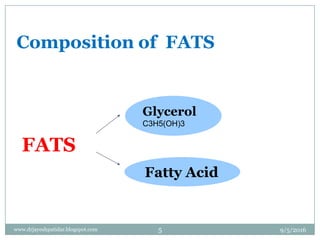
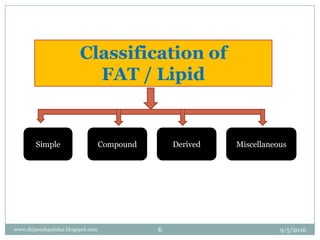
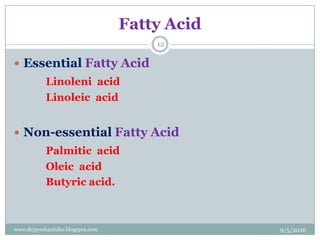
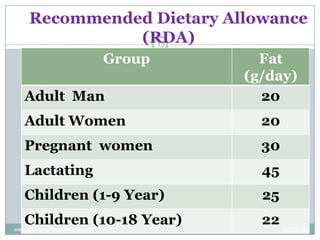
The document discusses fats (lipids), covering their composition, classification, fatty acids, recommended dietary allowance, functions, digestion, metabolism, and storage. It emphasizes the role of fats in providing energy, aiding in the absorption of certain vitamins, and their impact on health, including the distinction between essential and non-essential fatty acids. Additionally, it addresses the consequences of fat deficiency and excess in the diet.