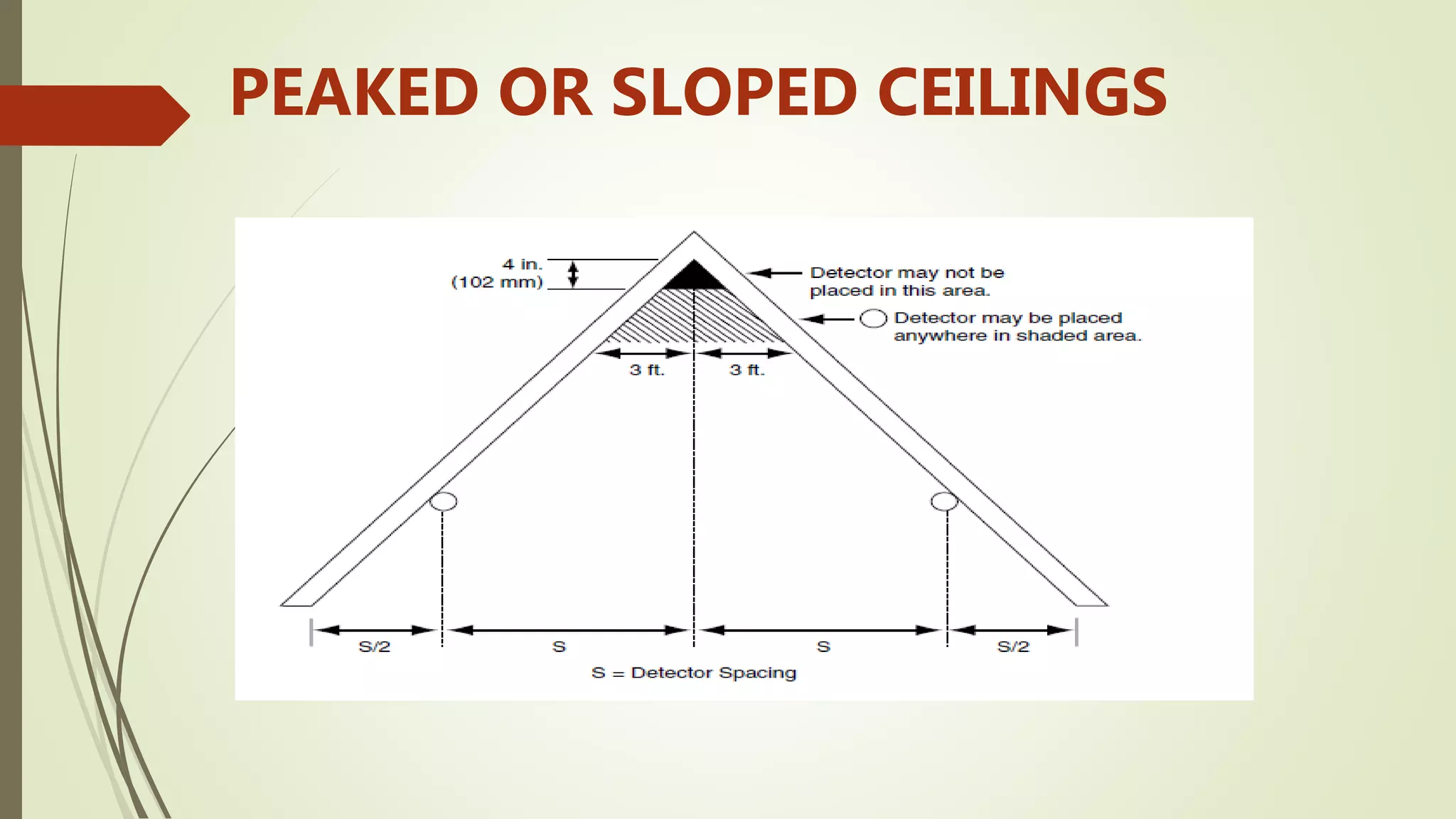
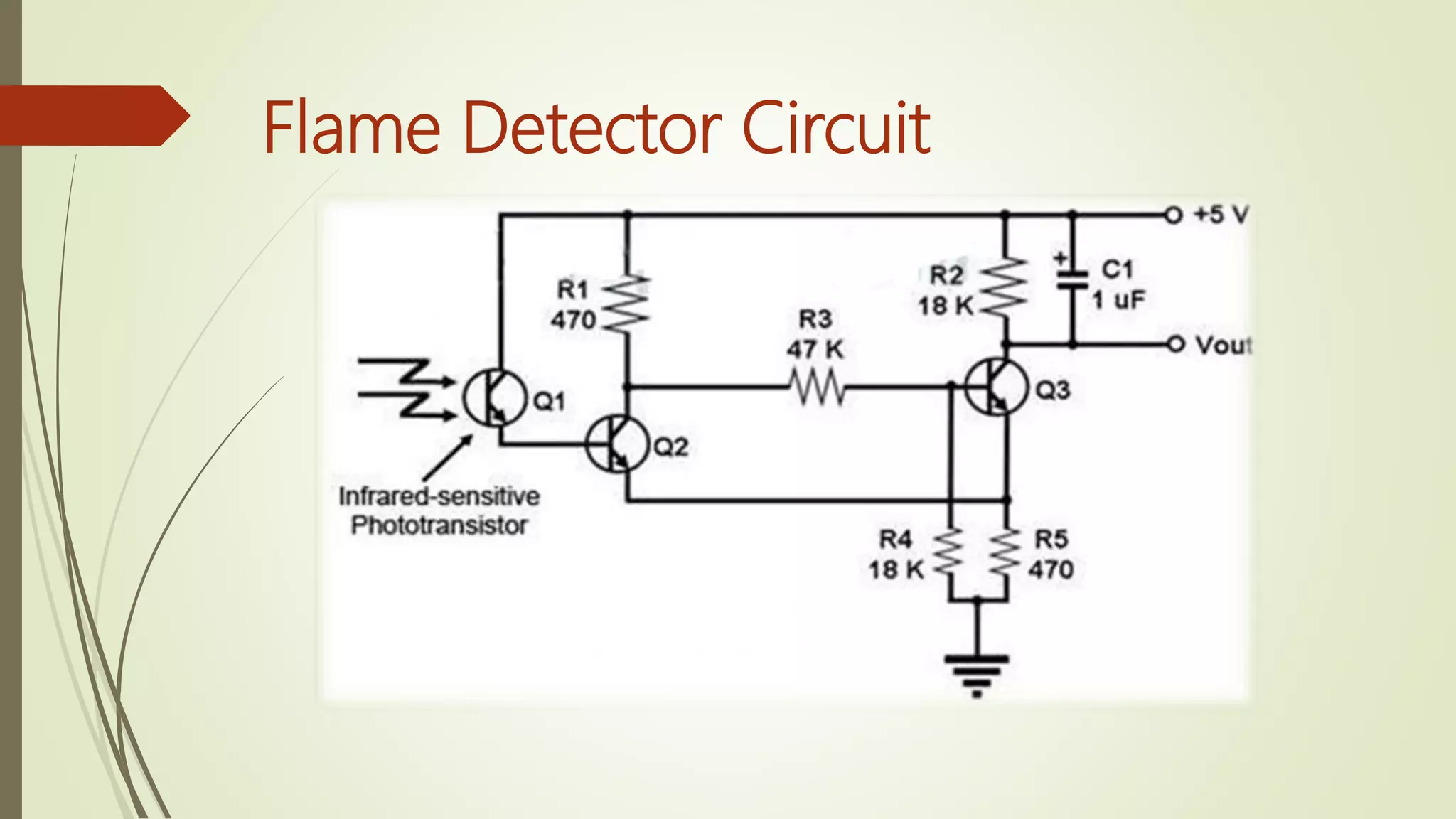
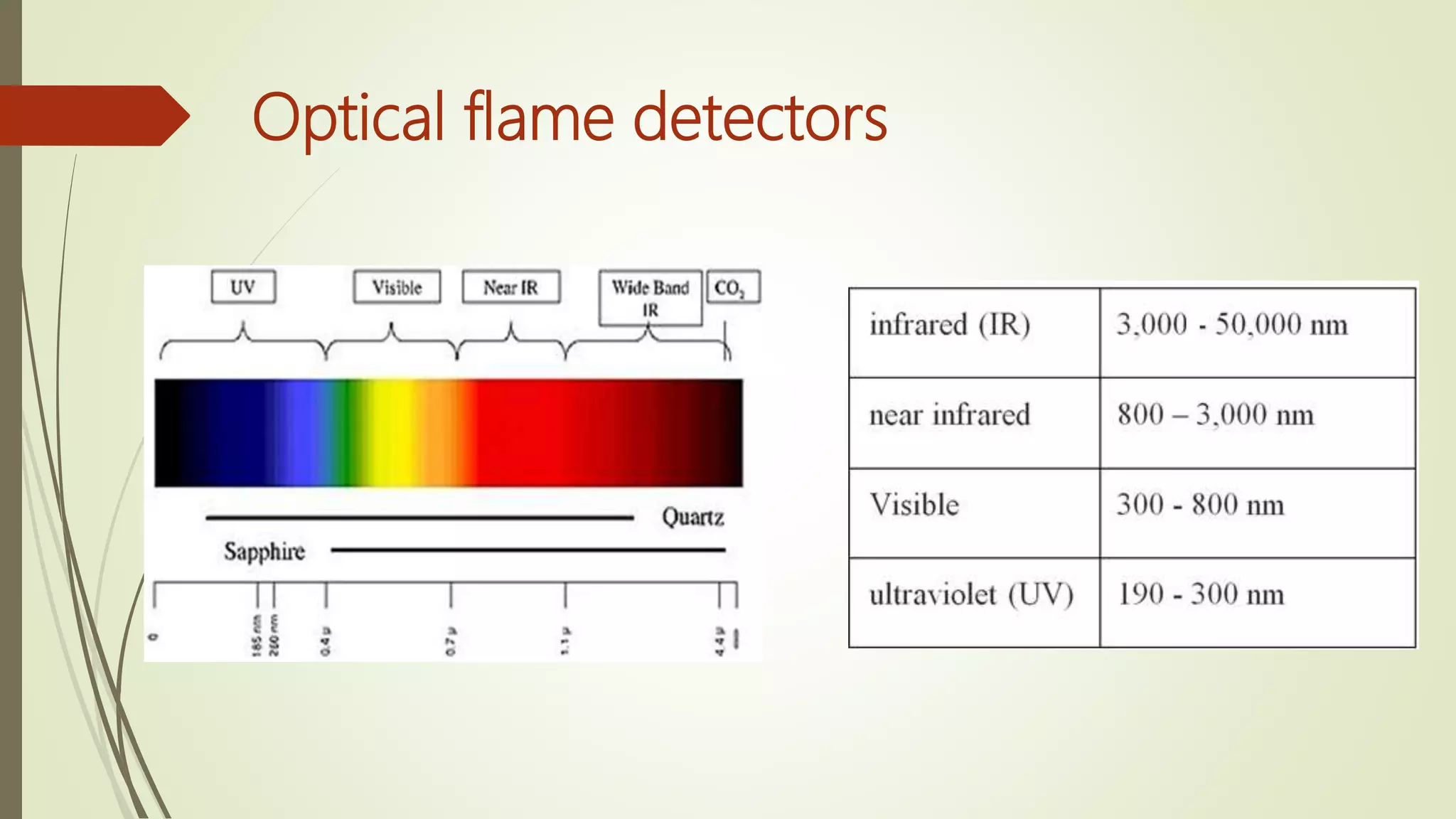
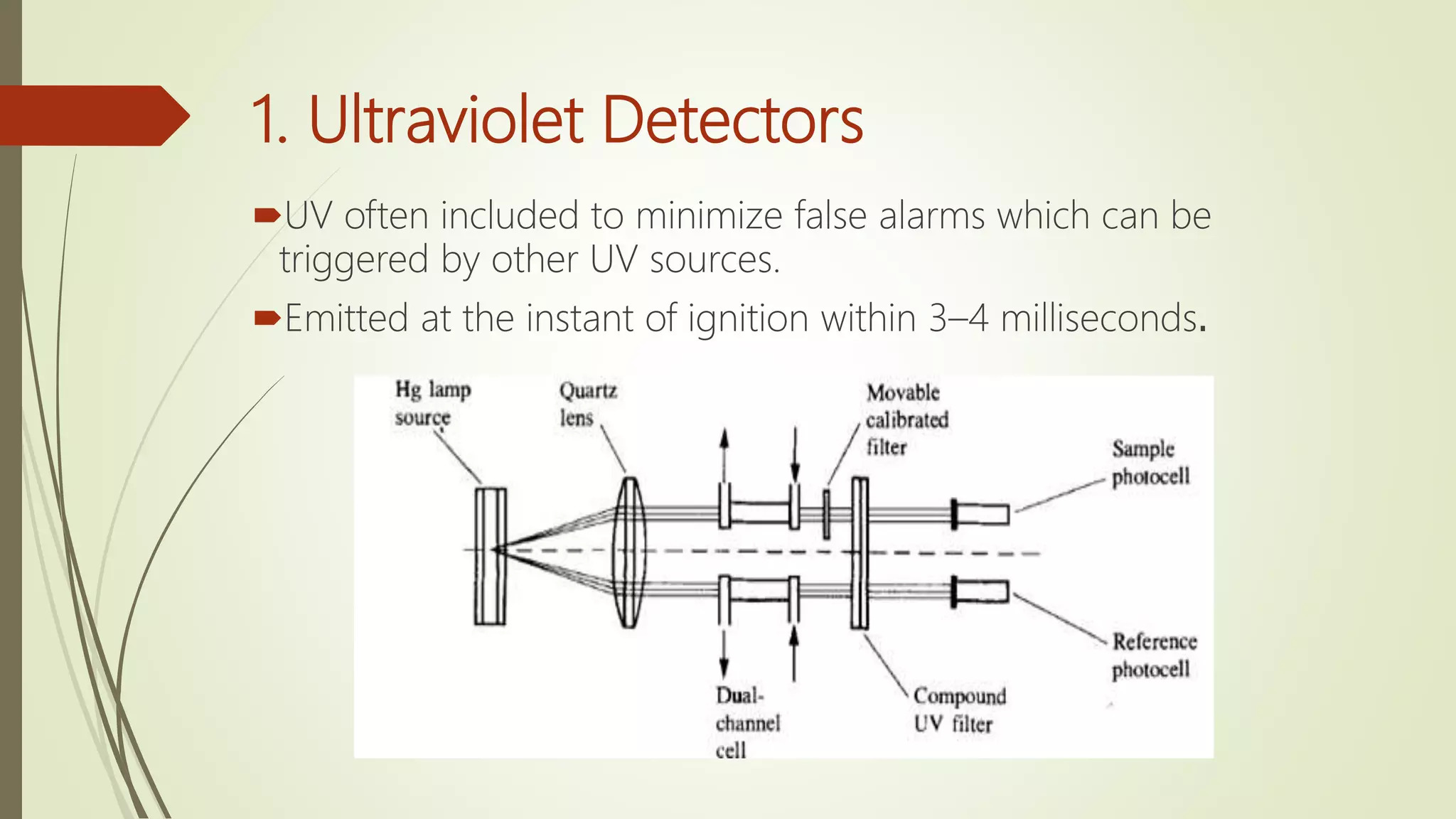
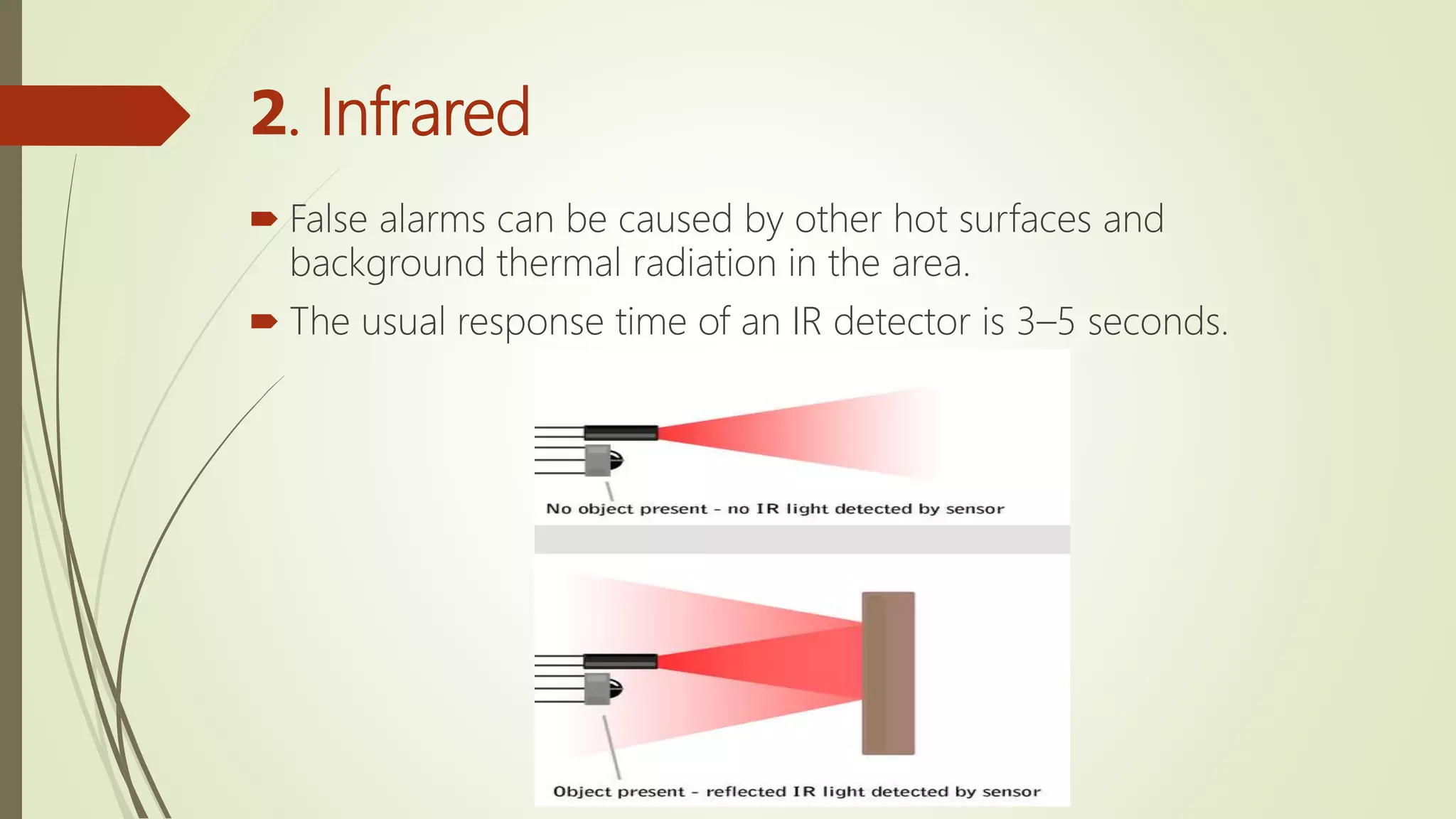
Fire alarm systems are installed to detect fires and notify occupants and emergency services. The document discusses the basic components of fire alarm systems including detectors, notification appliances, and control panels. It describes different types of smoke detectors including ionization and photoelectric, and flame detectors. Placement and spacing of smoke detectors is also covered. The summary provides a high-level overview of the key topics and components discussed in the document.