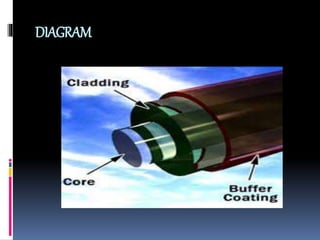
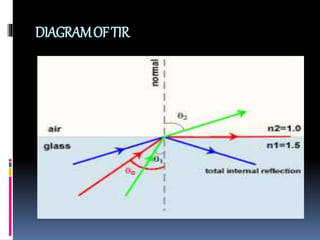
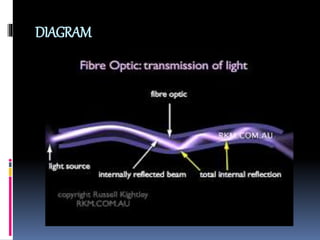
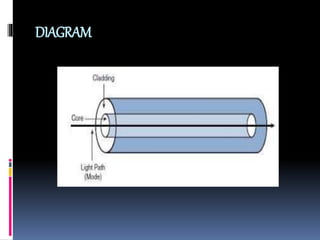
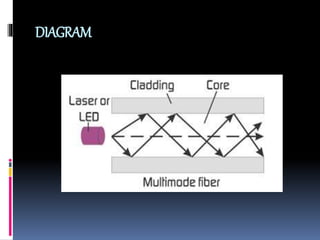
This document discusses optical fiber and its advantages. It defines optical fiber as long, thin strands of pure glass that transmit light signals over long distances. It describes the evolution of optical fiber from the 1880s to its use as the backbone of long distance telephone networks in the 1980s. The key components of optical fiber are the core where light travels and the cladding that surrounds the core. Optical fiber works through the phenomenon of total internal reflection, where light bouncing off the cladding remains trapped in the core. The main types are single mode fiber for long distances and multi-mode fiber for shorter runs. Advantages of optical fiber include high bandwidth, low power loss, immunity to interference, small size and weight, safety,