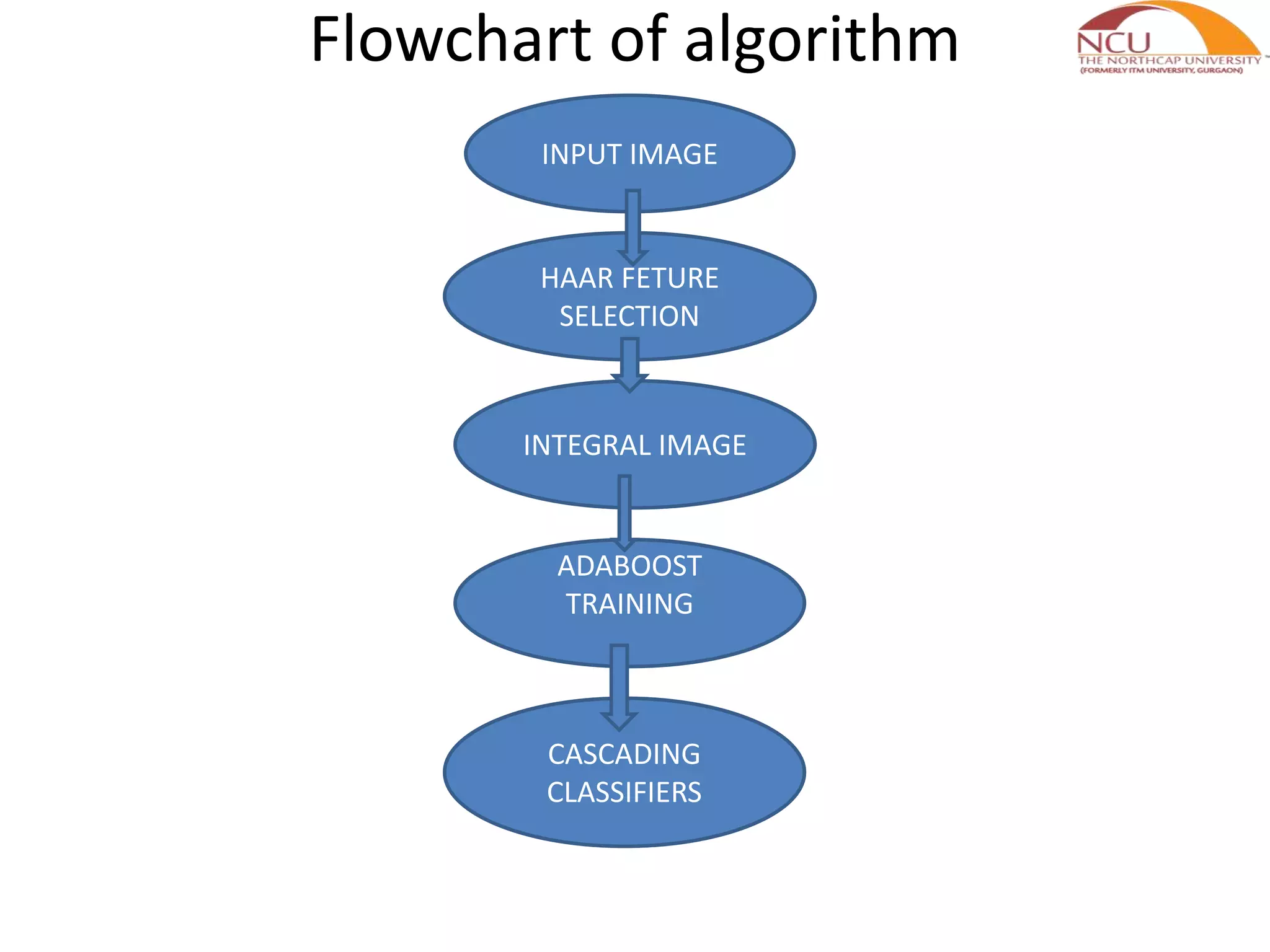
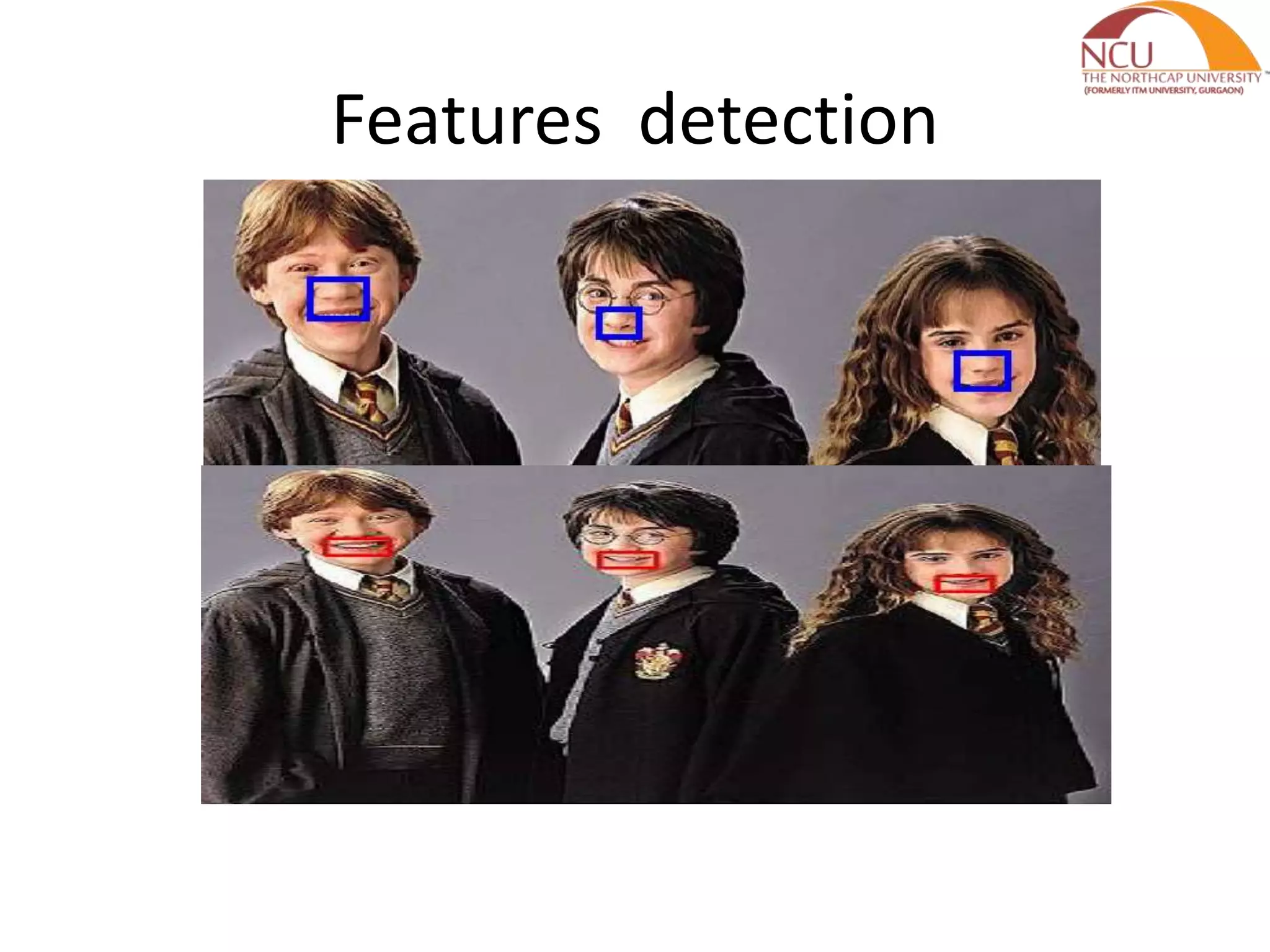
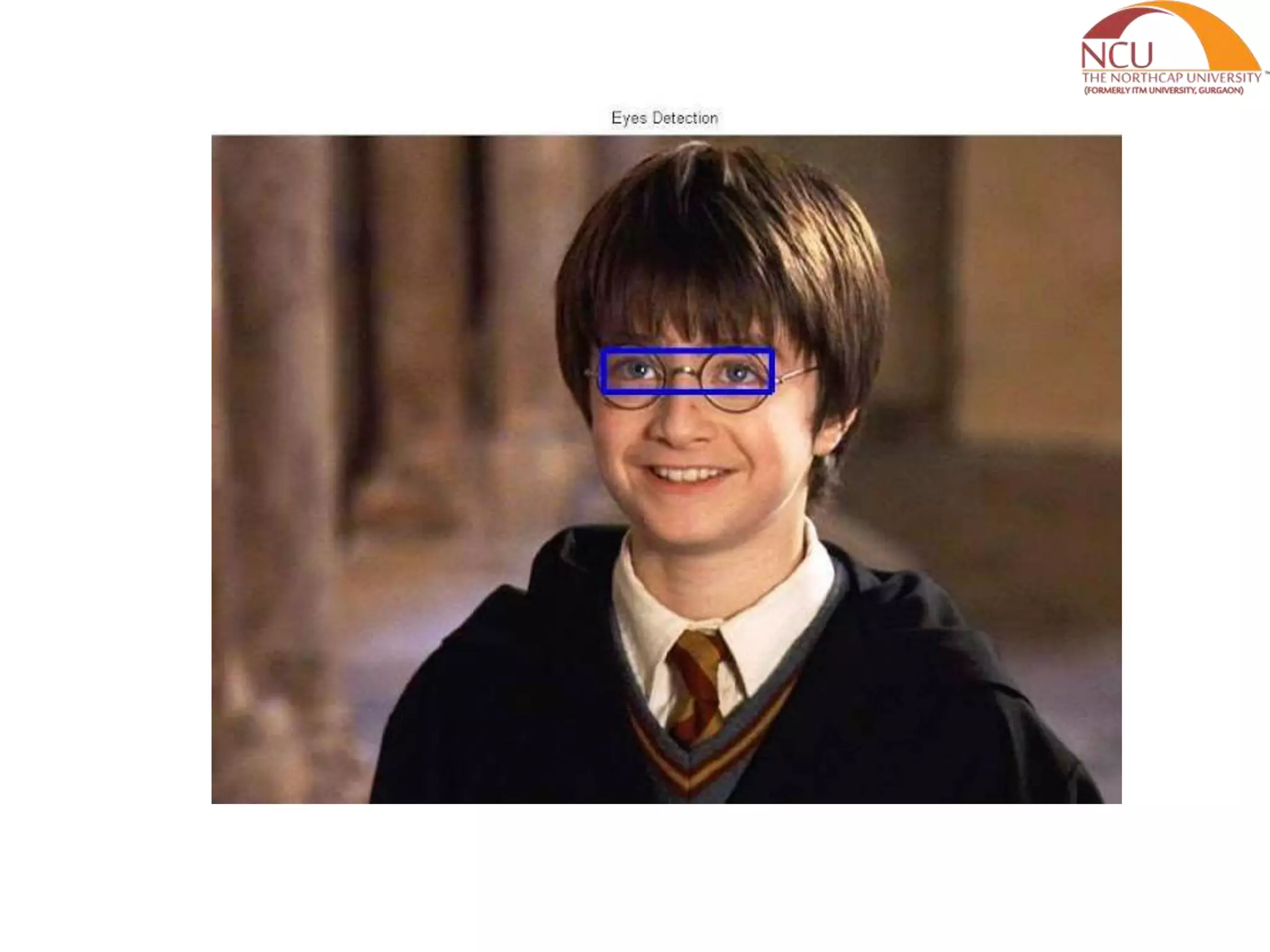
This document presents a literature review and proposed work plan for face recognition using a back propagation neural network. It summarizes the Viola-Jones face detection algorithm which uses Haar features and an integral image for real-time detection. The algorithm has high detection rates with low false positives. Future work will apply back propagation neural networks to extract features and recognize faces from a database of facial images in order to build a facial recognition system.