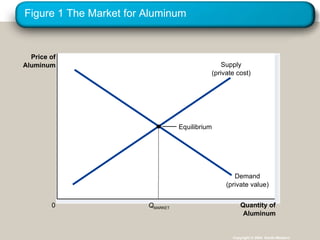
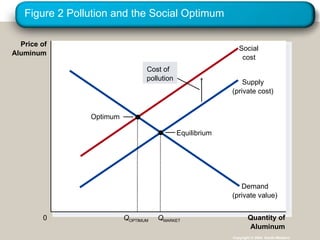
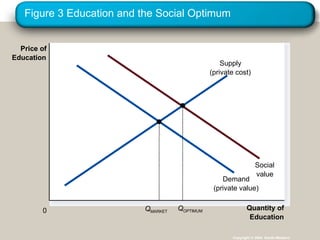
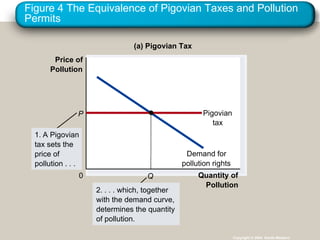
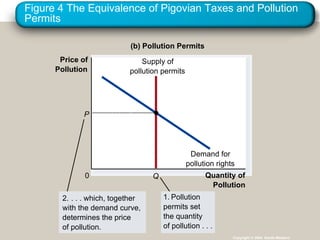
Externalities refer to uncompensated impacts of one party's actions on another. Negative externalities occur when costs are imposed on third parties, leading to an equilibrium quantity that is larger than socially optimal. Positive externalities occur when benefits are conferred on third parties, leading to an equilibrium quantity that is smaller than socially optimal. Private solutions sometimes address externalities through bargaining, but transaction costs may impede agreement. When private solutions fail, governments may regulate behavior directly through commands or internalize externalities using Pigovian taxes or tradable pollution permits.