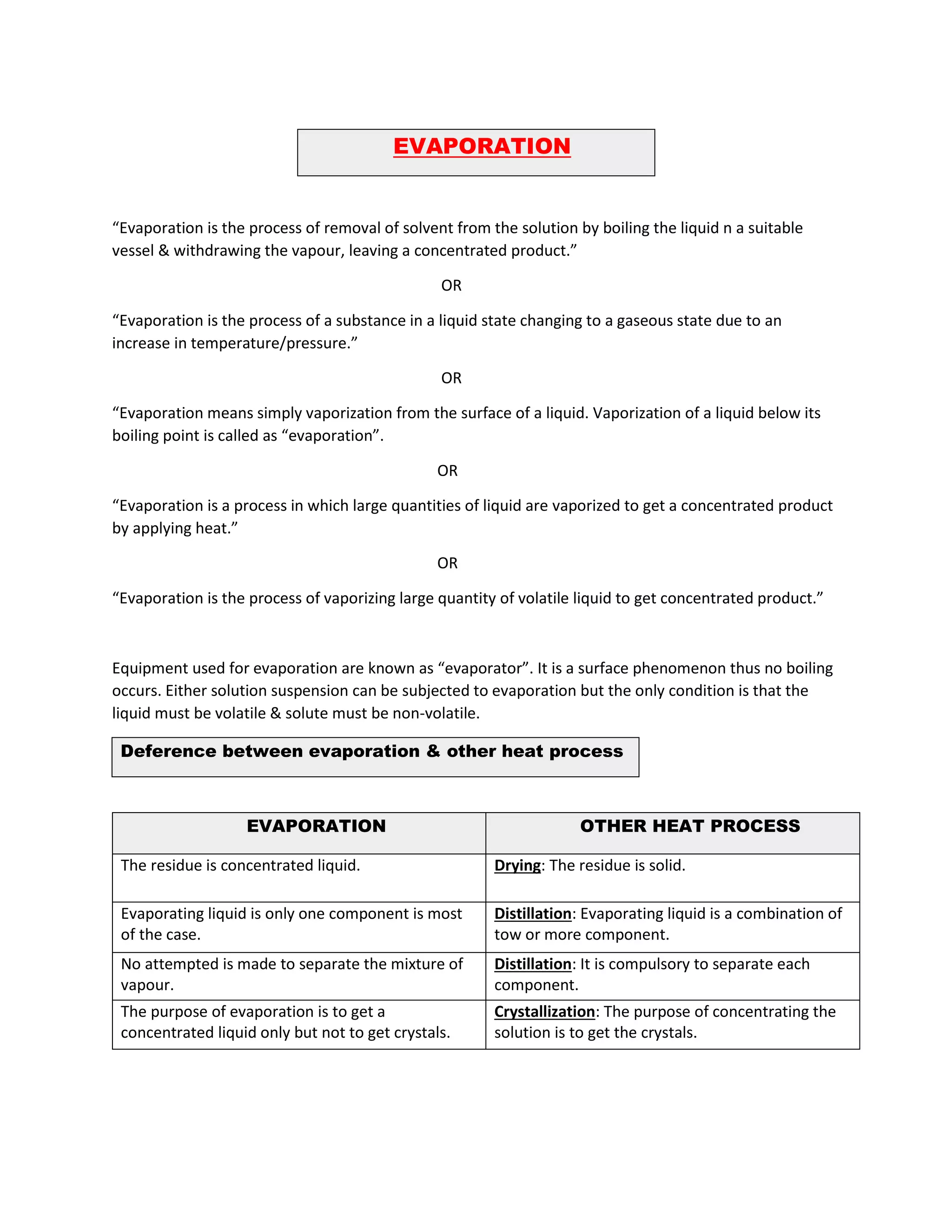
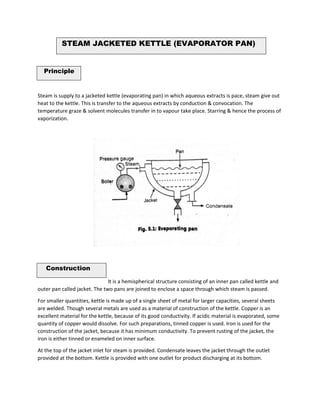
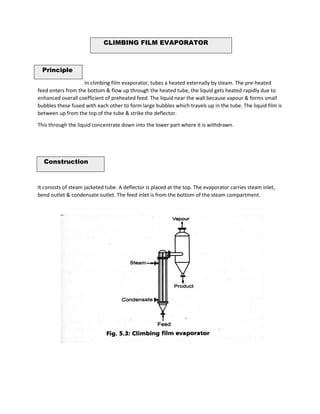
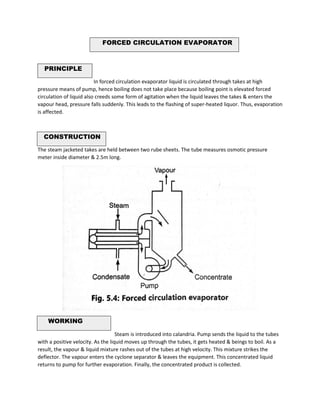
Evaporation is the process of removing solvent from a solution by applying heat, leaving a concentrated product. It occurs below the boiling point through vaporization from the liquid surface. Key factors that affect the evaporation rate include temperature, vapor pressure, surface area, and time. Various types of evaporators are used for evaporation, including steam jacketed kettles, horizontal tube evaporators, climbing film evaporators, and forced circulation evaporators. The type of evaporator used depends on factors like the product properties and desired concentration.