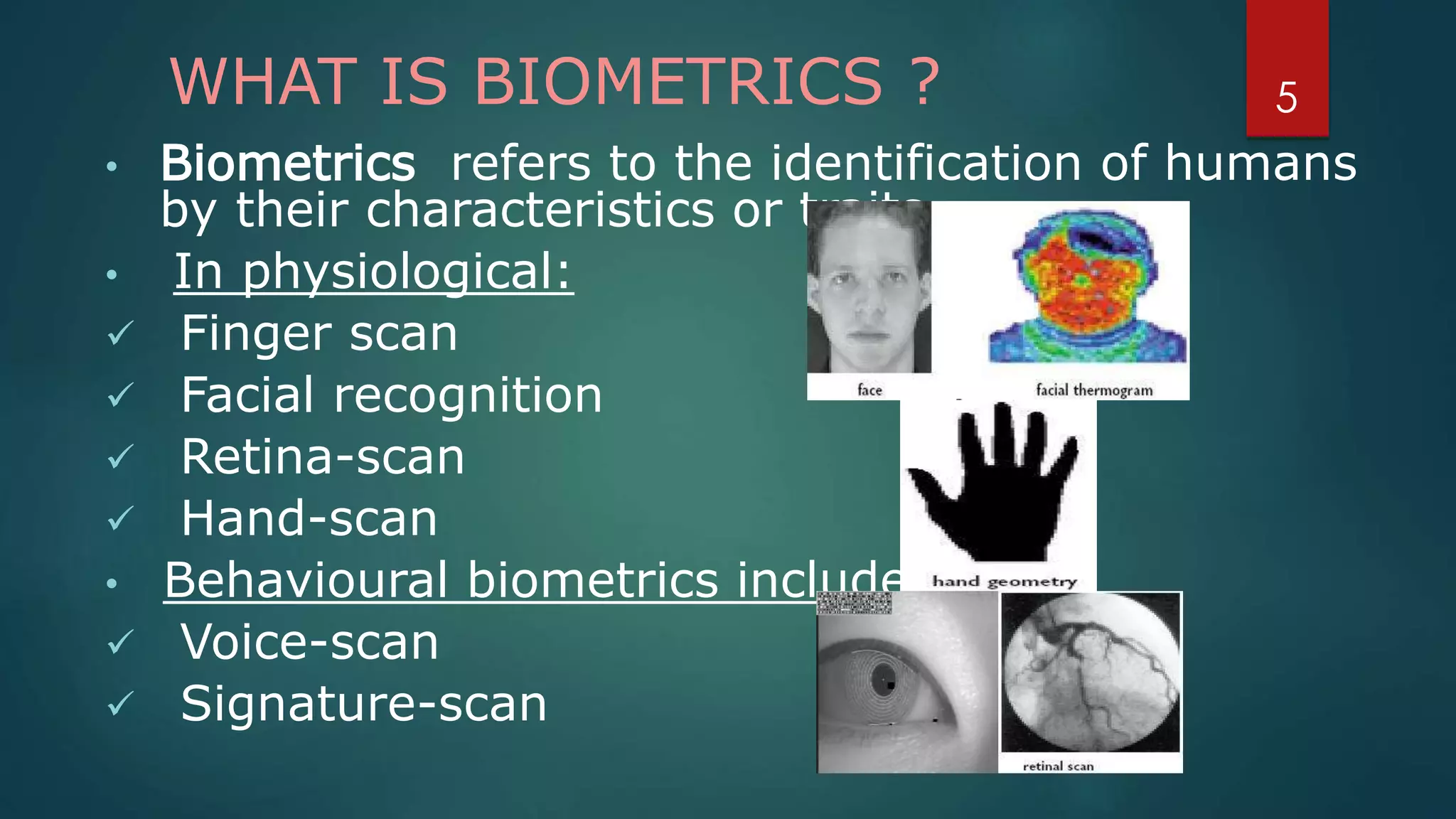
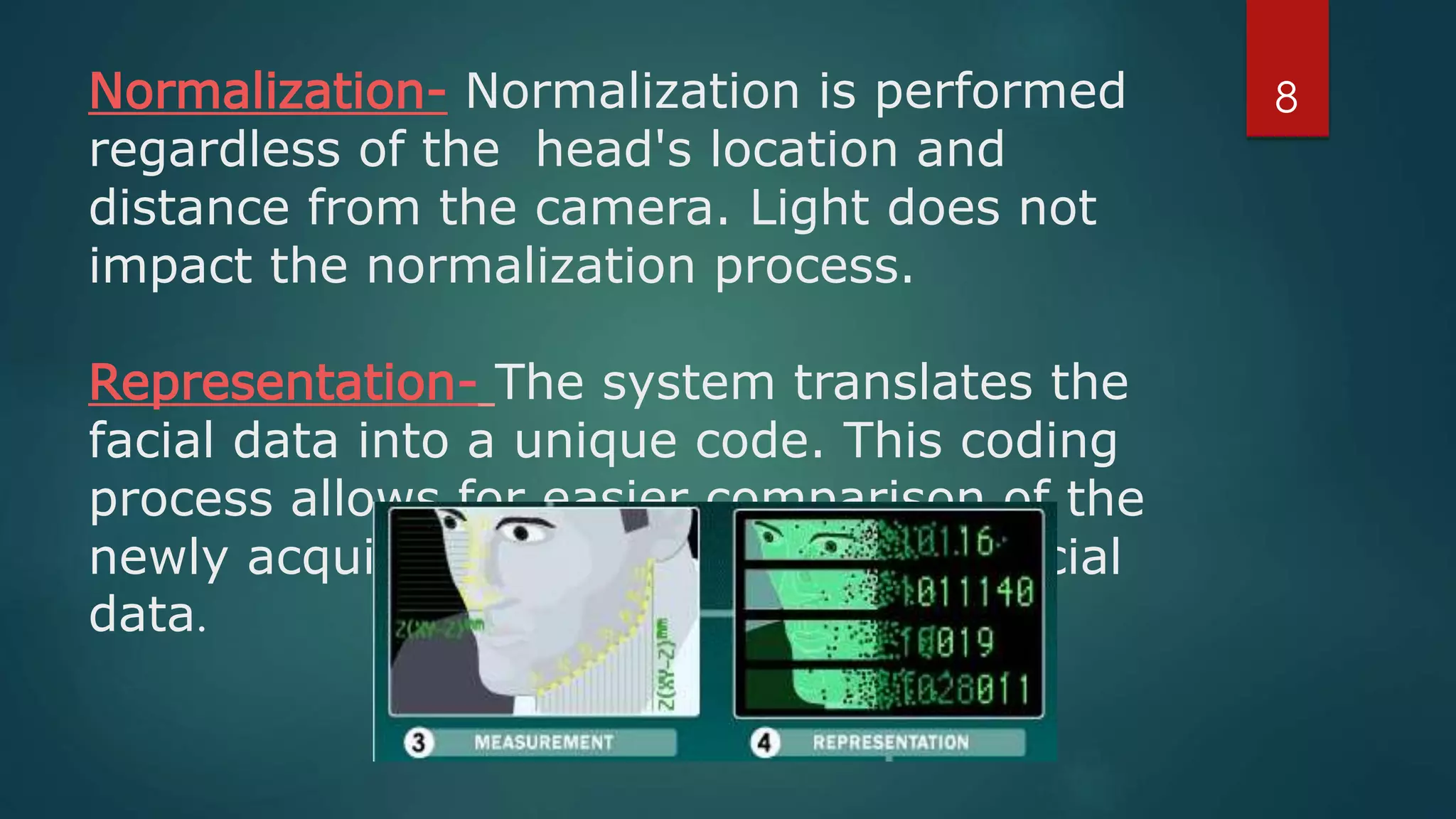
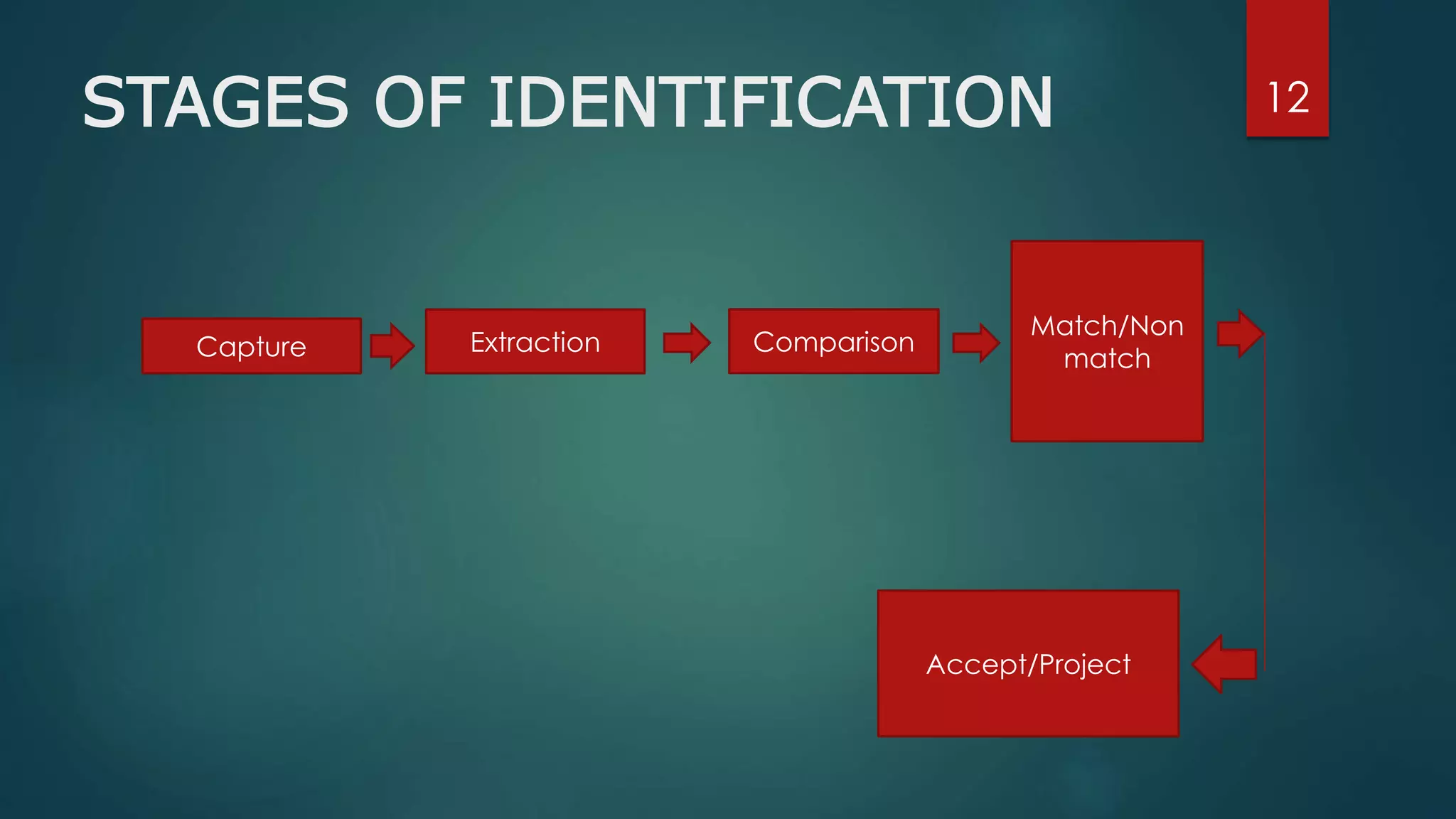
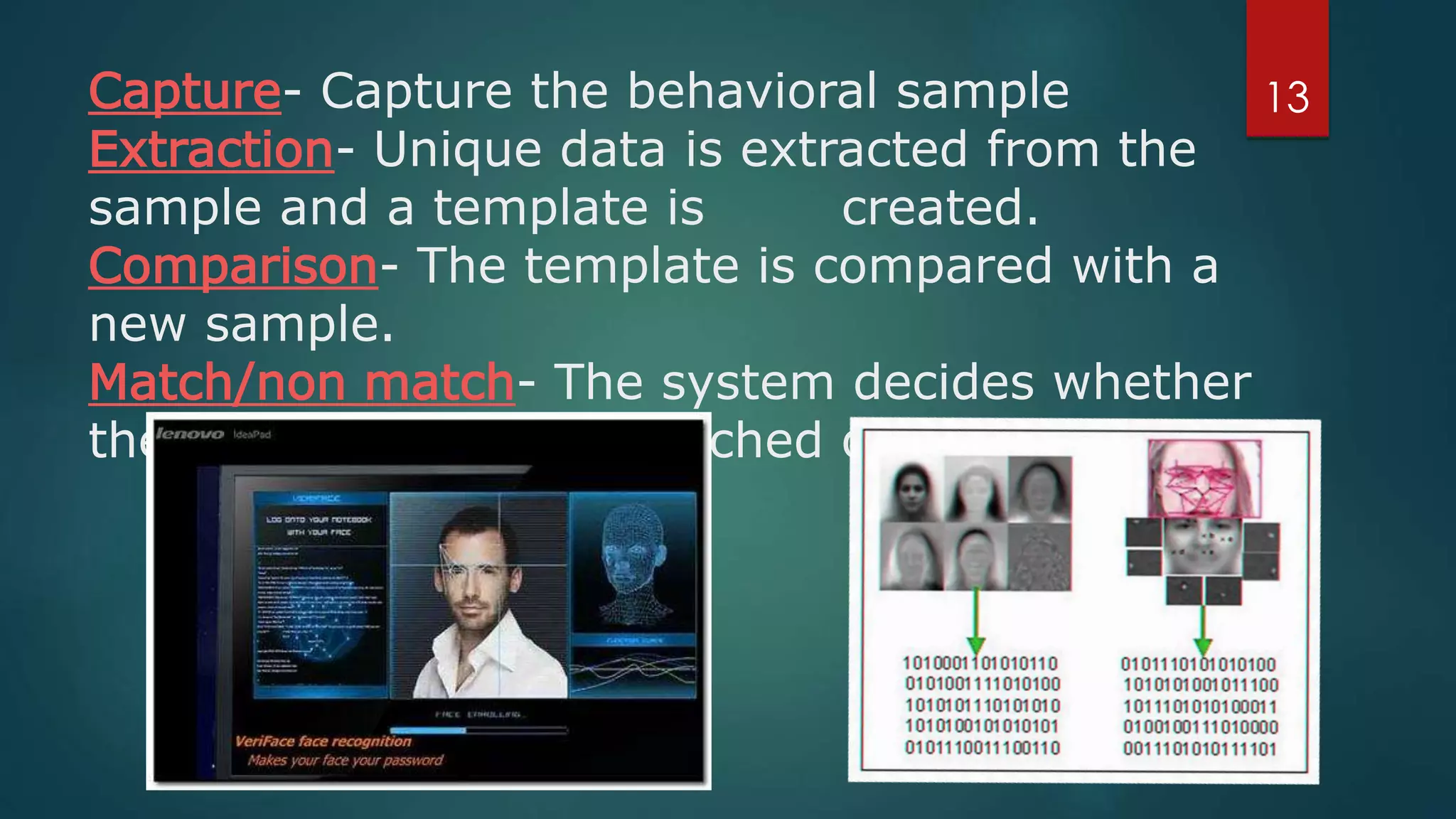
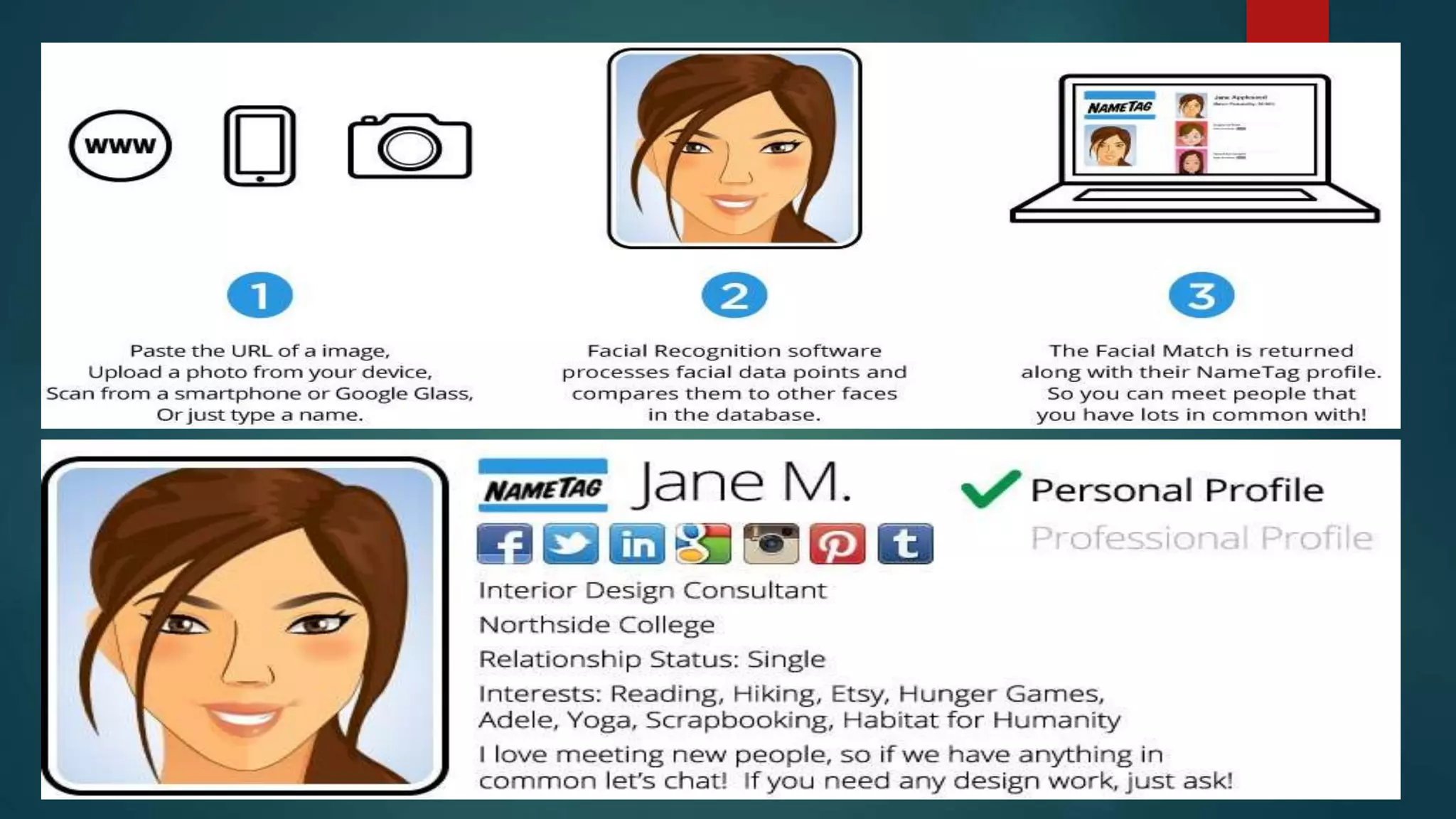
Face recognition is a computer application that automatically identifies or verifies an individual from a digital image or video footage. It works by detecting faces, aligning and normalizing them, representing the facial features with unique codes, and then matching new images to stored facial data. It has various applications including commercial uses like daycare sign-in/out systems, residential security cameras, and banking ATMs. While fast and convenient, face recognition has disadvantages like being impacted by changes in appearance and an inability to distinguish identical twins.