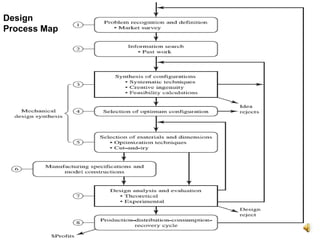
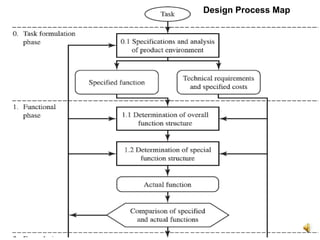
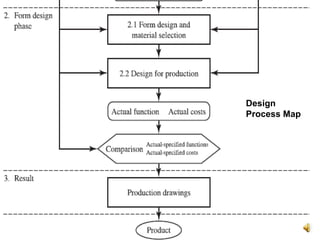
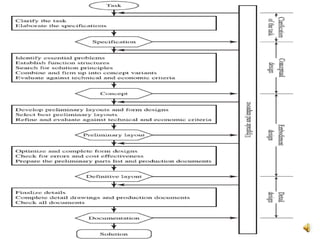
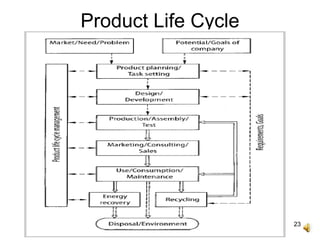
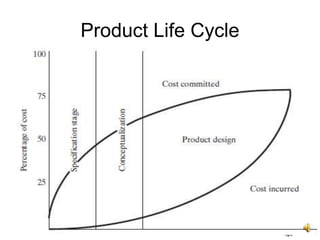
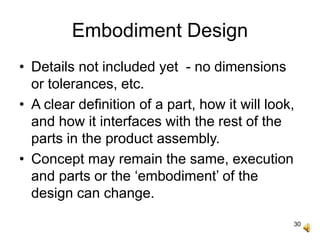
The document outlines the design process involved in creating a new product, emphasizing the balance between evolutionary and innovative design. It details stages such as identifying customer needs, market analysis, defining goals, and the iterative nature of design from conception to prototype. Additionally, it provides insights on effective communication and marketing strategies necessary for successful product development.