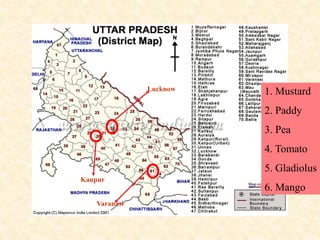
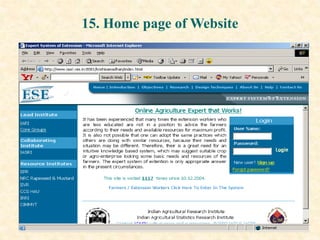
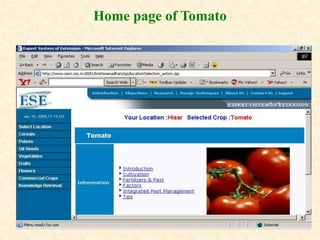
This document describes a proposed expert system for agricultural extension in India. It provides details on the institutions and researchers involved, rationale for the system, selected crops and regions, requirement analysis, development of the knowledge base including expert groups for different crops, linkages with other organizations, and design of the system including its architecture, components, and user interface. The system is intended to help farmers make appropriate decisions by providing up-to-date information and recommendations tailored to their specific resources and needs.