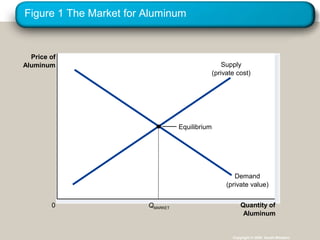
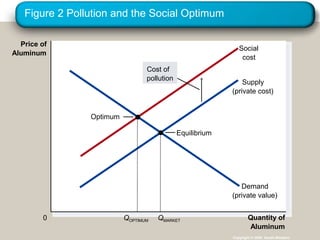
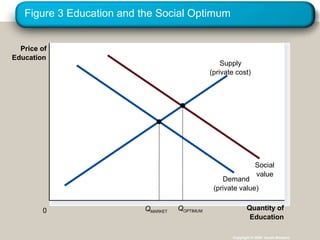
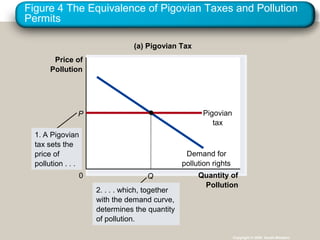
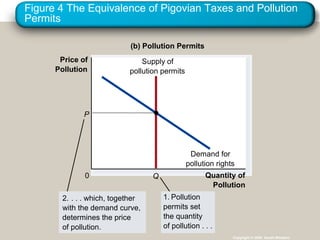
This document discusses externalities and how they can lead to market failures. It defines externalities as uncompensated impacts of one person's actions on another. Negative externalities cause markets to overproduce goods, while positive externalities cause underproduction. The document outlines different policy approaches governments can use to correct externalities, such as Pigouvian taxes, regulation, and tradable pollution permits. It also discusses how private solutions may work using Coase theorem, but often high transaction costs require public policy interventions.