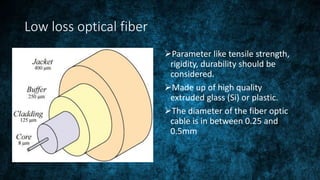
Fiber optic communication uses lightwave technology to transmit data over long distances and local networks. It has three main elements: a compact light source like an LED or laser, low loss optical fiber made of glass or plastic, and a photo detector to convert light signals back to electrical signals. Fiber optic communication works by converting electrical signals to light signals using a light source in the transmitter, carrying the light beam through the fiber optic cable, and converting it back to an electrical signal using a receiver circuit with a photo detector. This allows for gigabit transmission of data, voice, video, and telemetry over longer distances than traditional copper wire networks.