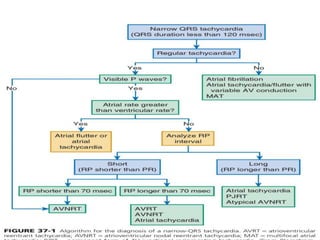
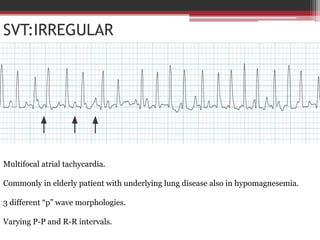
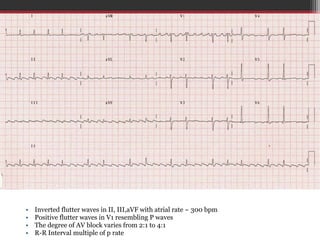
1. The document describes various types of narrow complex tachycardia (NCT), including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, multifocal atrial tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), and atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT).
2. Key aspects that help differentiate the NCTs include the presence or absence of P waves, regularity of the rhythm, P wave morphology, and the RP and PR intervals.
3. Aspects like an irregular rhythm with no P waves indicate atrial fibrillation, while regular rhythms with varying