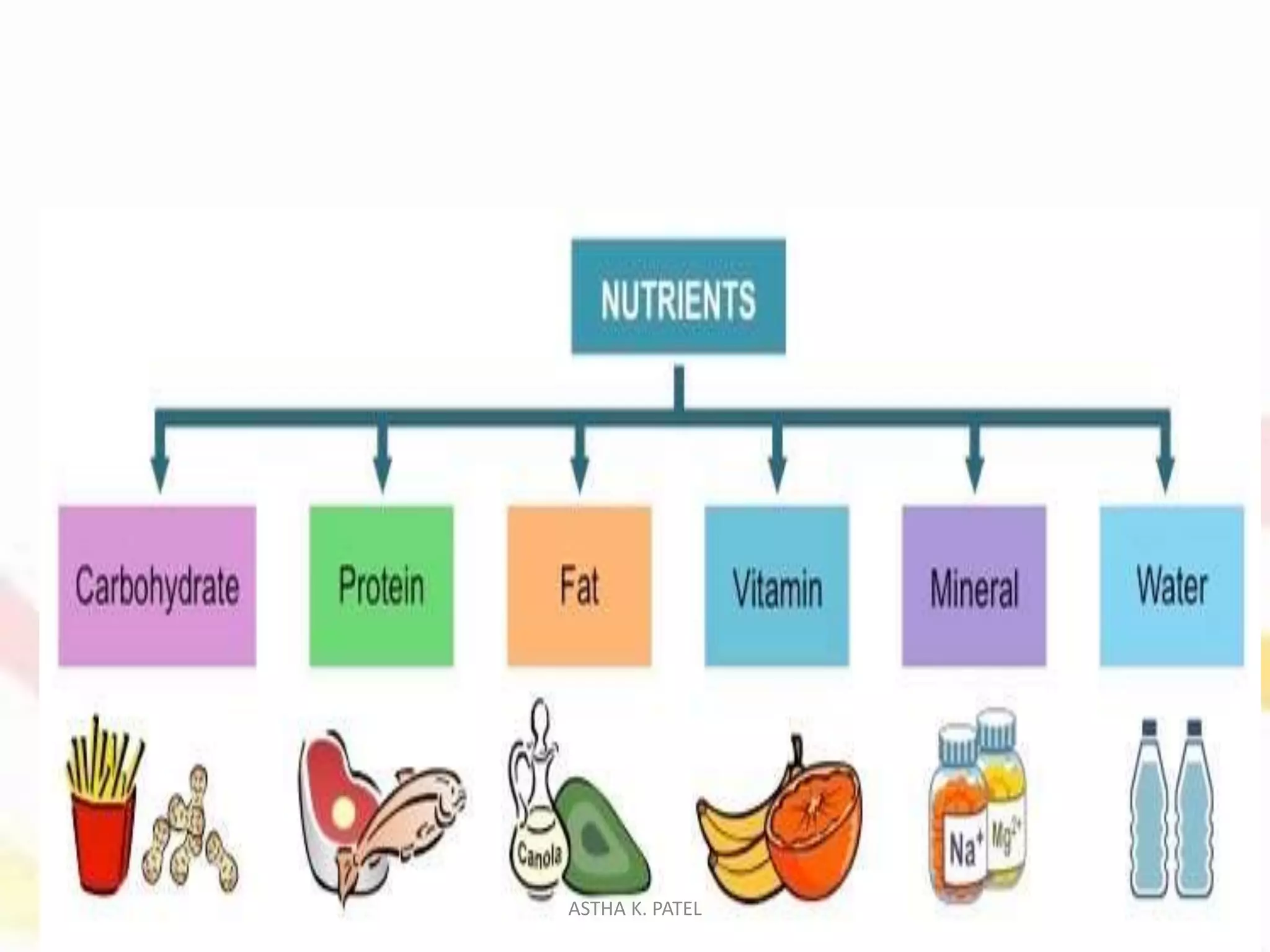
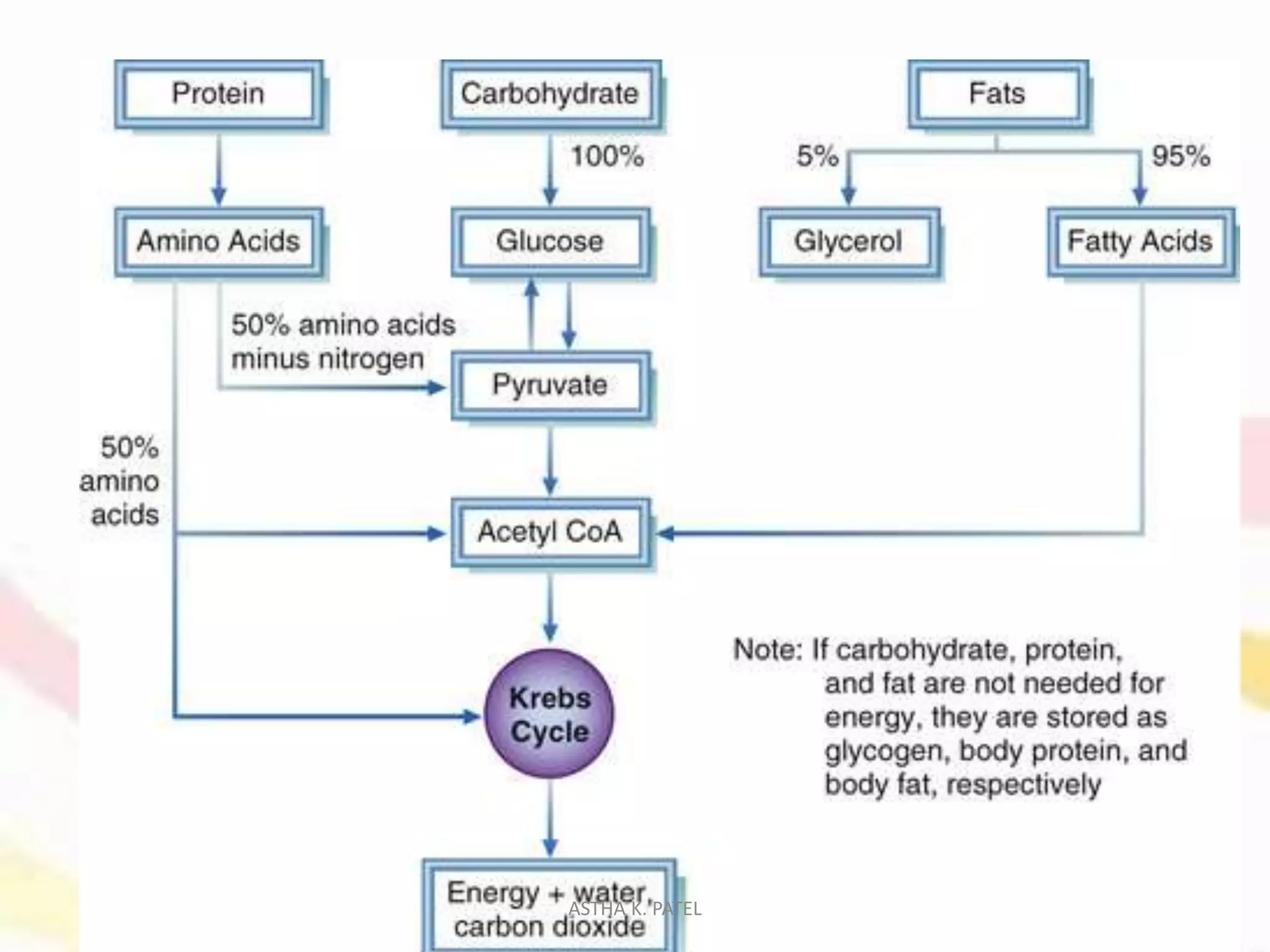
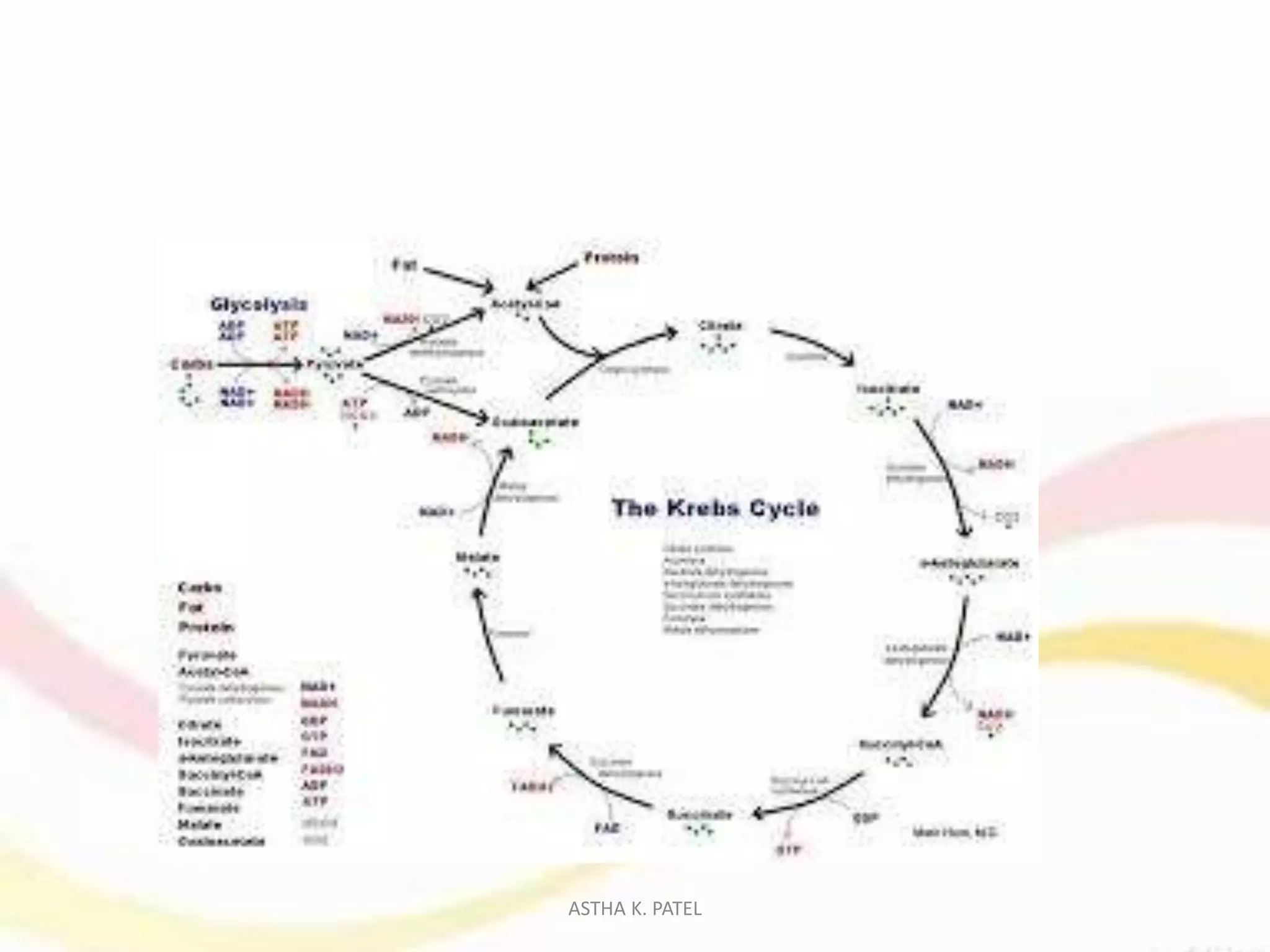
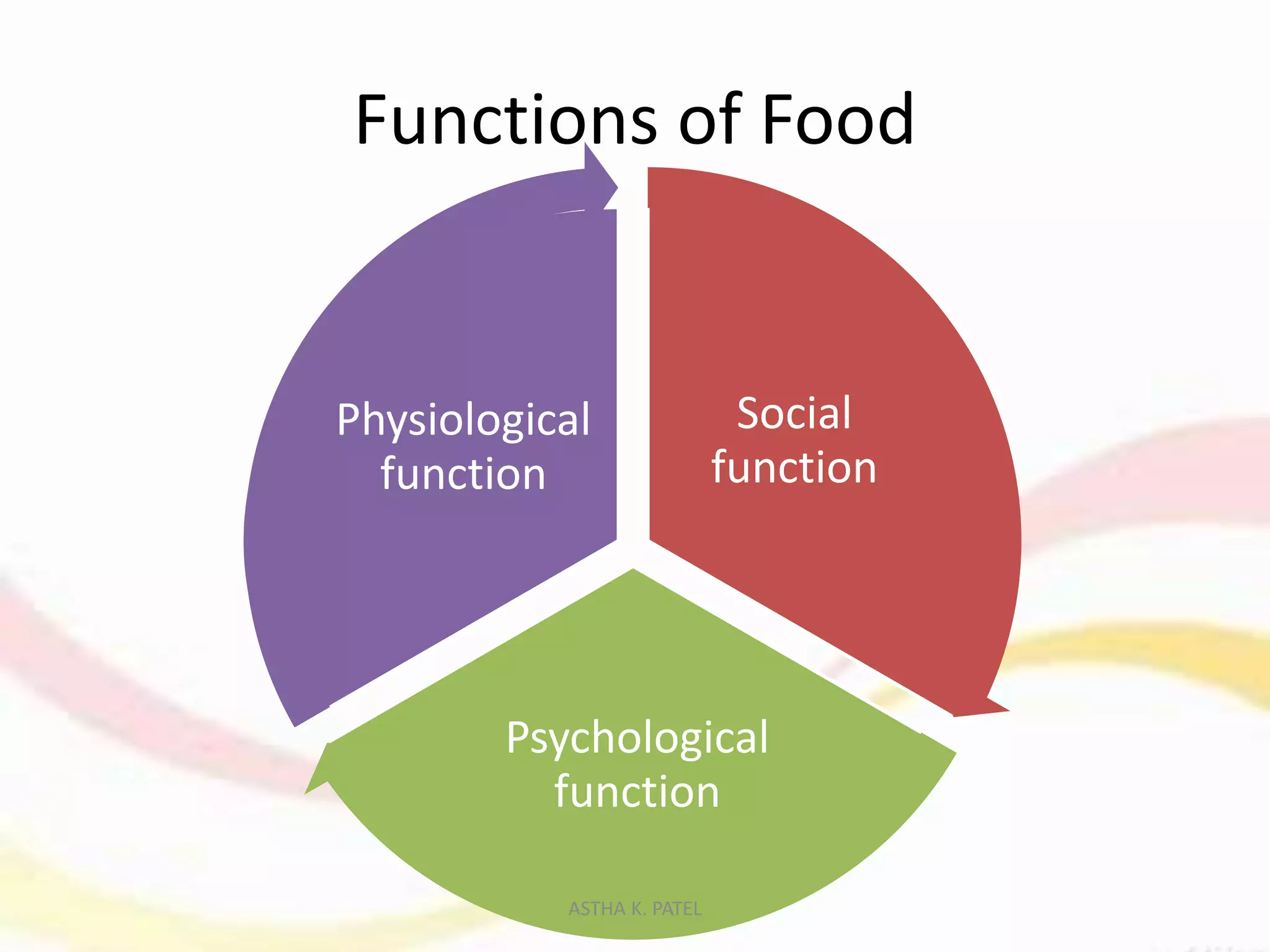
Food is essential for life, providing maintenance, growth, and energy through the nutrients it contains. Nutrition, the science of food and its impacts on health, has evolved through history with significant discoveries contributing to our understanding of its physiological, social, and psychological functions. The roles of food include energy yielding, body building, and protective/regulatory functions, all of which are crucial for sustaining life and facilitating social connections.