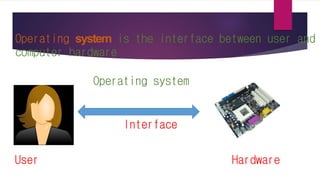
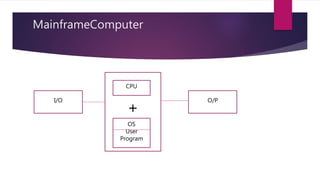
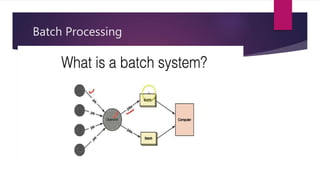
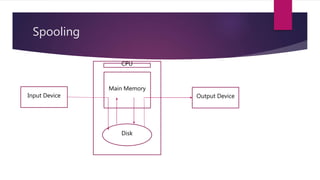
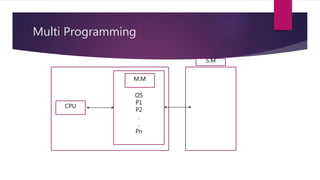
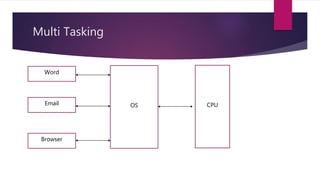
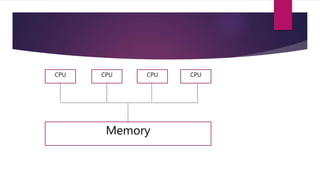
The document discusses the evolution of operating systems from early mainframe systems to modern personal computers. It describes how early operating systems facilitated batch processing on mainframes using punch cards for input/output. Later, developments like multiprogramming, time-sharing, and multiprocessing increased CPU utilization and allowed multiple users/processes. Modern operating systems build on these foundations, with the first PC operating system being DOS and early versions of Windows sitting on top of DOS.