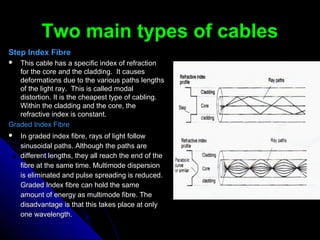
Fibre optics is a system that uses glass or plastic threads to transmit data by light signals. It has several advantages over metal cables like greater bandwidth capacity and lighter weight. Fibre optic systems work by converting electrical signals to infrared light signals that are transmitted through the fibre optic cable and then back to electrical signals. There are two main types of fibre optic cables that differ in how they transmit light signals to reduce distortions. While fibre optics provides huge benefits, there are also installation challenges and the cables can be fragile. It is poised to revolutionize communication systems with its ability to transmit huge volumes of data and will likely become the primary method of data transmission.