This document discusses several components of animal excretory systems:
1. The excretory system regulates chemical composition of body fluids by removing waste and maintaining proper water, salt, and nutrient levels.
2. Osmoregulation controls water balance in aquatic, terrestrial, and hyperosmotic environments using different processes depending on the animal. Aquatic animals regulate to match surrounding water, while terrestrial animals conserve water through impermeable surfaces and kidneys.
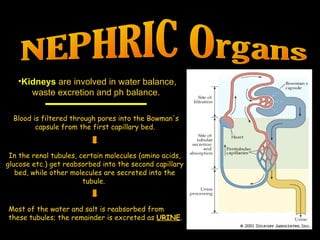
3. Kidneys filter blood, reabsorb useful molecules, and excrete waste as urine, regulating water, waste, and pH balance.