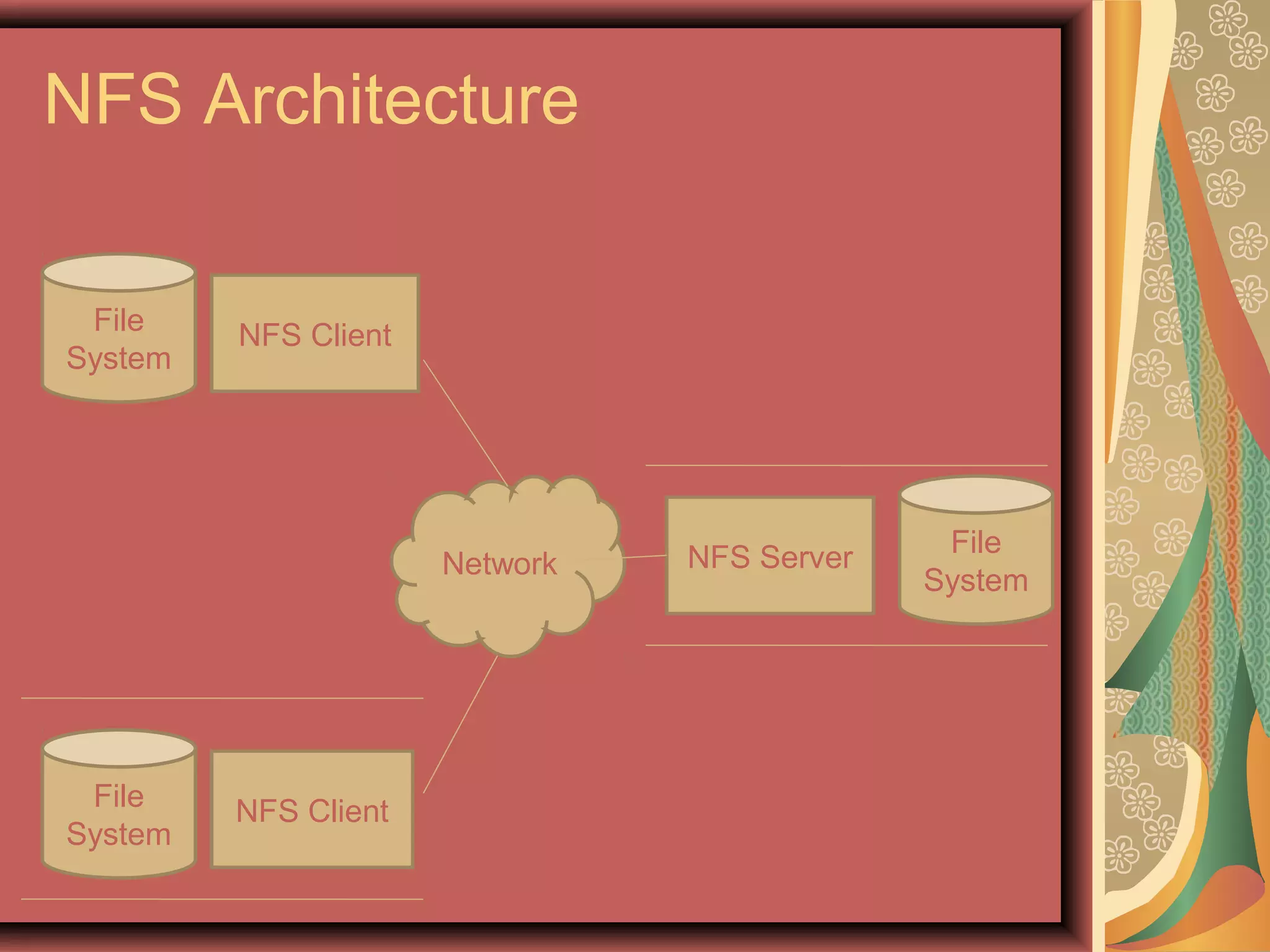
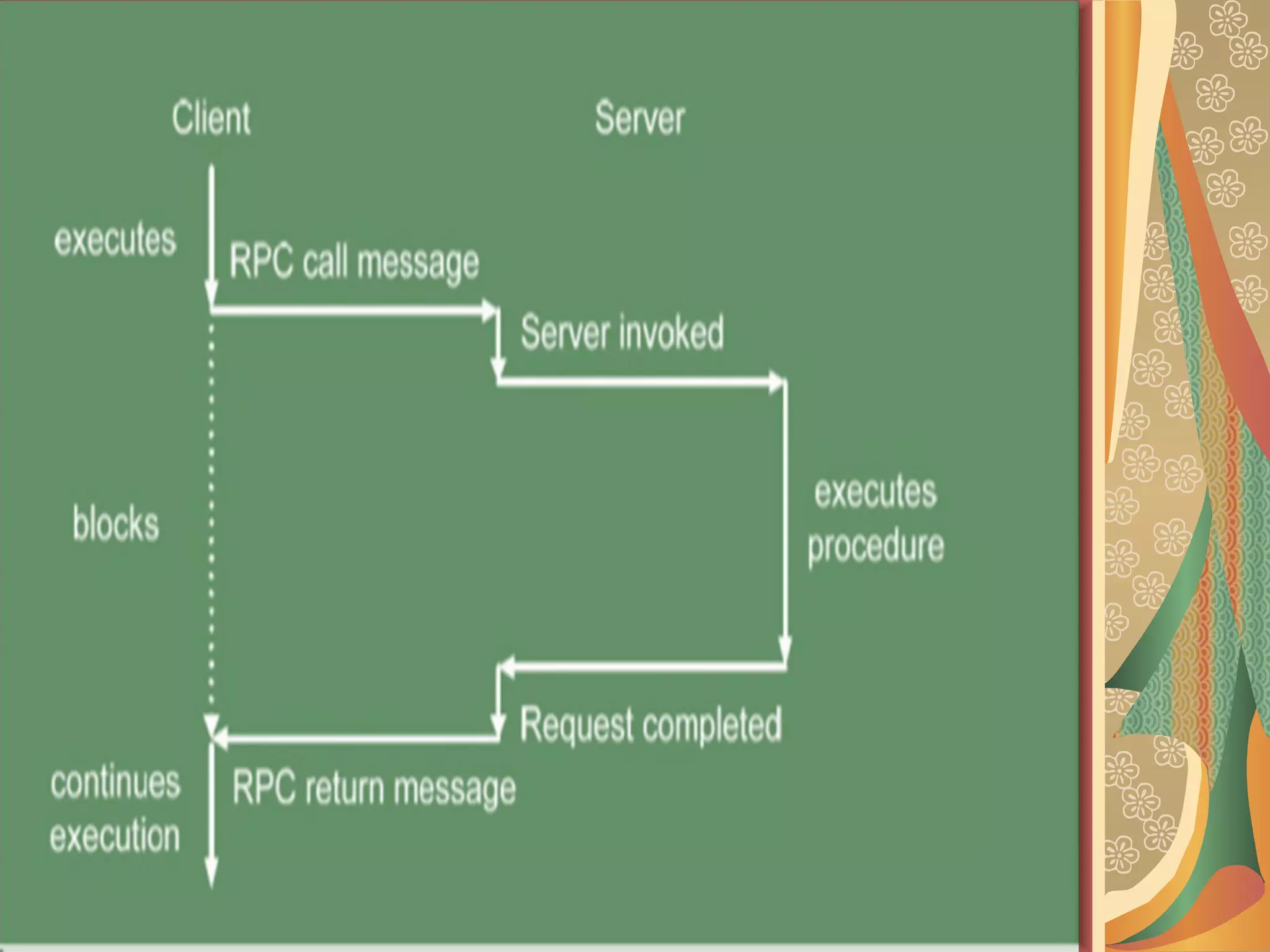
Network File System (NFS) allows users to access and share files located on remote computers. It builds on ONC RPC and has evolved through several versions. NFS uses a client-server model where the client makes RPC requests to access files on the NFS server's file system. This allows for flexible sharing of resources but introduces some security and performance disadvantages compared to a local file system. Overall NFS is a widely used distributed file system protocol.