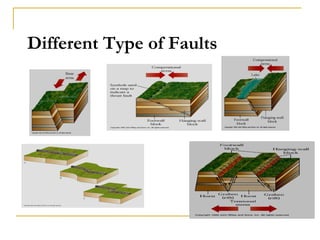
Faults are fractures where there is movement parallel to the fault plane. There are several types of faults including normal faults, thrust faults, strike-slip faults, and transform faults. Normal faults occur when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall, while thrust faults occur when the hanging wall moves up. Strike-slip faults involve lateral movement along the fault plane in either a left-lateral or right-lateral direction. Transform faults specifically link different tectonic plates.




![Strike-Slip FaultStrike-Slip Fault
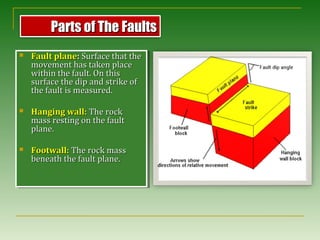
Strike-slip Faults: Are faults
that have movement along
strikes.
There are two types of strike
slip faults:
A] Right lateral strike-slip fault
(dextral): Where the side
opposite the observer moves
to the right.
B] Left lateral strike-slip fault
(sinistral): Where the side
opposite the observer moves
to the left.
Note that the same sense ofNote that the same sense of
movement will also bemovement will also be
observed from the other sideobserved from the other side
of the fault.of the fault.
Strike-SlipStrike-Slip
FaultsFaults](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalfault-150301050250-conversion-gate01/85/Final-fault-8-320.jpg)