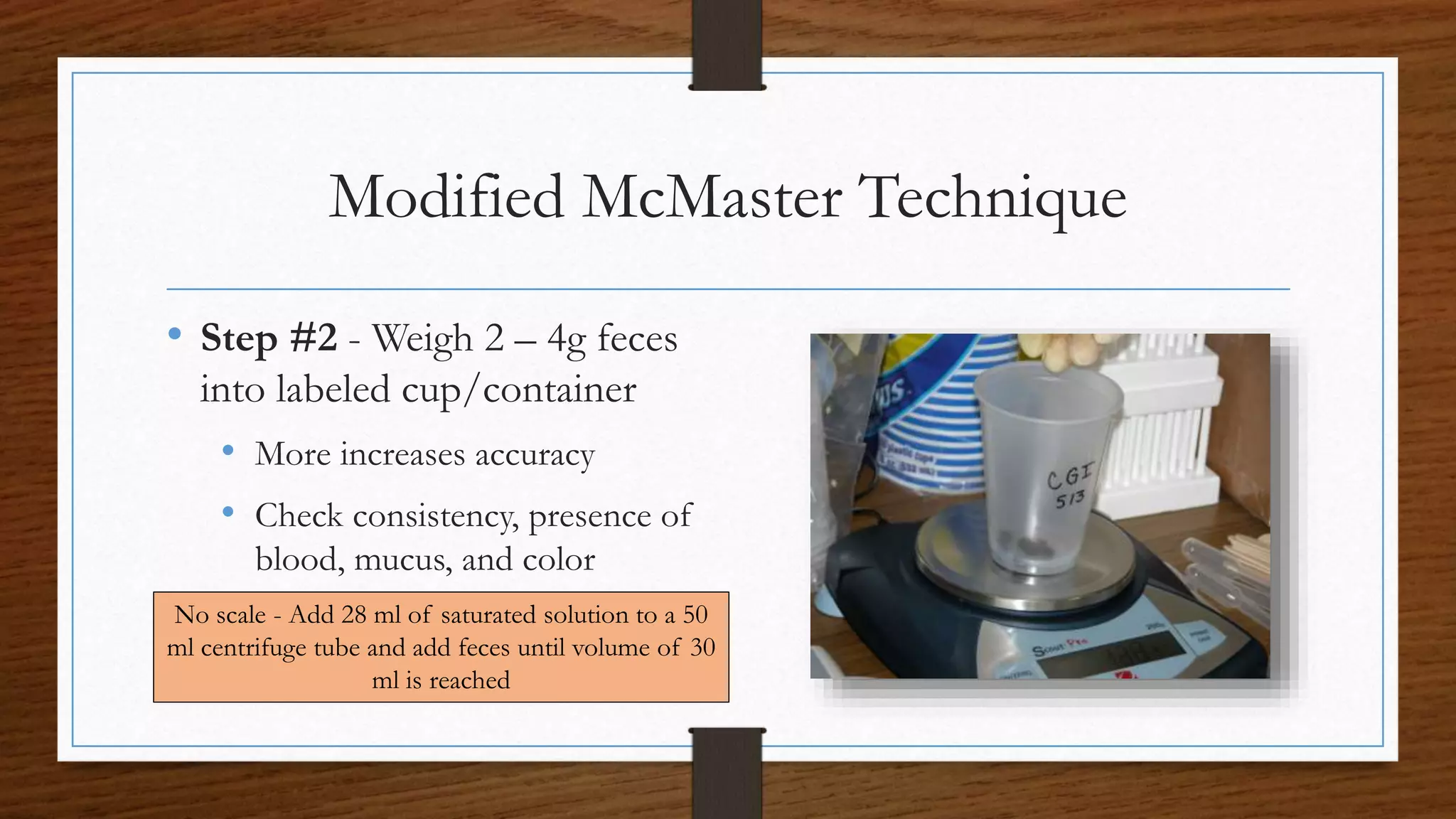
This document provides instructions for performing a fecal egg count (FEC) to quantify the number of parasite eggs present in small ruminant feces. It explains that FEC allows farmers to monitor pasture contamination, assess increases in worm numbers, determine when to move animals, and test for drug resistance. The procedure involves weighing feces, mixing it with a flotation solution, straining the mixture, counting eggs observed under a microscope, and calculating eggs per gram. FEC has limitations as eggs cannot be identified to species level and counts may not be accurate, but it provides a quantitative measure of parasite burden to inform management decisions.