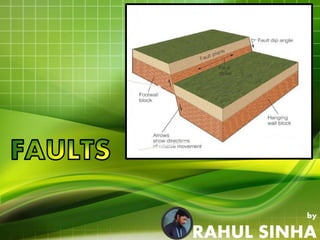
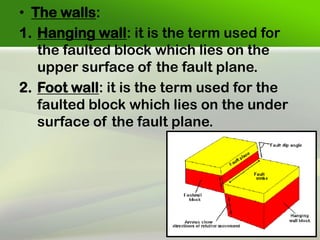
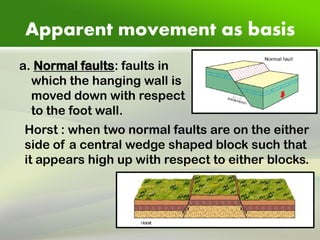
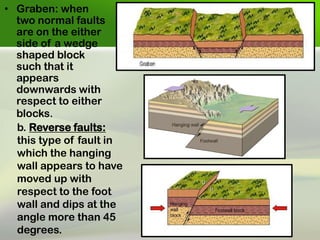
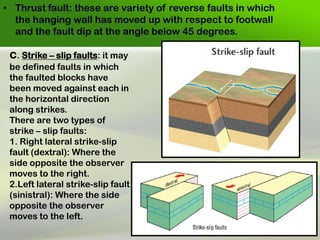
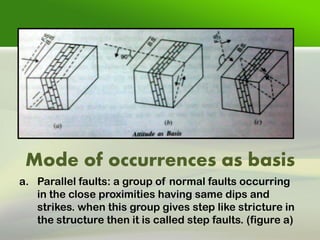
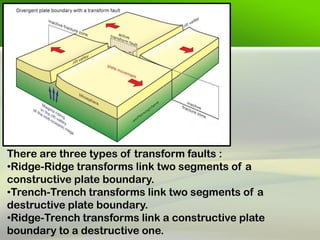
Faults are fractures in rock where there has been relative movement between the two sides. The fault plane is the surface where displacement occurs. The hanging wall is the rock above the fault plane, and the foot wall is below. Slip can be strike slip along the fault strike, dip slip along the dip, or oblique. Faults are classified based on movement, direction of slip, and geometry. Common types are normal faults where the hanging wall moves down, reverse faults where it moves up, and strike-slip faults where movement is horizontal. Faults can impact engineering by weakening foundations and providing pathways for water.