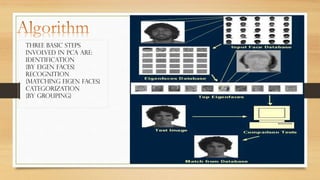
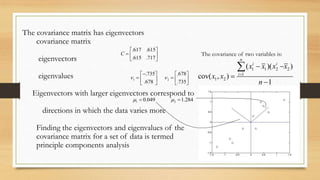
PCA is used for face recognition. It involves calculating eigenvectors from a training set of face images to define a feature space called "eigenfaces". A new face is recognized by projecting it onto this space and comparing to existing faces. PCA works by identifying directions of maximum variance in the training data, capturing the most important information about faces with fewer vectors. Potential applications include identification, security, and human-computer interaction. However, it is sensitive to changes in lighting and expression.