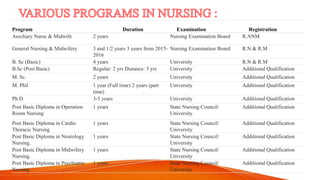
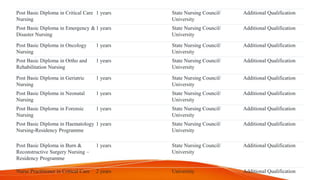
The document discusses guidelines for establishing and evaluating nursing education programs in India. It outlines the requirements to start general nursing, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral programs. Requirements include having an affiliated hospital, meeting physical infrastructure standards, and maintaining appropriate faculty-student ratios. The document also describes various models for conducting program evaluations, emphasizing the importance of ongoing, systematic assessment of curricula, outcomes, teaching effectiveness, and other components to ensure program quality.