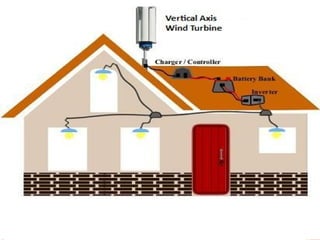
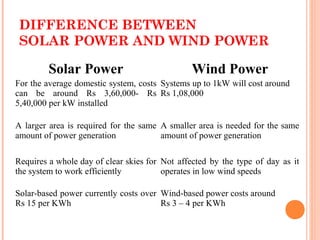
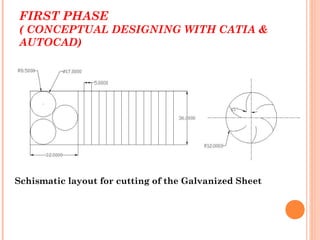
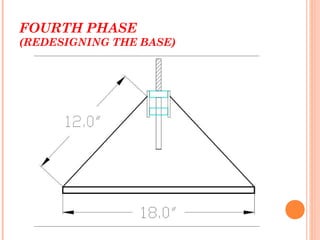
This document describes a student project to design and build a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT). It provides background on wind energy and different types of wind turbines. It then details the design and construction process for the VAWT, including conceptual designs, fabrication of blades and supports, and testing specifications. The summary concludes that VAWTs provide an efficient and low-cost way to harness wind power for small-scale energy production.