The document provides information about polynomials including:
1) A polynomial is an expression constructed from variables and constants using operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponents.
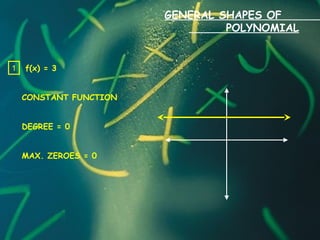
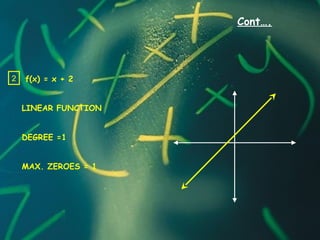
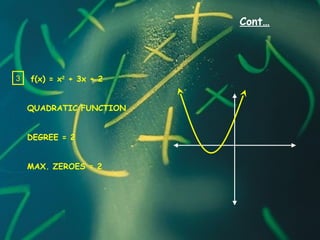
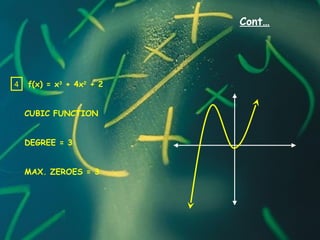
2) The degree of a polynomial refers to the exponent of its highest term. For example, a quadratic polynomial is degree 2 and a cubic is degree 3.
3) The zeros of a polynomial are the values that make the polynomial equal to 0. Finding the zeros involves solving the polynomial equation.
4) The relationships between the zeros and coefficients of a polynomial can be used to find unknown coefficients or zeros.