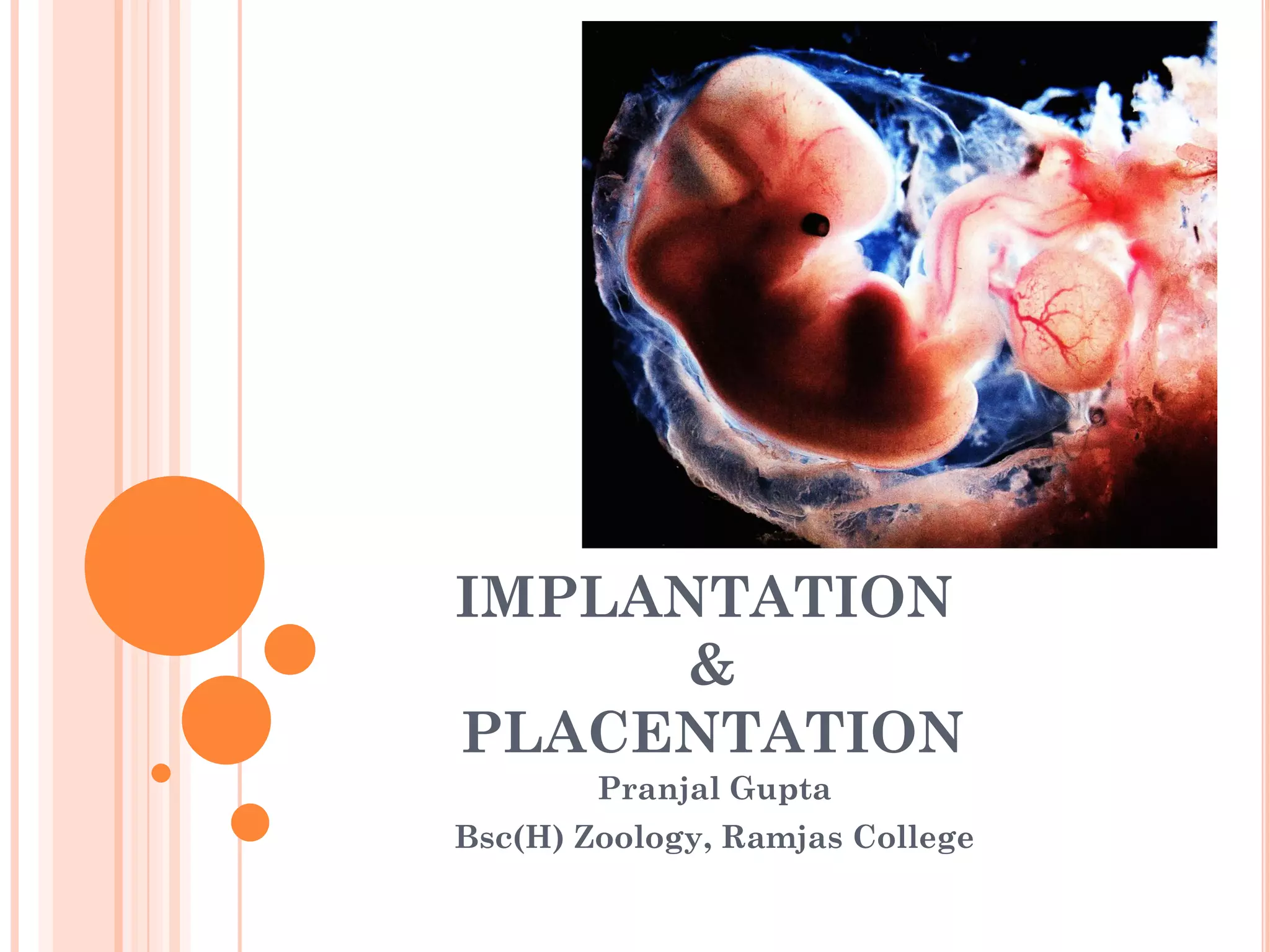
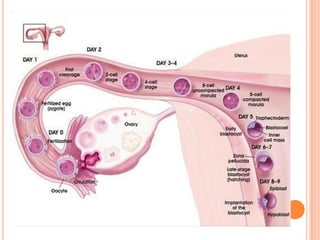
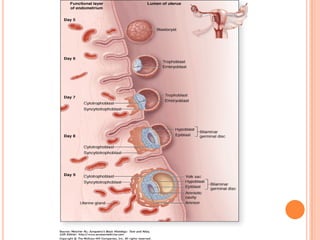
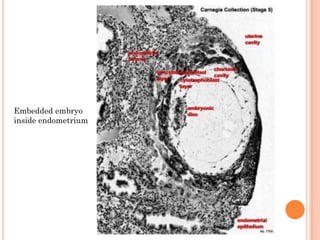
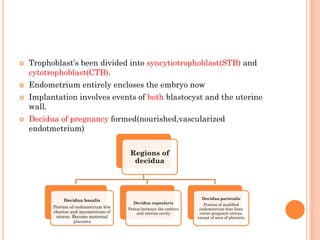
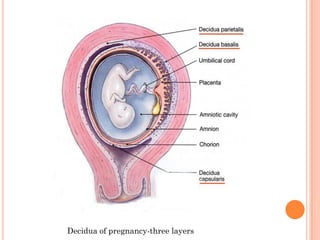
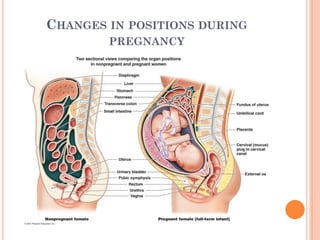
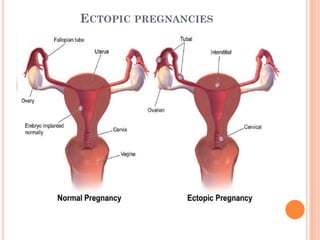
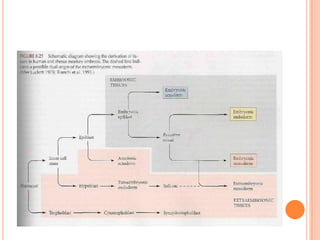
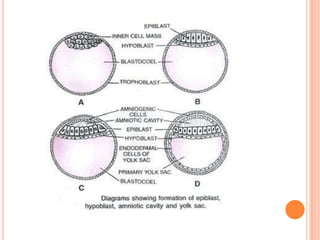
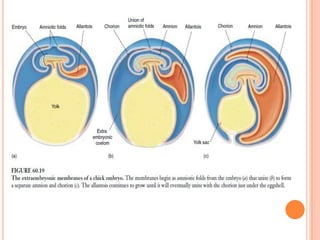
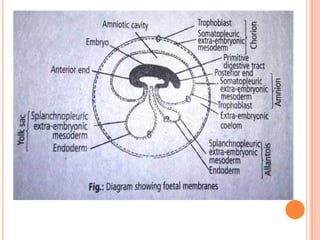
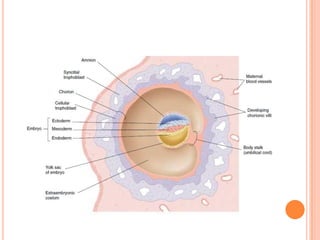
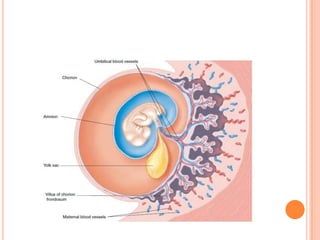
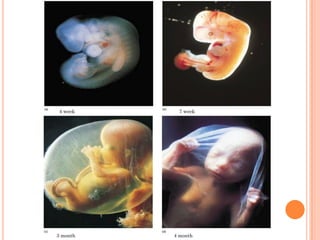
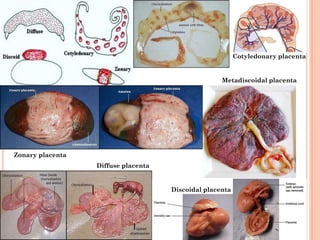
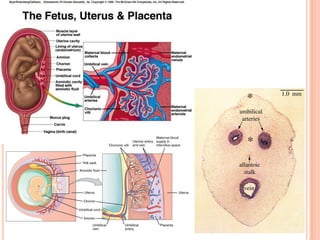
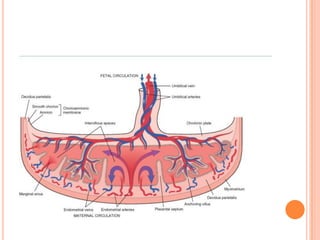
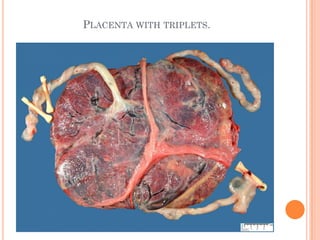
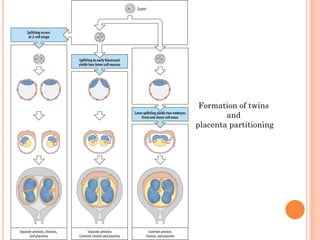
The document provides a comprehensive overview of human embryonic development, including cleavage, implantation, gastrulation, and the formation of extra-embryonic membranes. It details the processes from fertilization to the establishment of the placenta, including the roles of trophoblasts and layers of the endometrium. The document also discusses placentation types and functions in both mammals and birds.