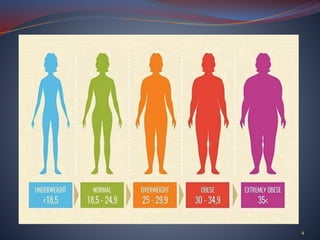
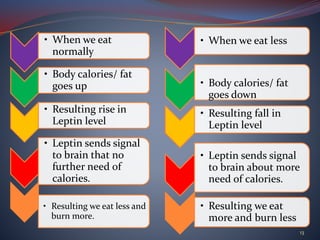
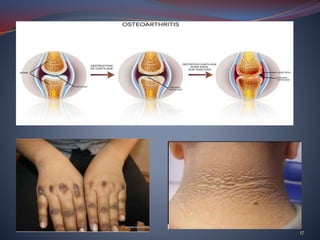
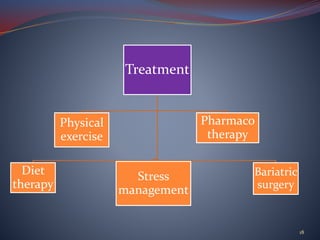
The document discusses obesity and underweight conditions, exploring their causes, pathophysiology, symptoms, and treatment options. Obesity results from factors like genetics, eating habits, and a sedentary lifestyle, and is measured using BMI and waist circumference, while underweight conditions stem from inadequate calorie intake and can lead to various health complications. Treatment strategies for both conditions include dietary adjustments, physical exercise, and medical interventions.