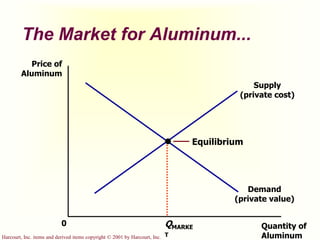
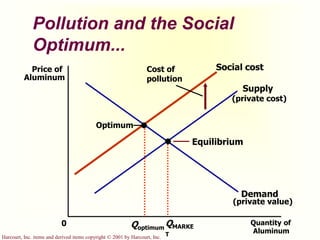
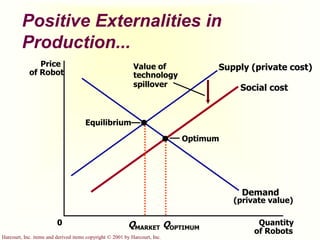
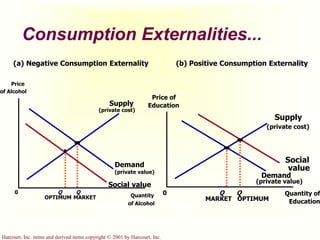
The document discusses externalities and market failures. It defines externalities as side effects of market transactions that impact third parties not involved in the transactions. Externalities can be negative, like pollution, or positive, like education. The market equilibrium is inefficient in the presence of externalities, producing either too much or too little of a good compared to the social optimum. Government policies like taxes and subsidies can help internalize externalities and correct inefficient market outcomes.