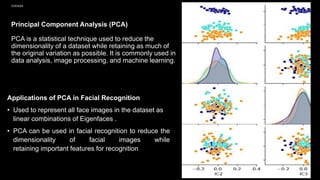
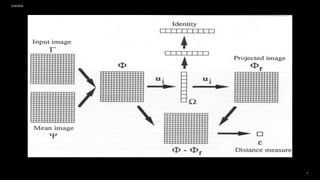
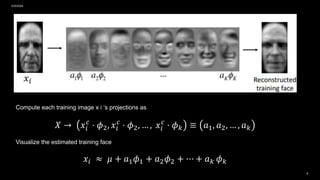
The document discusses face recognition methods, primarily focusing on eigenfaces and fisherfaces, which utilize statistical techniques like PCA and LDA for dimensionality reduction while improving classification accuracy. Eigenfaces are derived from covariance matrices of face images, while the fisherface method enhances PCA by maximizing class separation. The effectiveness of both algorithms is examined in terms of their application to face recognition, with fisherfaces showing superior performance under varying conditions.










![• Fisherface is one of the popular algorithms used in face recognition and is widely believed to be superior to
other techniques, such as eigenface because of the effort to maximize the separation between classes in the
training process[1].
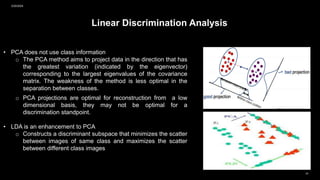
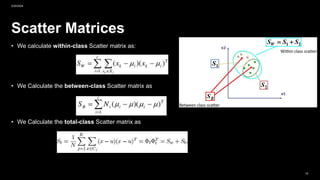
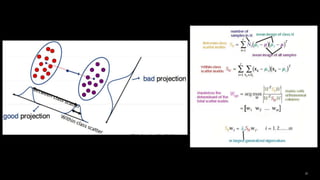
• This method is a combination of PCA and LDA methods. The PCA method is used to solve singular problems by
reducing the dimensions before being used to perform the LDA process. But the weakness of this method is that
when the PCA dimension reduction process will cause some loss of discriminant information useful in the LDA
process.
• The face image to be used must go through the preprocessing stage first. This stage includes image acquisition,
and RBG image conversion to grayscale.
• Fisherface method is a method that is a merger between PCA and LDA methods [1].
2/20/2024
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eigenfacesfisherfacesanddimensionalityreduction-240220073527-0cb418fe/85/Eigenfaces-Fisherfaces-and-Dimensionality_Reduction-15-320.jpg)




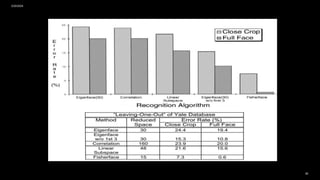
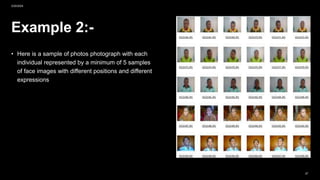
![Example 1:-
2/20/2024
• A group of pictures were analyzed using
different methods like (Eigenface –
Correlation - Linear Subspace –
Fisherface) to show the accuracy of each
method.
• This is done by using pictures with
difference lighting positions to see which
is more accurate in different conditions
using different data.
• The Yale database is available for
download from http://cvc.yale.edu [3].
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eigenfacesfisherfacesanddimensionalityreduction-240220073527-0cb418fe/85/Eigenfaces-Fisherfaces-and-Dimensionality_Reduction-22-320.jpg)