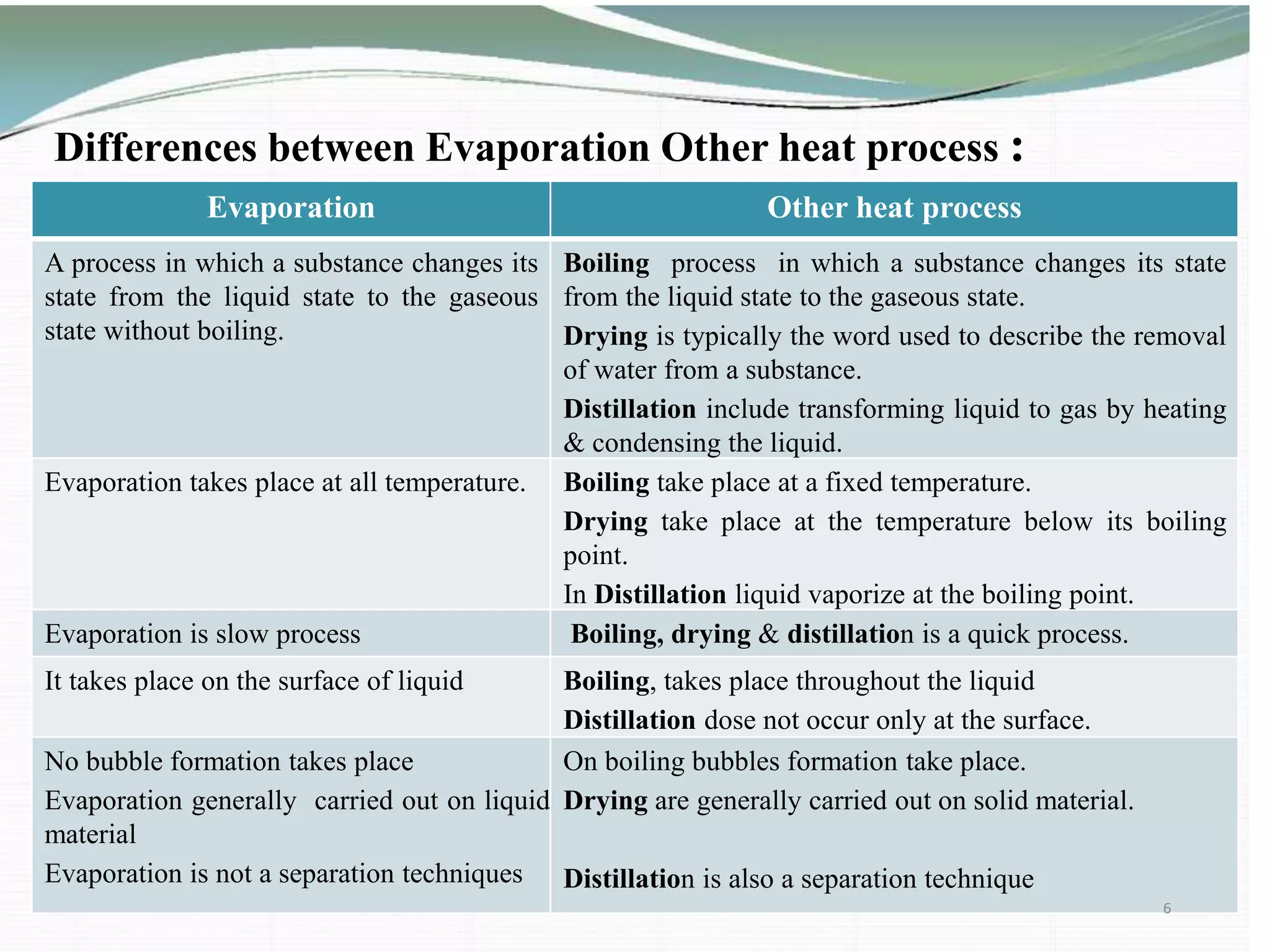
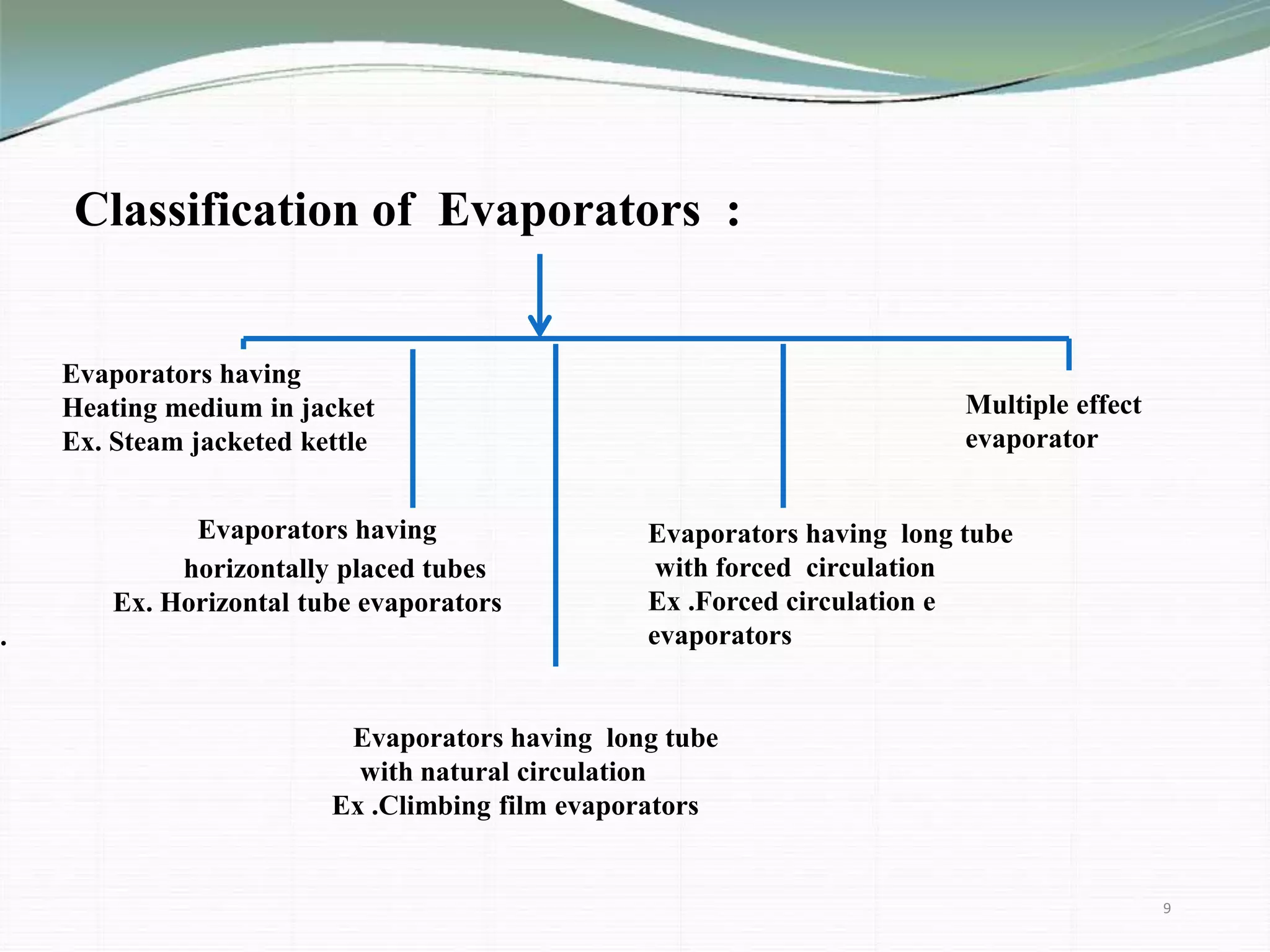
The document discusses the evaporation process in pharmaceutical engineering, detailing its importance, applications, and factors affecting it. It differentiates evaporation from other heat processes such as boiling and drying while highlighting various types of evaporators used in the industry. The summary concludes that evaporation is essential for manufacturing bulk drugs and other products in pharmaceutical and chemical industries.