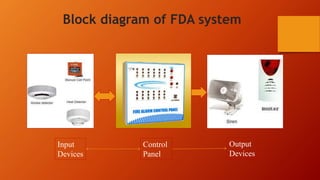
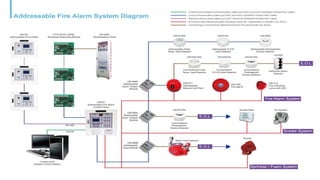
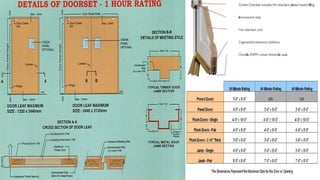
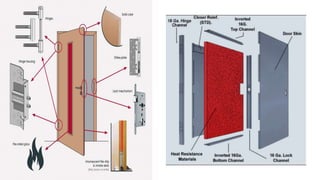
This document discusses different types of fire spread including internal, surface, and structure fire spread as well as external fire spread between buildings. It also discusses factors that influence each type of spread such as material properties, compartmentation, and roof coverings. The document then summarizes input and output devices for fire detection and alarm systems including manual pull stations, heat, smoke, flame, and gas detectors as well as how they function. It also provides a block diagram of a typical fire detection and alarm system. Finally, it briefly discusses smoke and heat venting systems and their components as well as sprinkler systems and classifications of fire extinguishers.