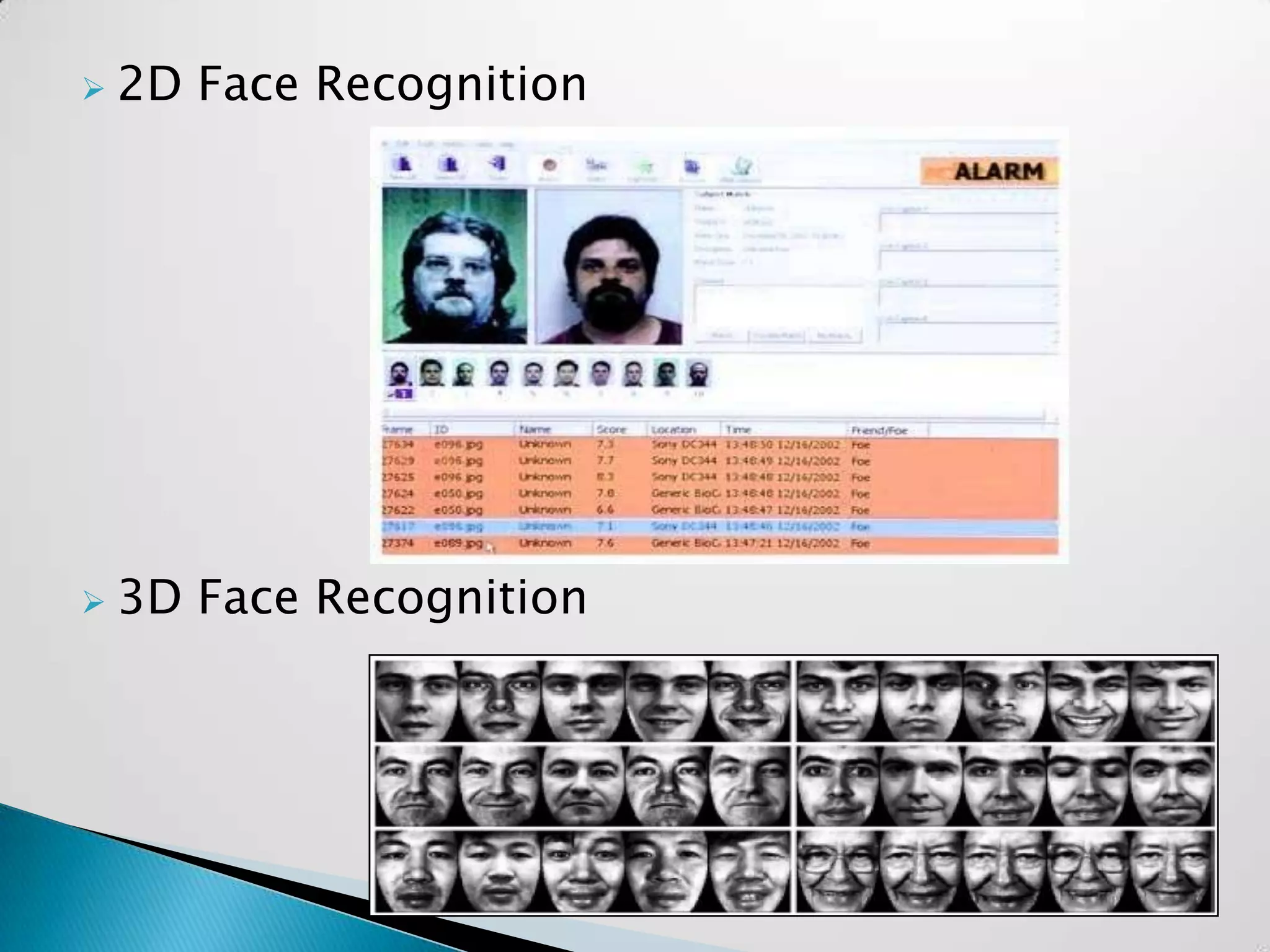
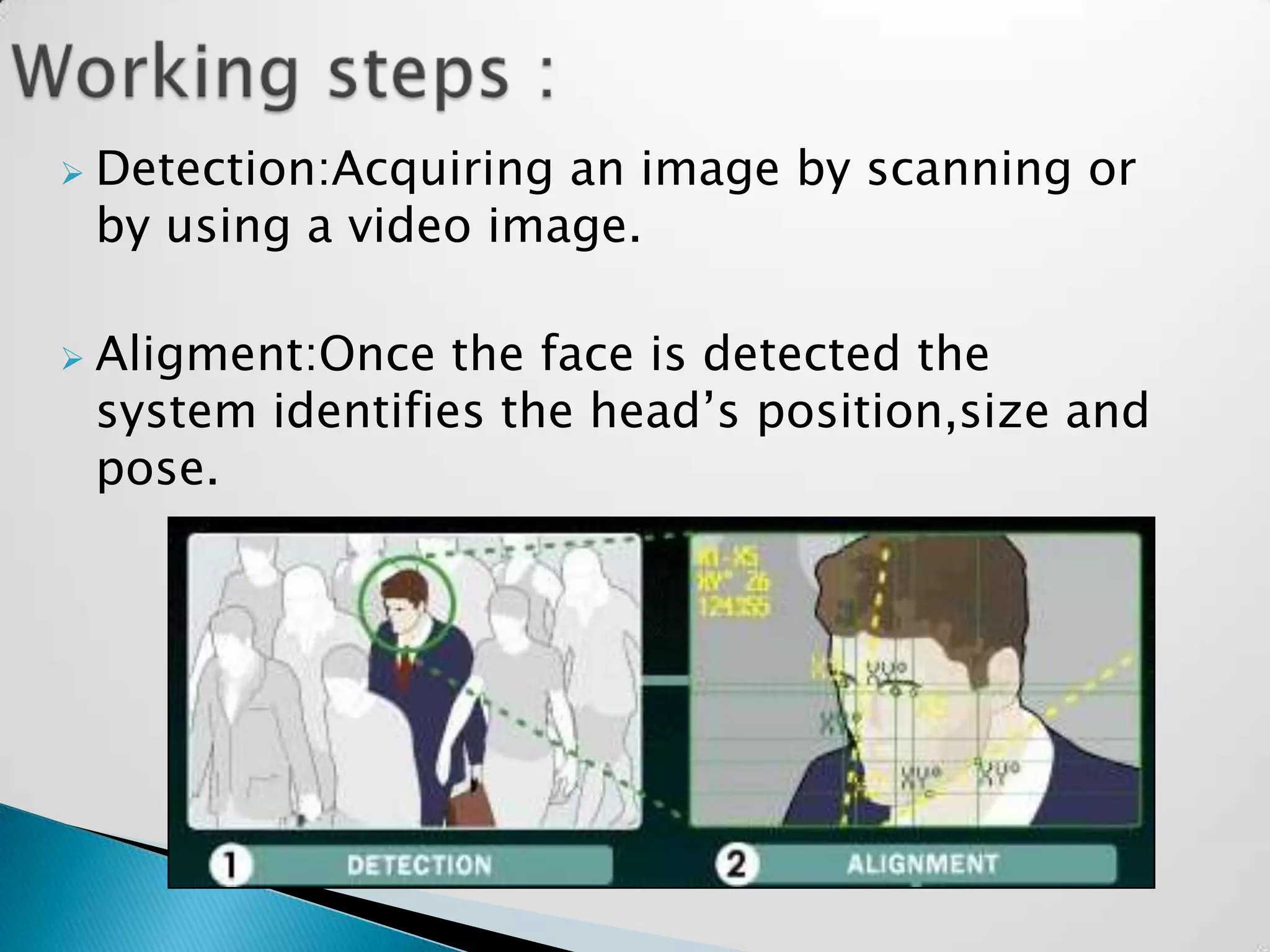
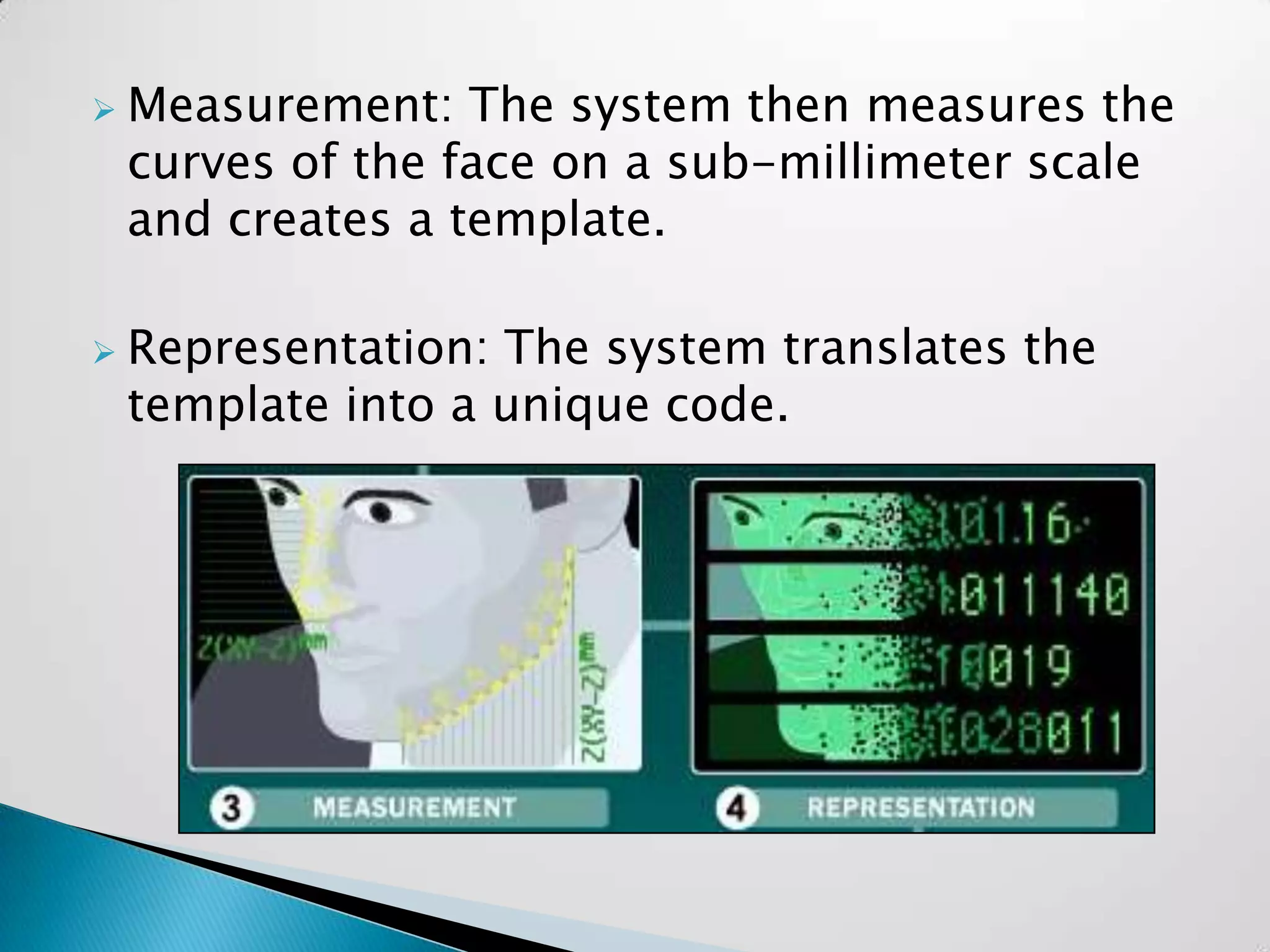
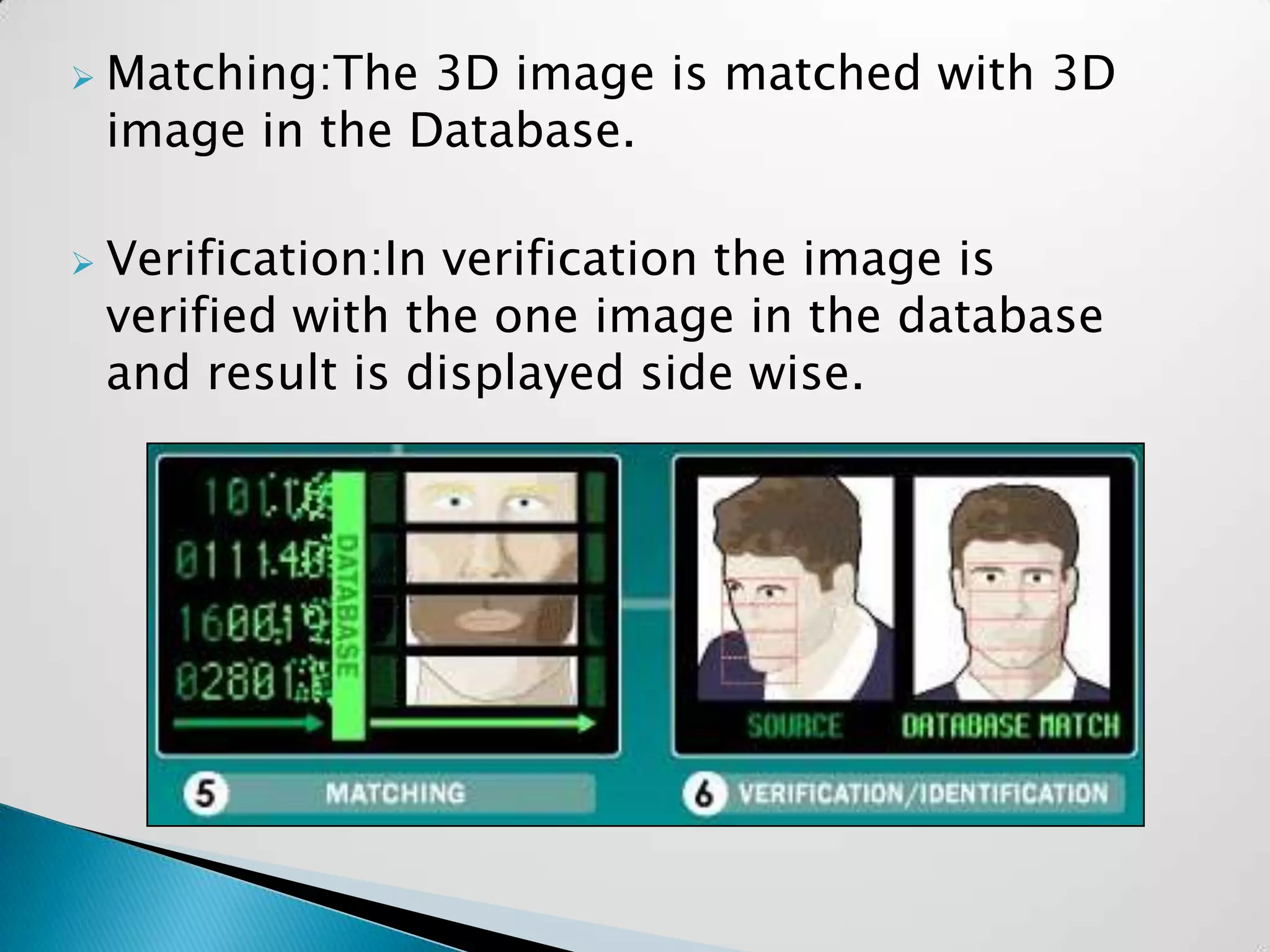
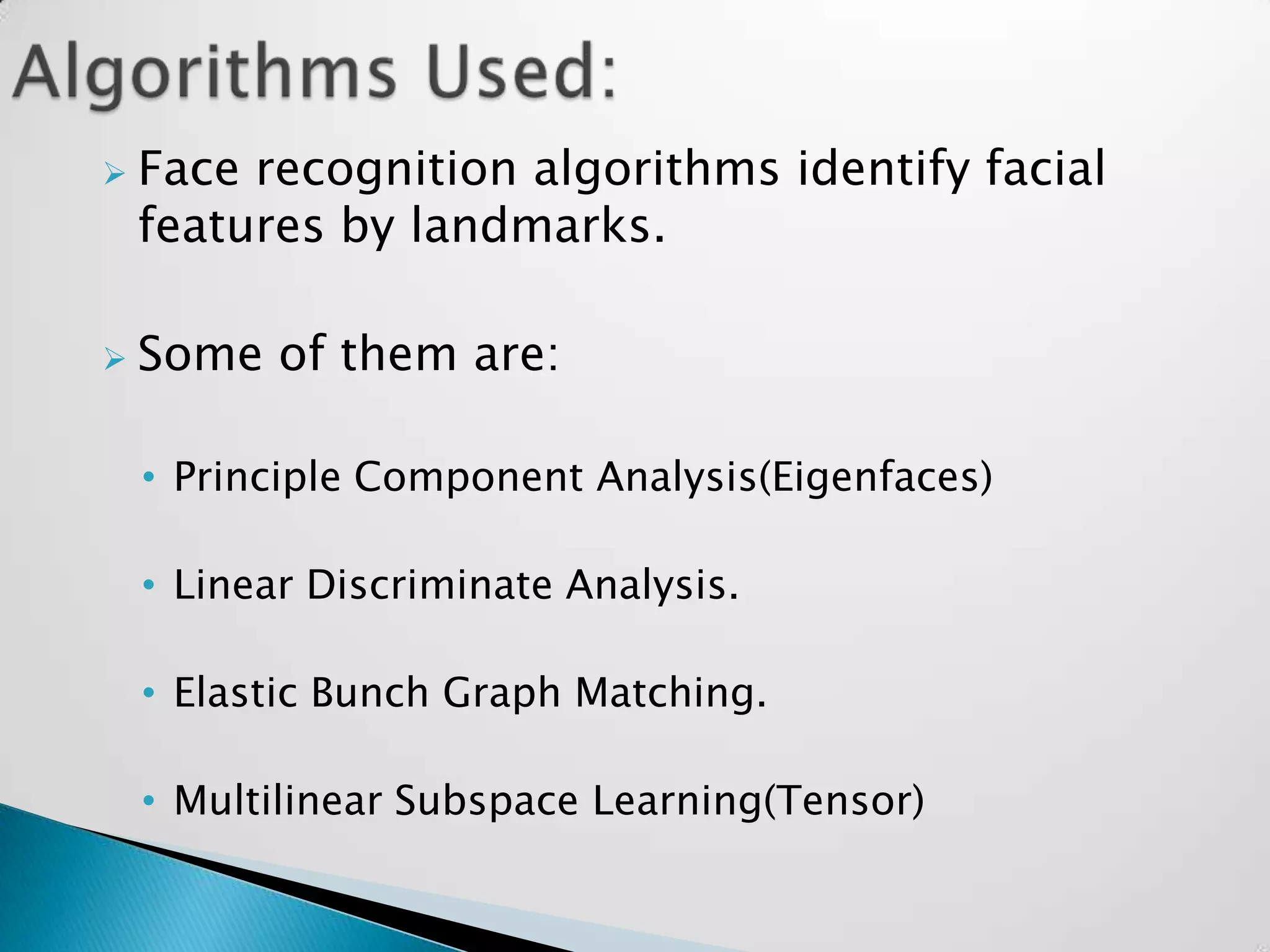
Sandeep Sharma presented on face recognition. He discussed the history and types of face recognition including 2D and 3D. He explained how face recognition works by measuring facial landmarks and using algorithms like PCA and LDA to analyze features. Challenges included disguises and large crowds. Future uses could include law enforcement, banking security, and airports. Advancements are still needed for widescale deployment.