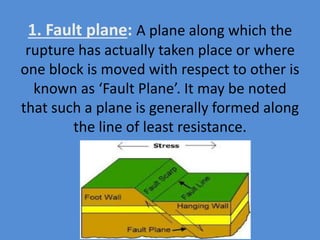
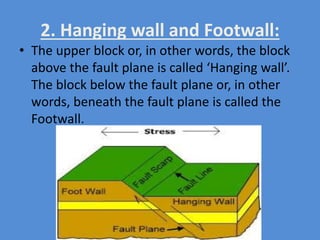
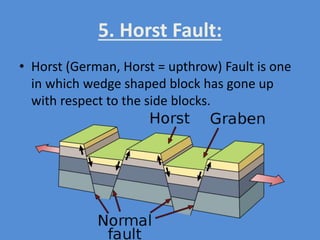
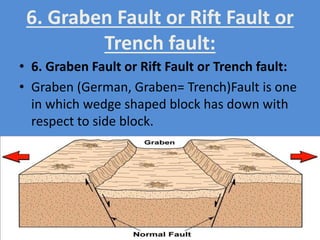
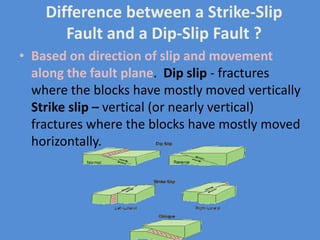
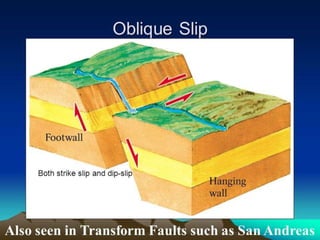
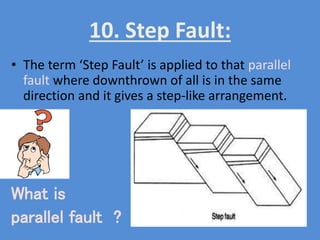
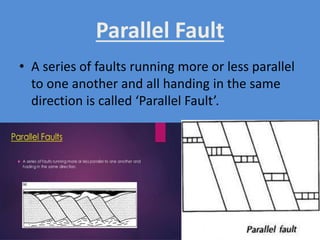
A fault is a fracture along which rocks have moved past each other, characterized by components such as the fault plane, hanging wall, and footwall. Types of faults include normal, reverse, thrust, vertical, dip-slip, strike-slip, oblique-slip, and step faults, each defined by their specific displacements and orientations. Evidence of faulting can be found in lithological and physiographic forms, including slickensides and fault scrapes.