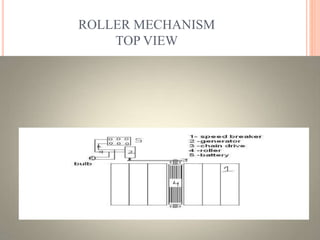
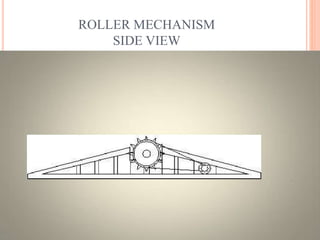
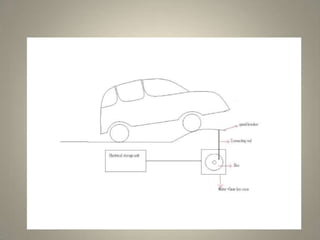
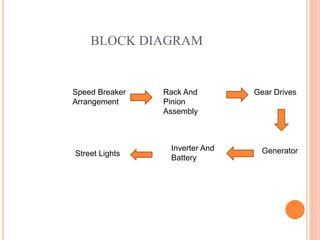
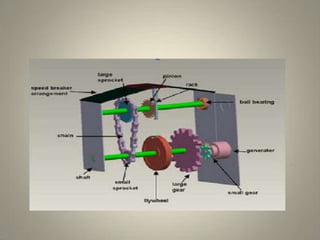
The seminar discusses a method of generating electricity from the energy dissipated at speed breakers using various mechanisms like roller, crank-shaft, and rack-pinion systems. It aims to lower energy costs, utilize readily available energy, and reduce the load on the national grid by converting potential energy from vehicles into electrical power. The presentation emphasizes the efficiency of the rack-pinion system and suggests future enhancements to improve power generation, advocating for implementation in India to address energy crises.