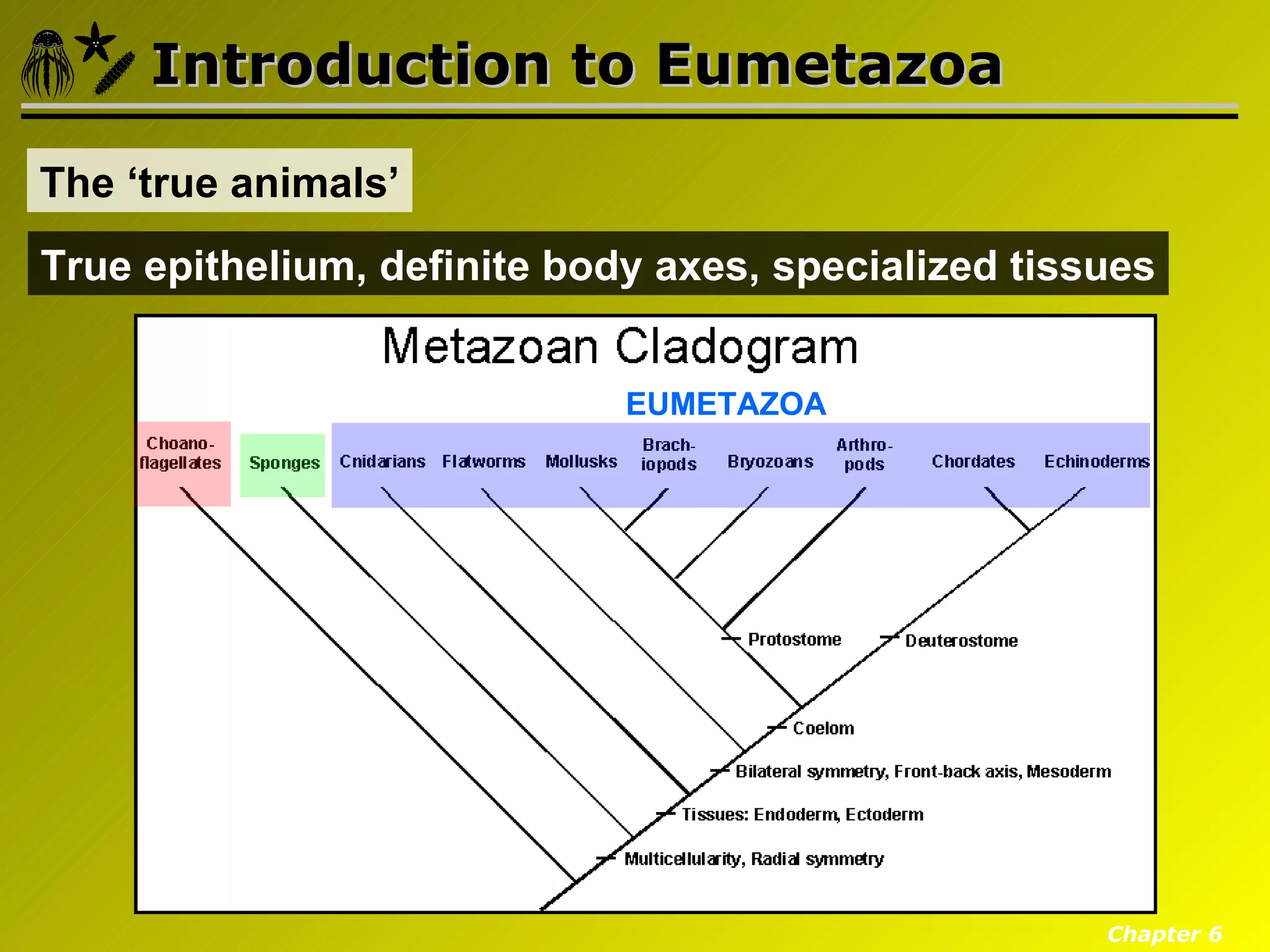
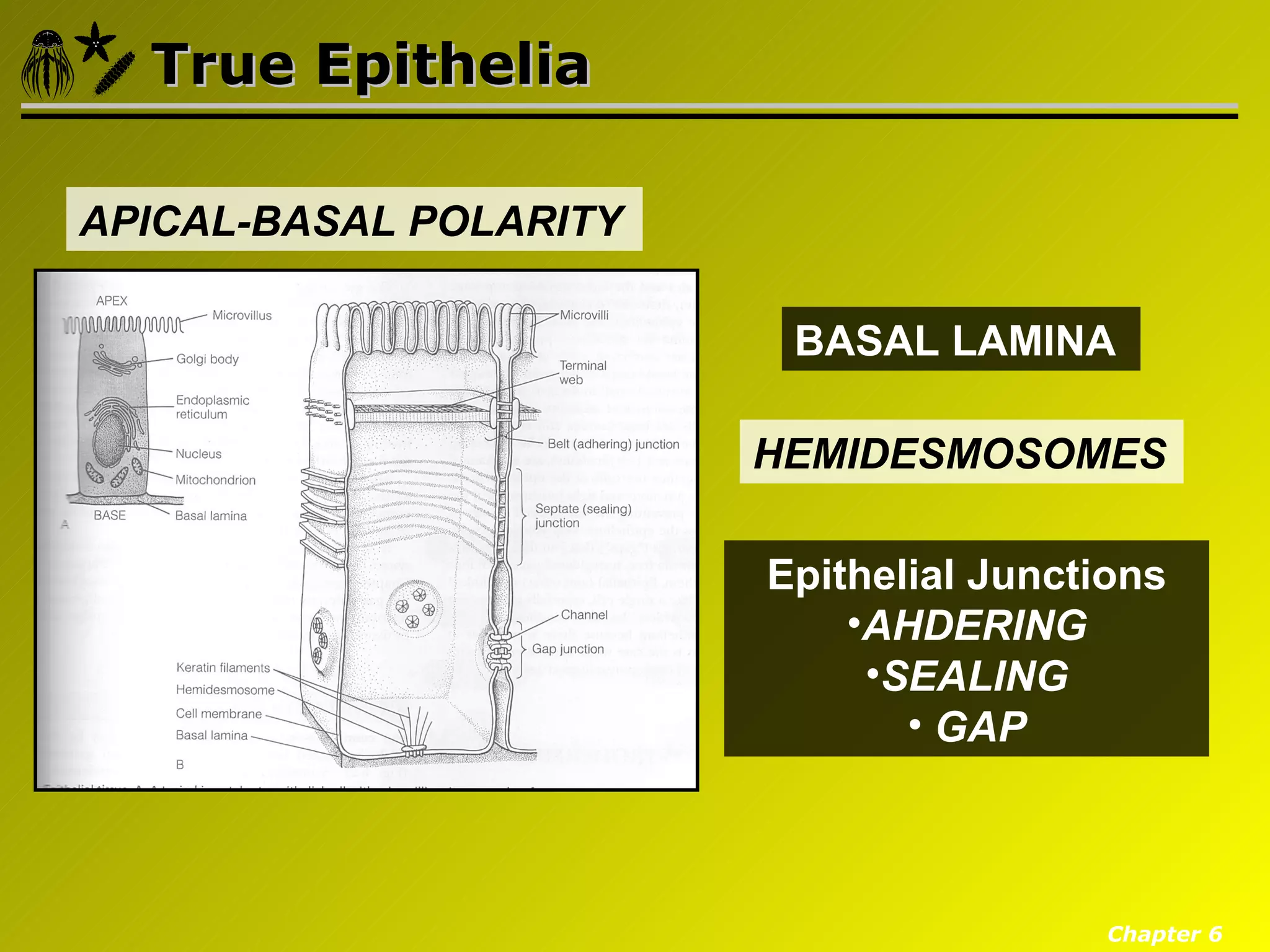
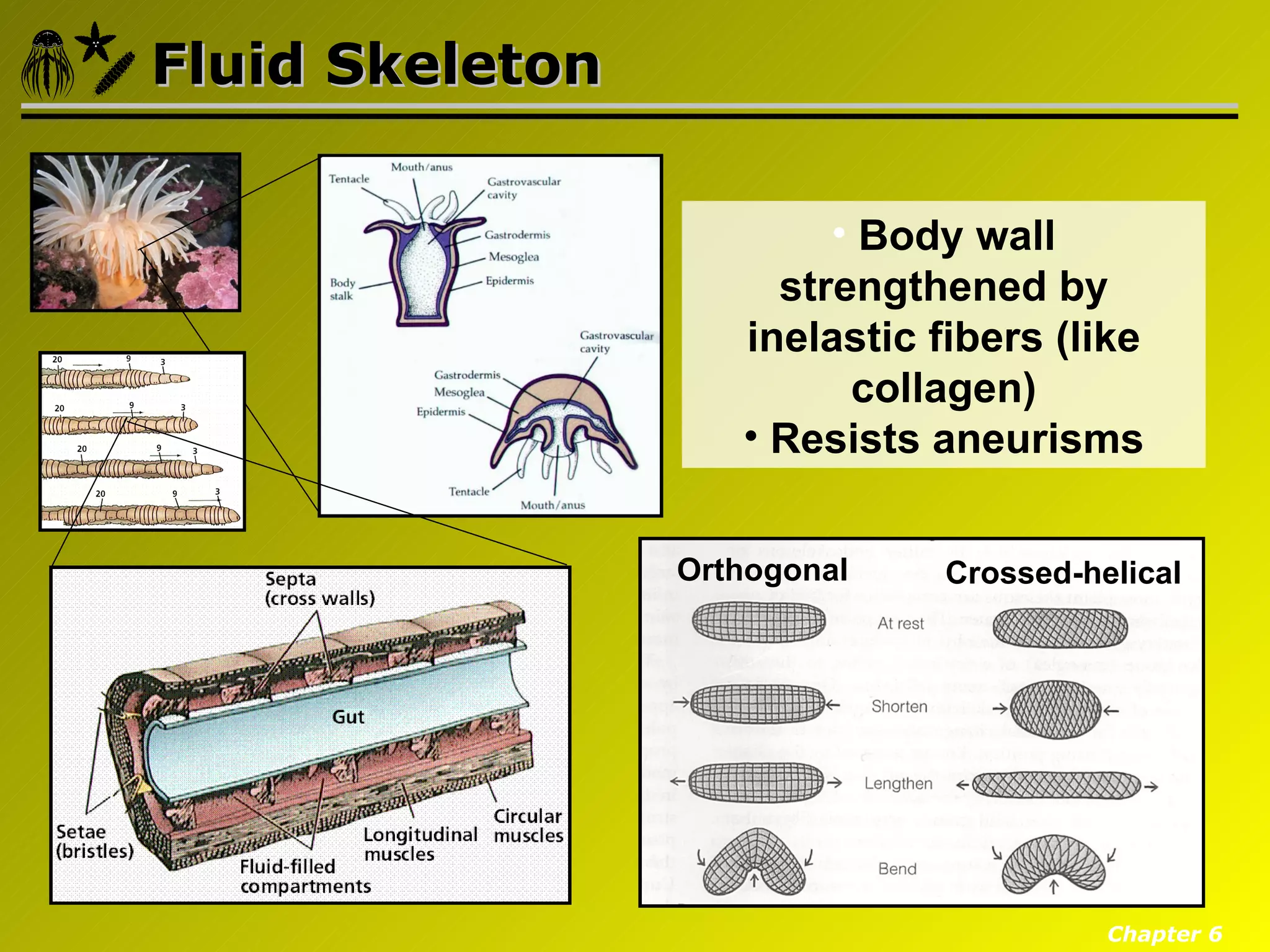
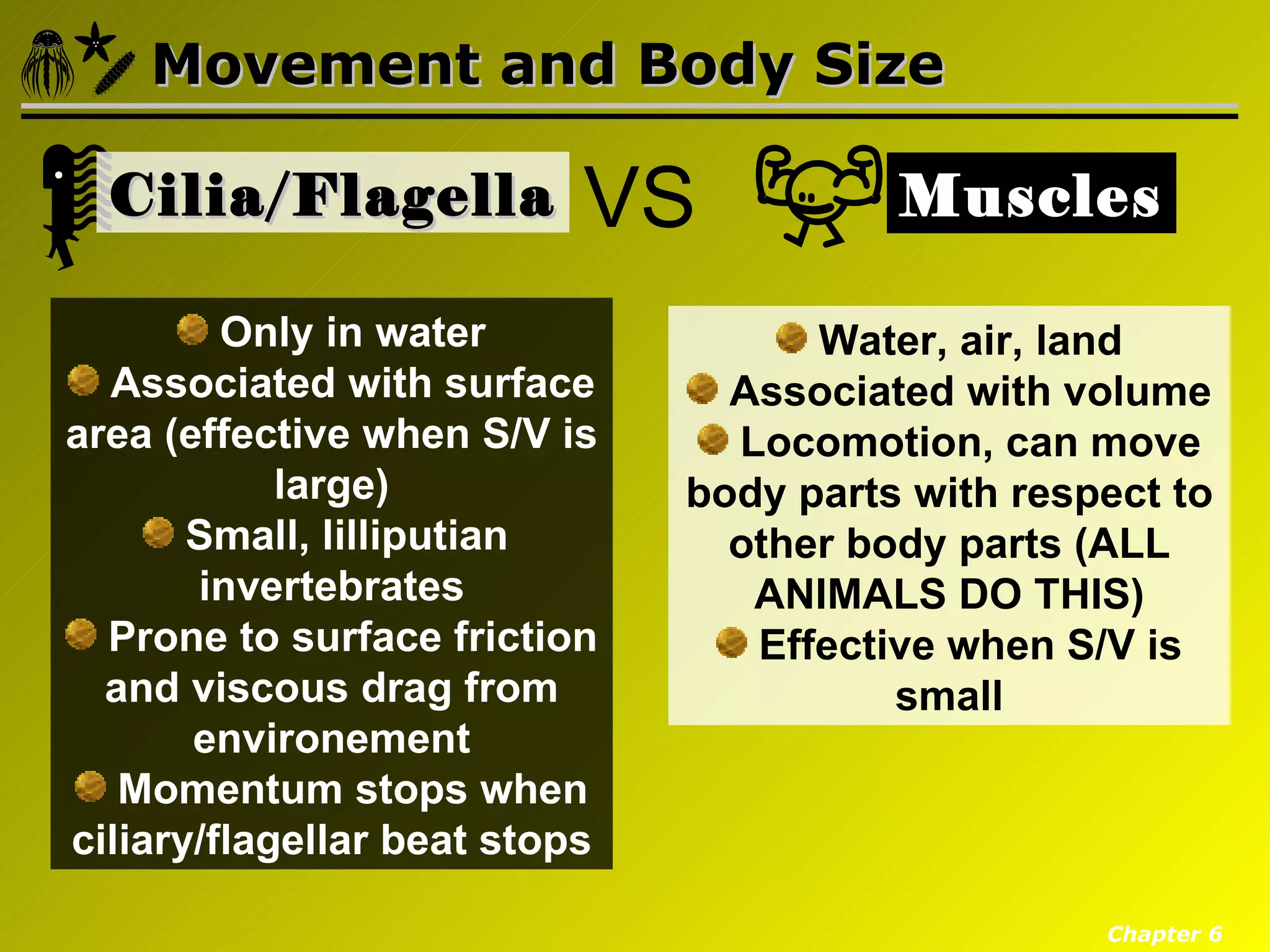
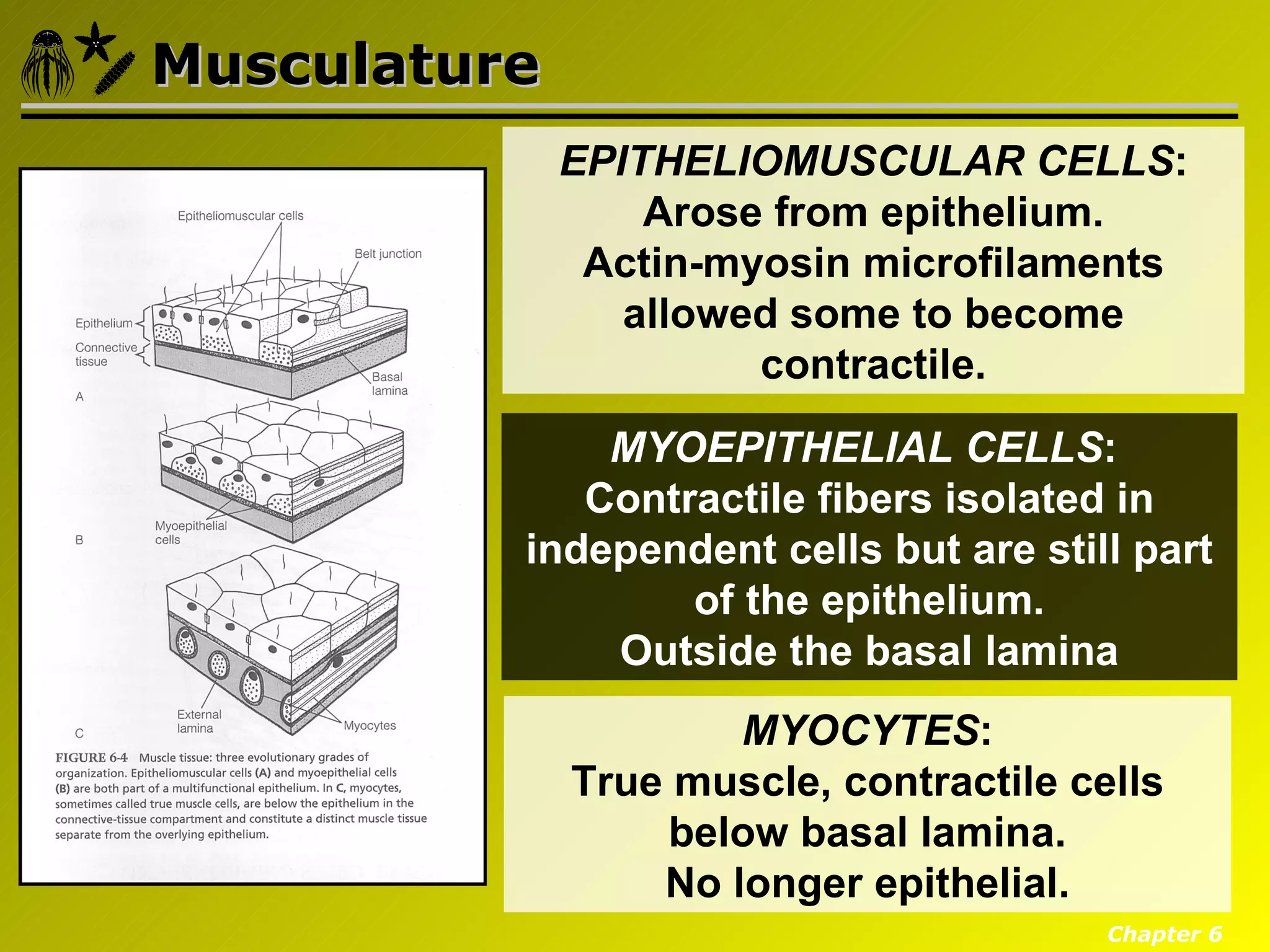
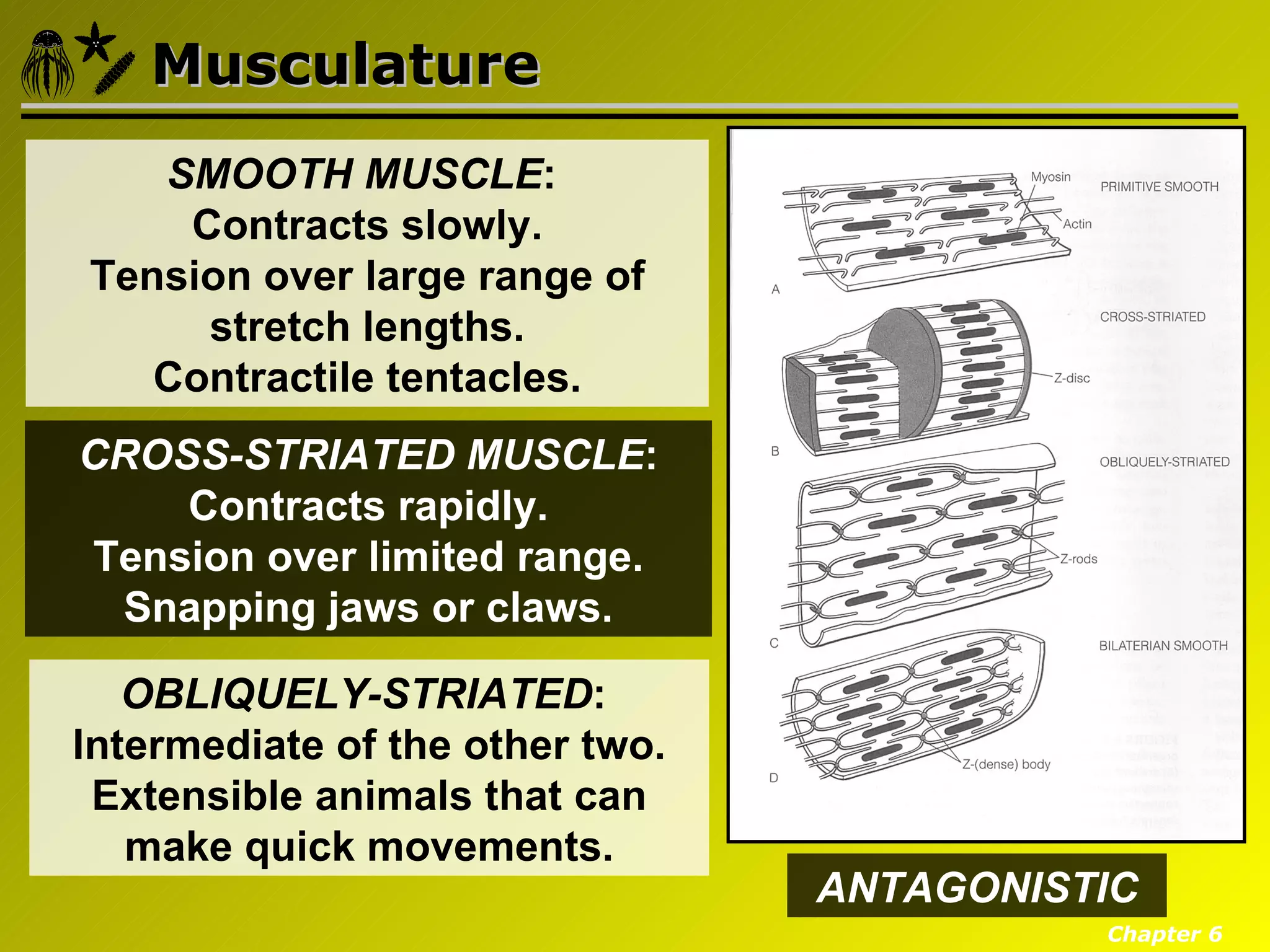
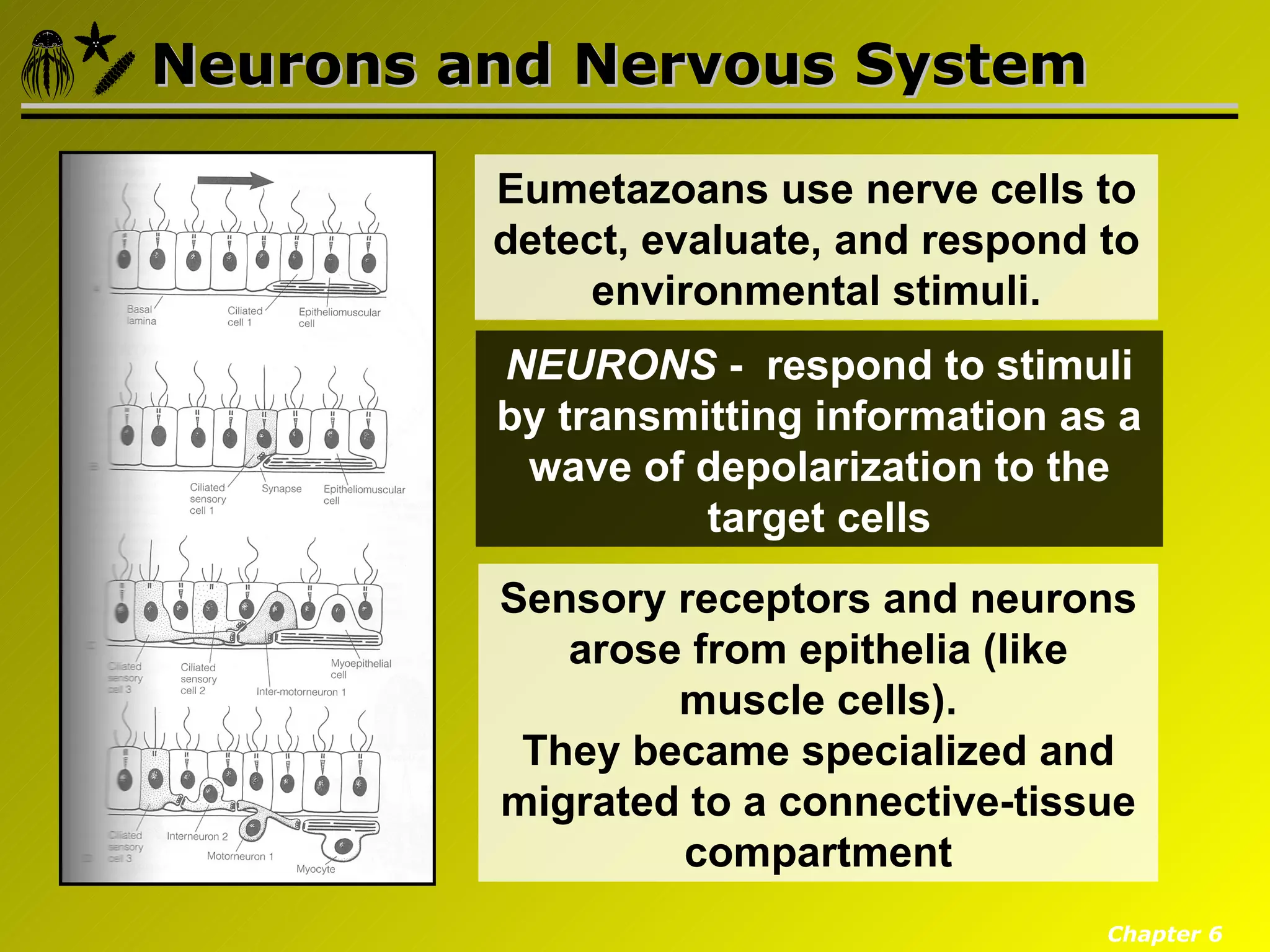
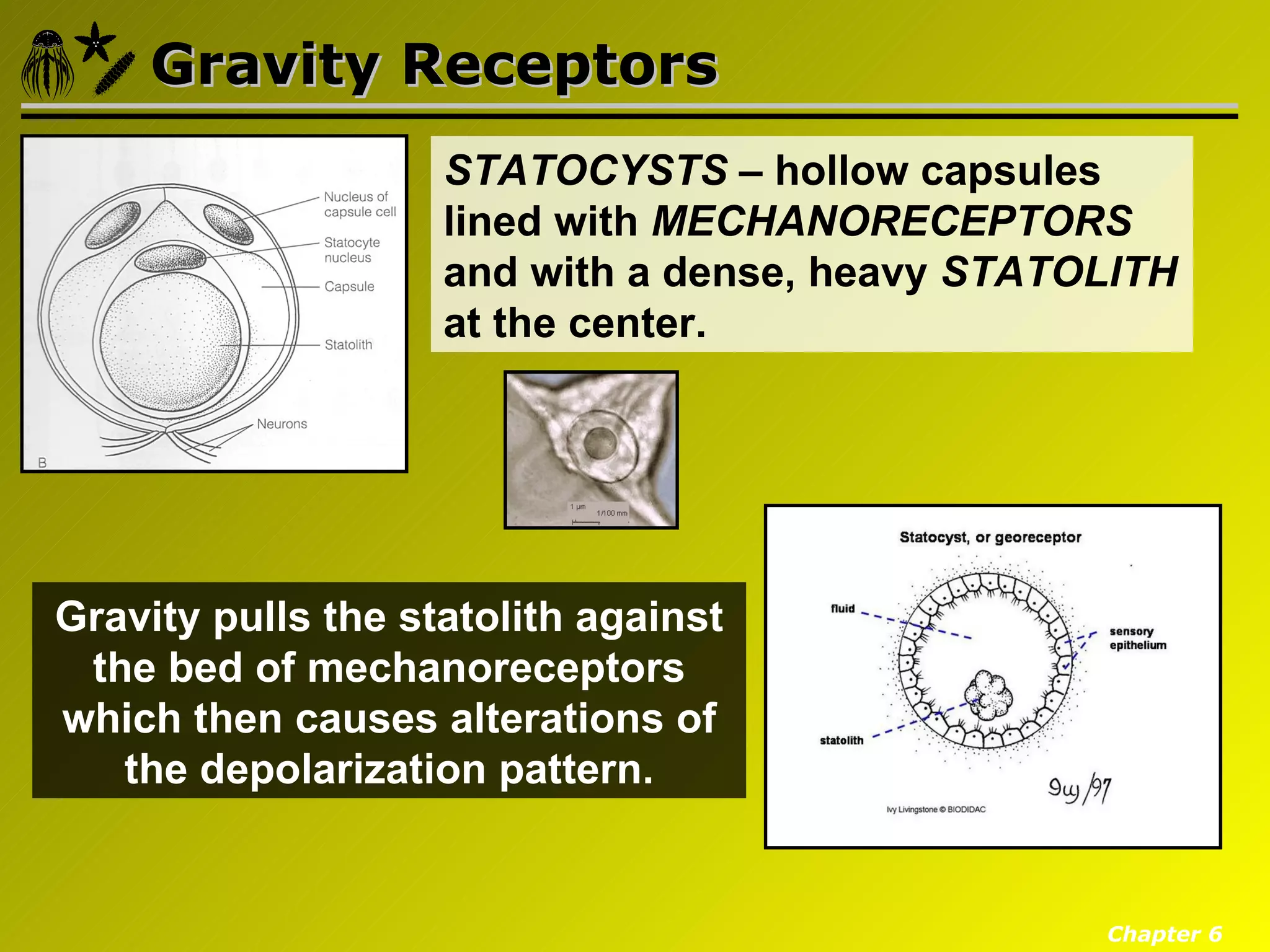
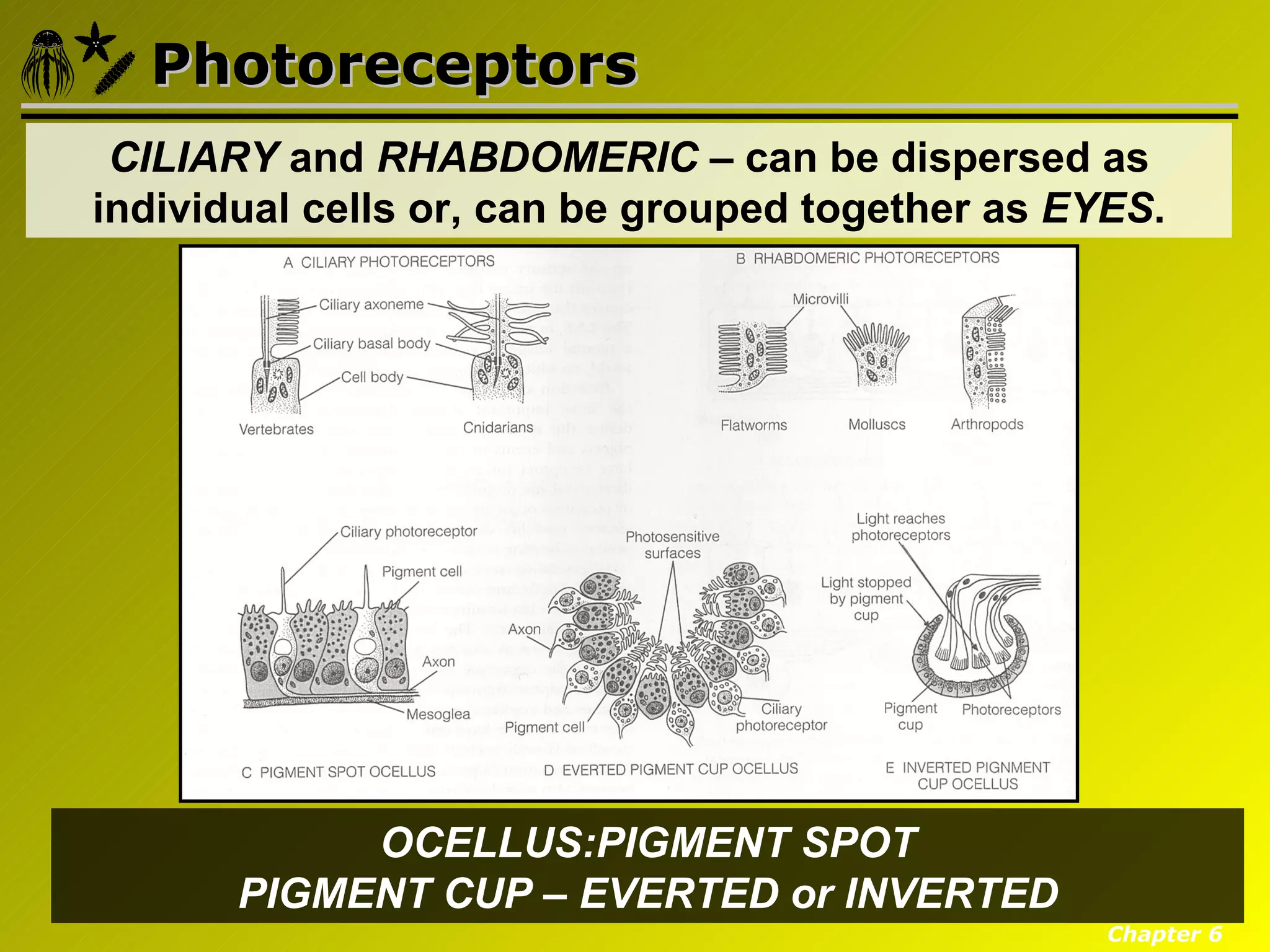
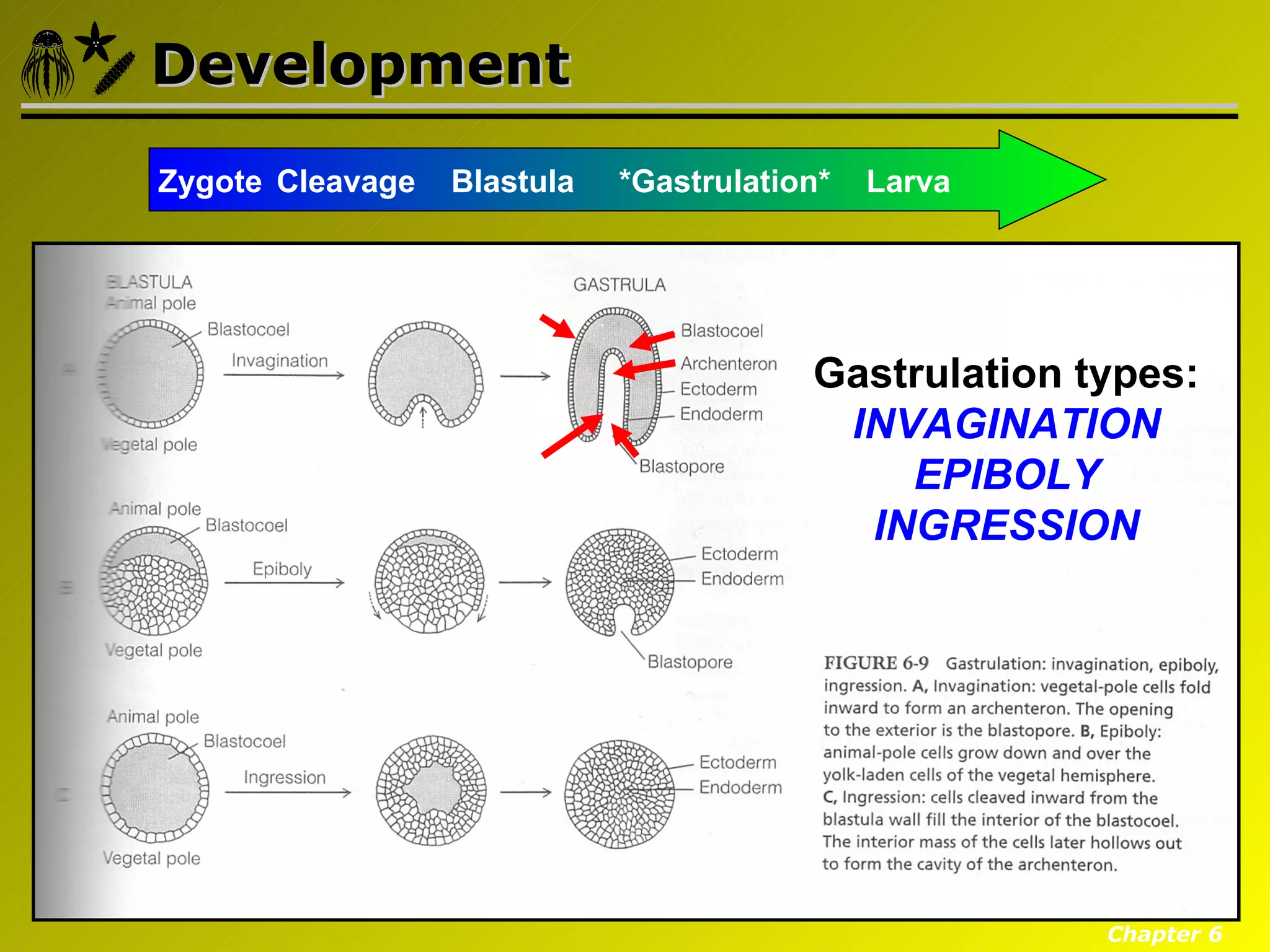
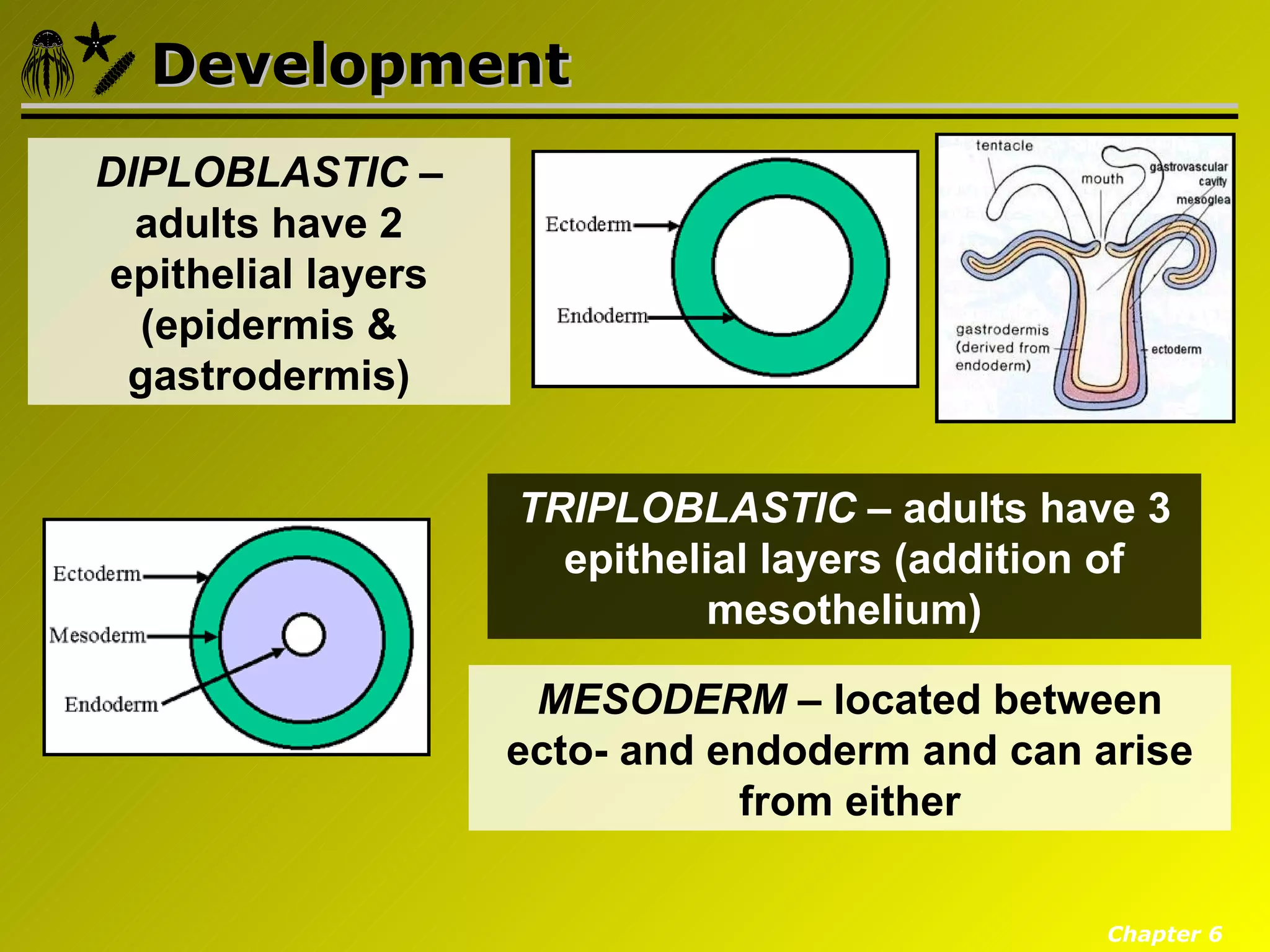
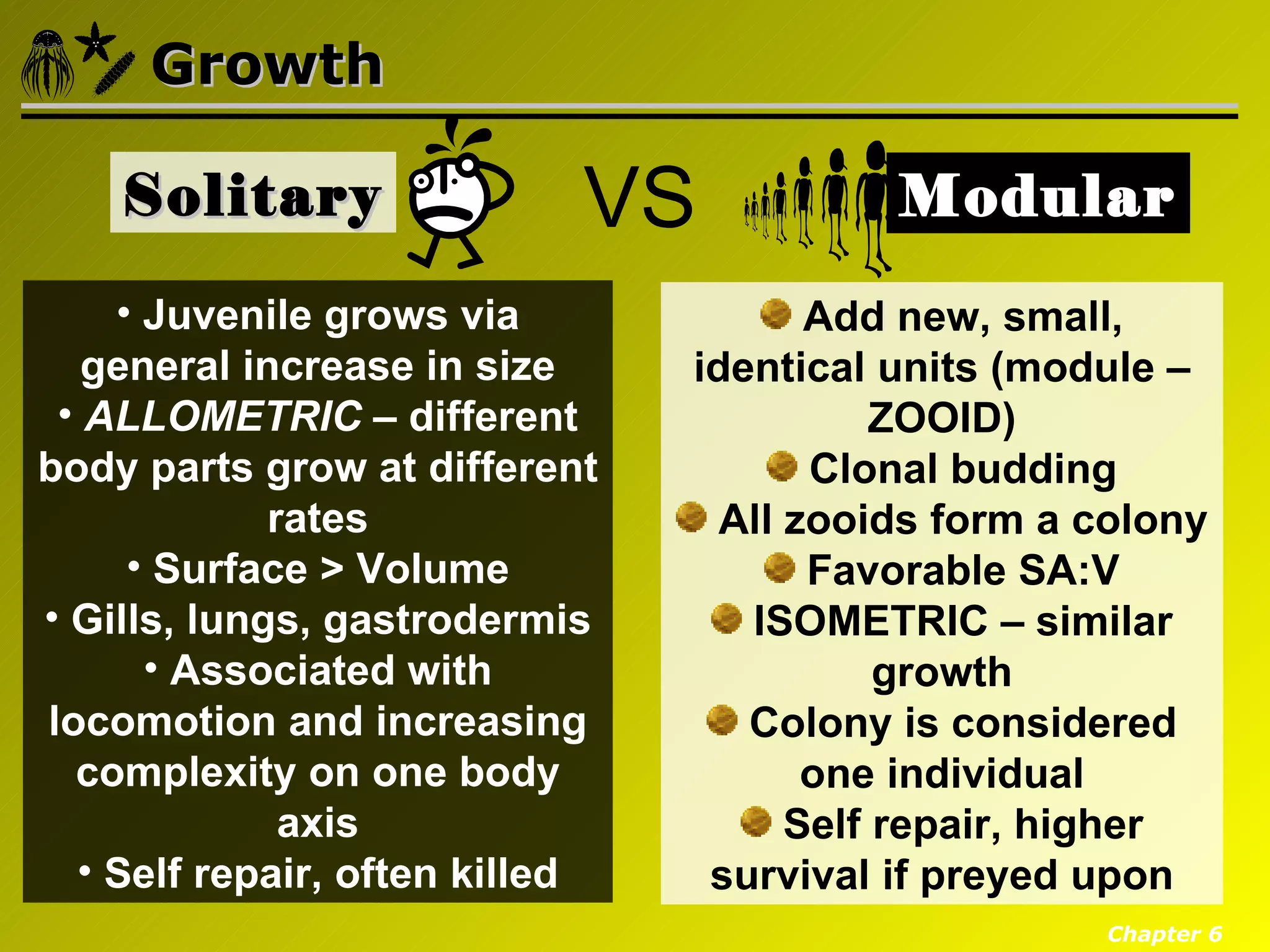
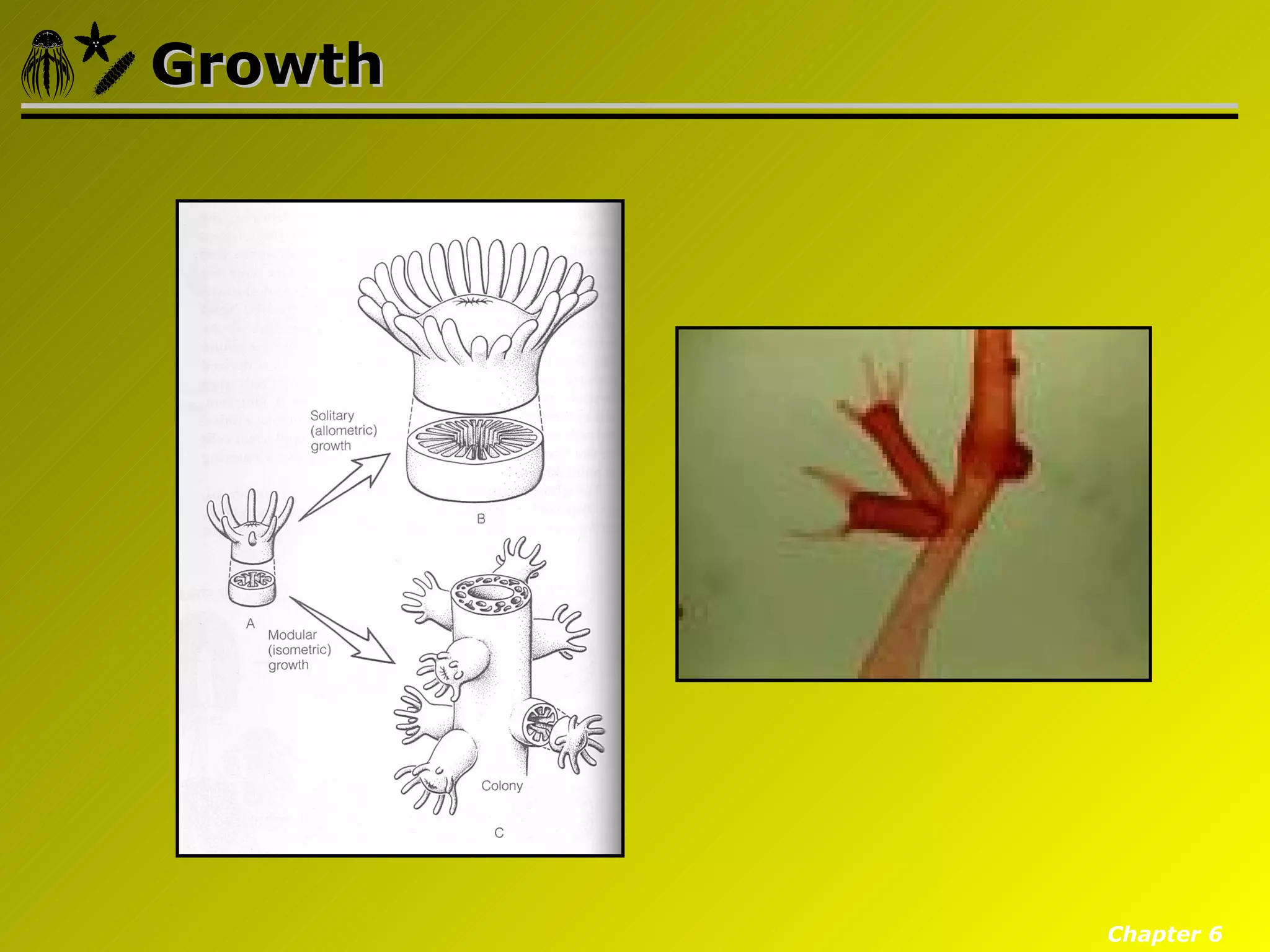
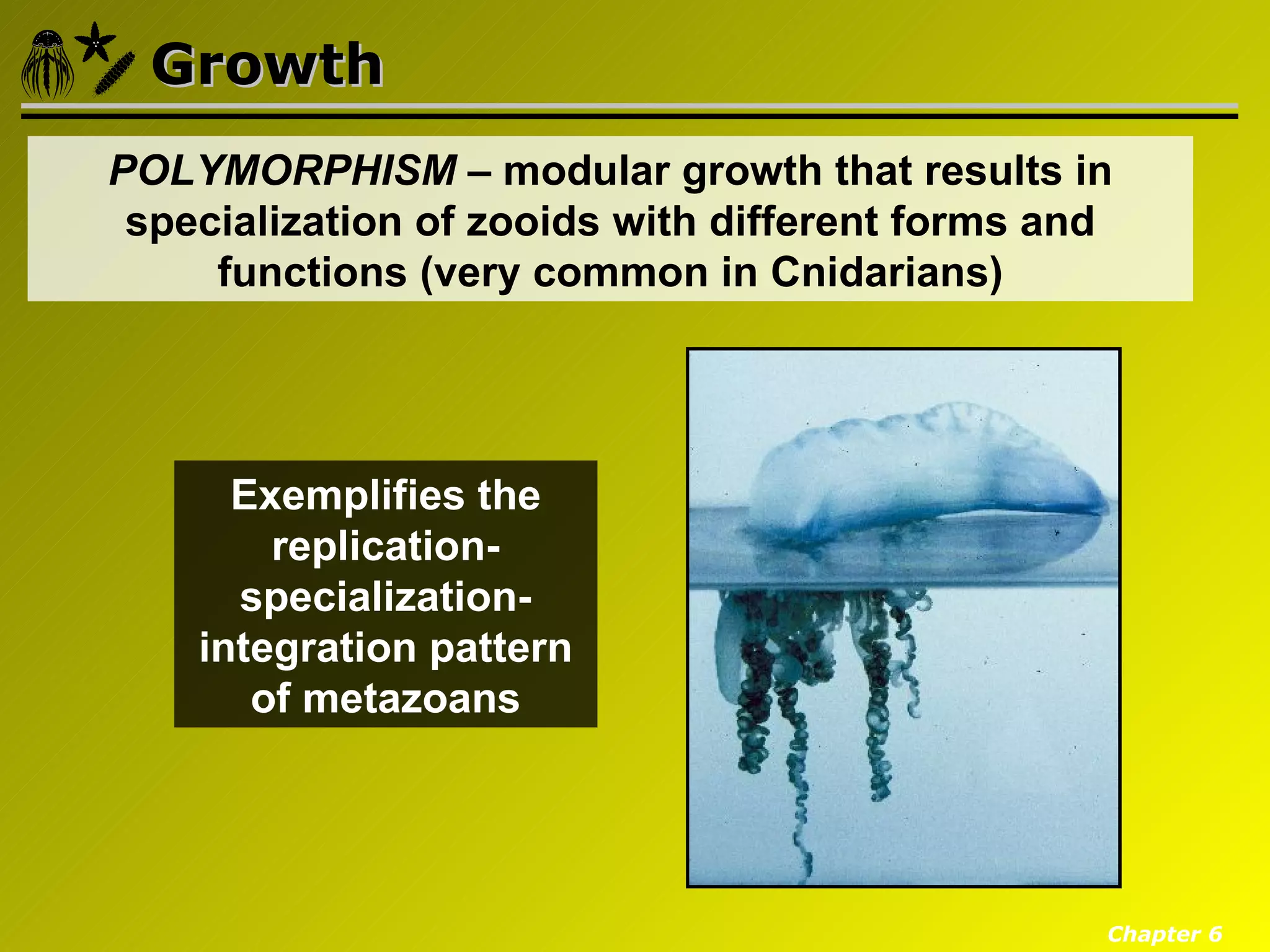
Eumetazoa are the "true animals" that possess true epithelia with basal laminae, definite body axes, and specialized tissues. They have several key characteristics including epithelial tissues that form protective barriers and regulate compartments, a hydrostatic skeleton that uses fluid pressure for support and movement, and muscles, neurons, and senses that allow for complex responses to the environment. Eumetazoans undergo gastrulation during development to form the three primary germ layers and have diverse growth forms ranging from solitary to modular colonial organisms.