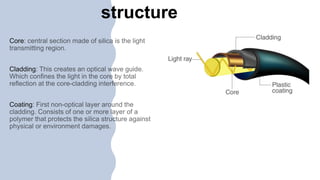
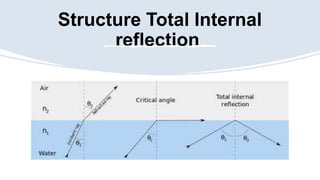
Fiber optics use total internal reflection to transmit data in the form of light pulses through glass or plastic fibers. The fiber consists of a core surrounded by cladding and a protective coating. Data is converted to light signals using a light source like an LED or laser, transmitted through the fiber, and converted back to electrical signals by a photodetector. Fiber optics provide high-speed, stable data transmission unaffected by electromagnetic interference and are used widely in telecommunications and networking.