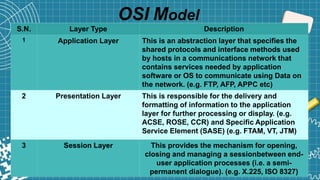
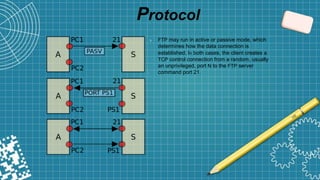
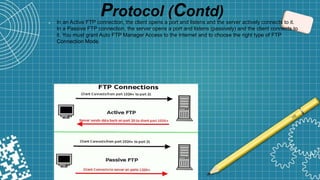
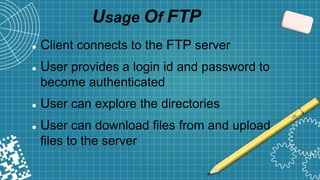
FTP is a standard network protocol used to transfer files between a client and server. It uses separate control and data connections and operates at the application layer of the OSI model. FTP supports both active and passive modes of connection. While FTP allows transferring multiple files and directories with resume capability, it has security issues as usernames, passwords and files are sent in clear text.