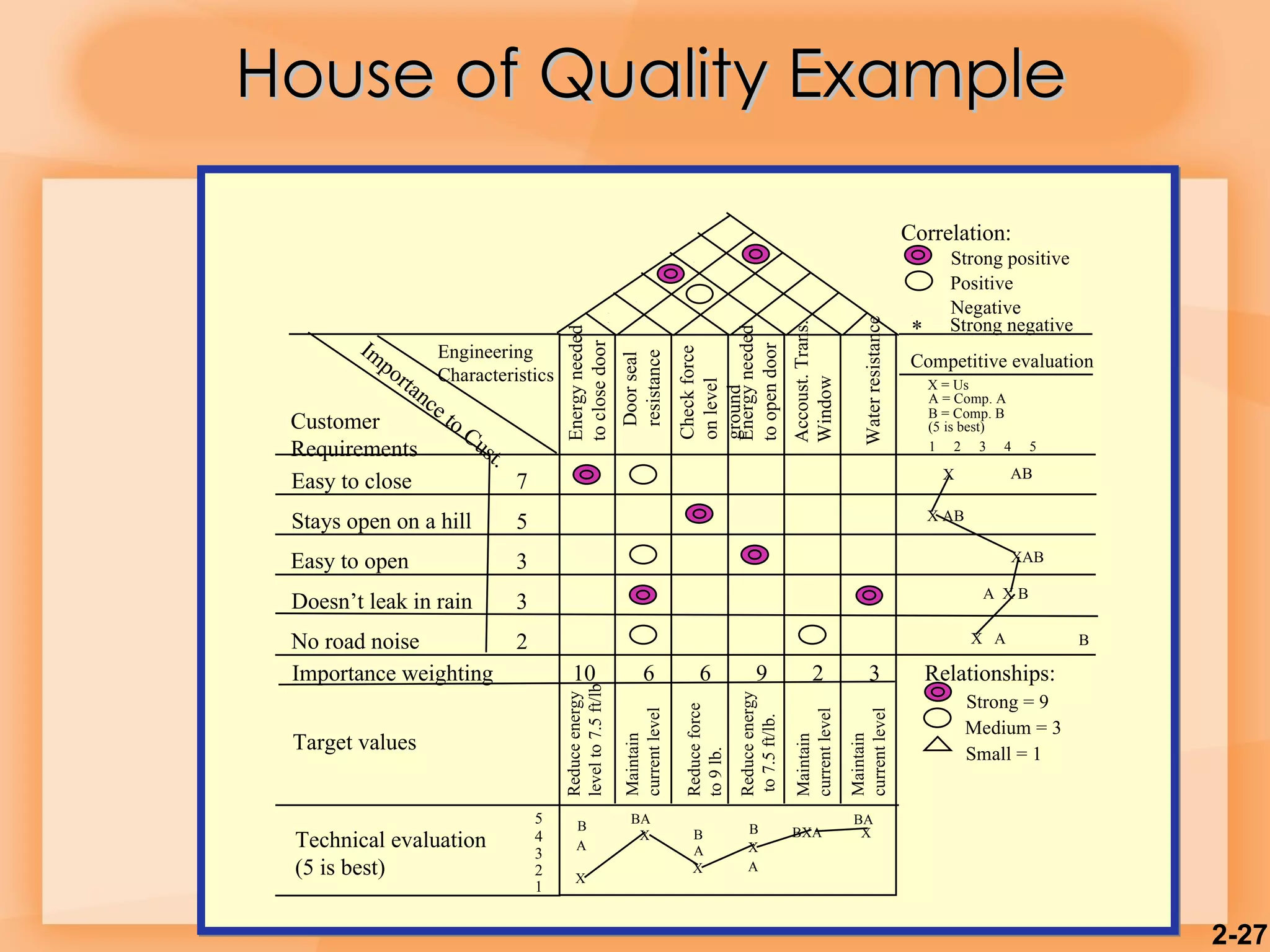
The document discusses various aspects of product and service design including:
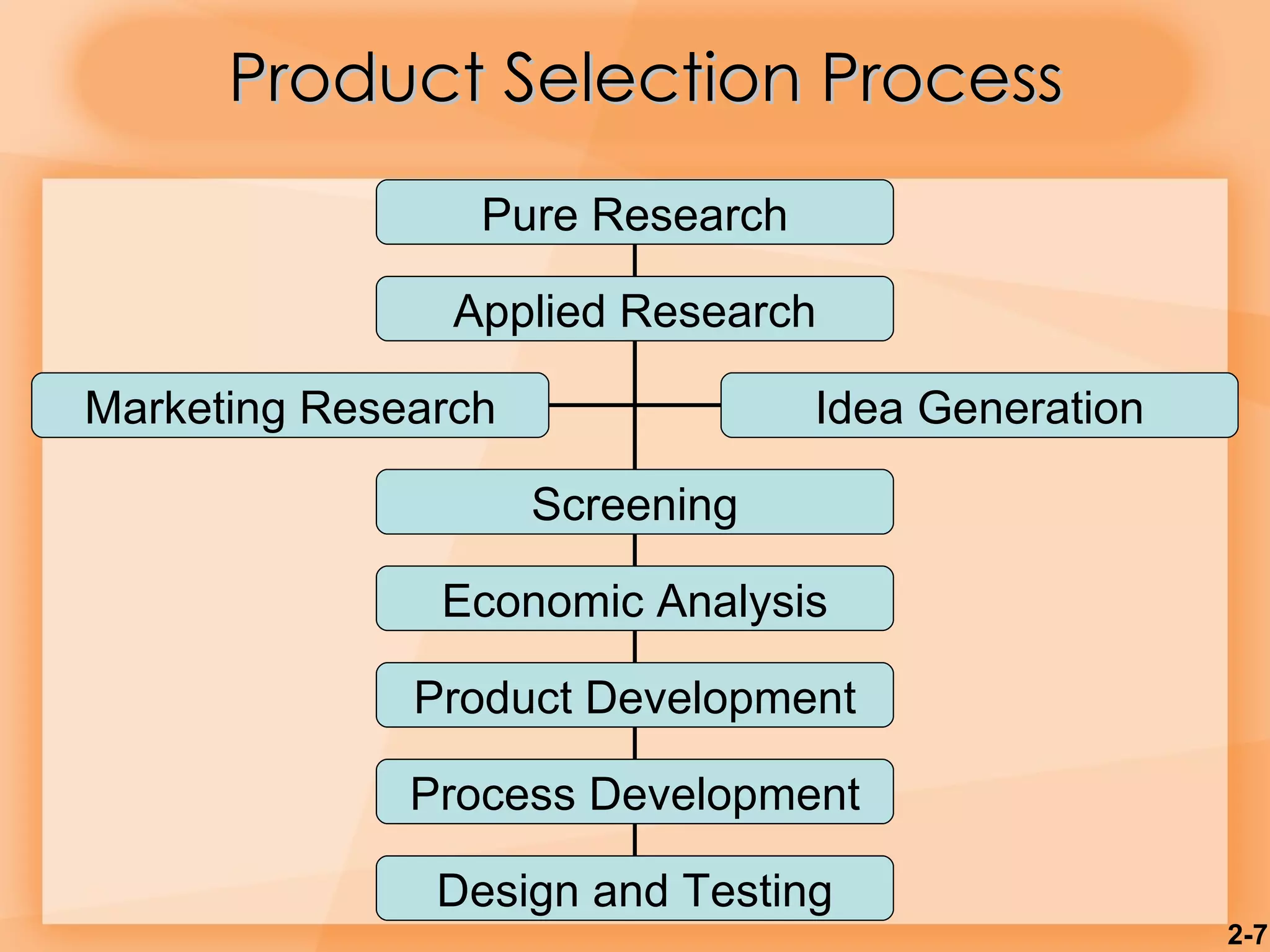
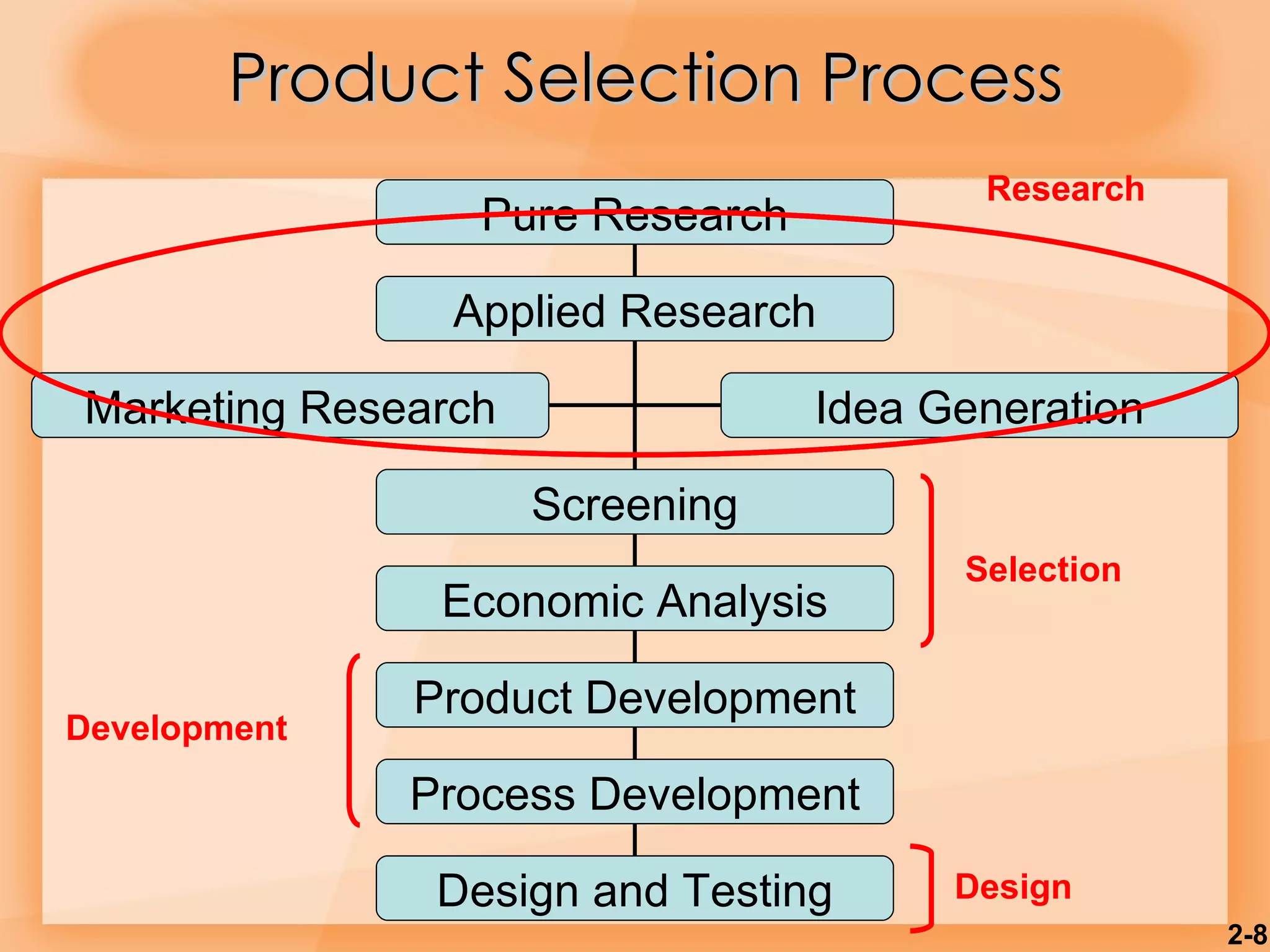
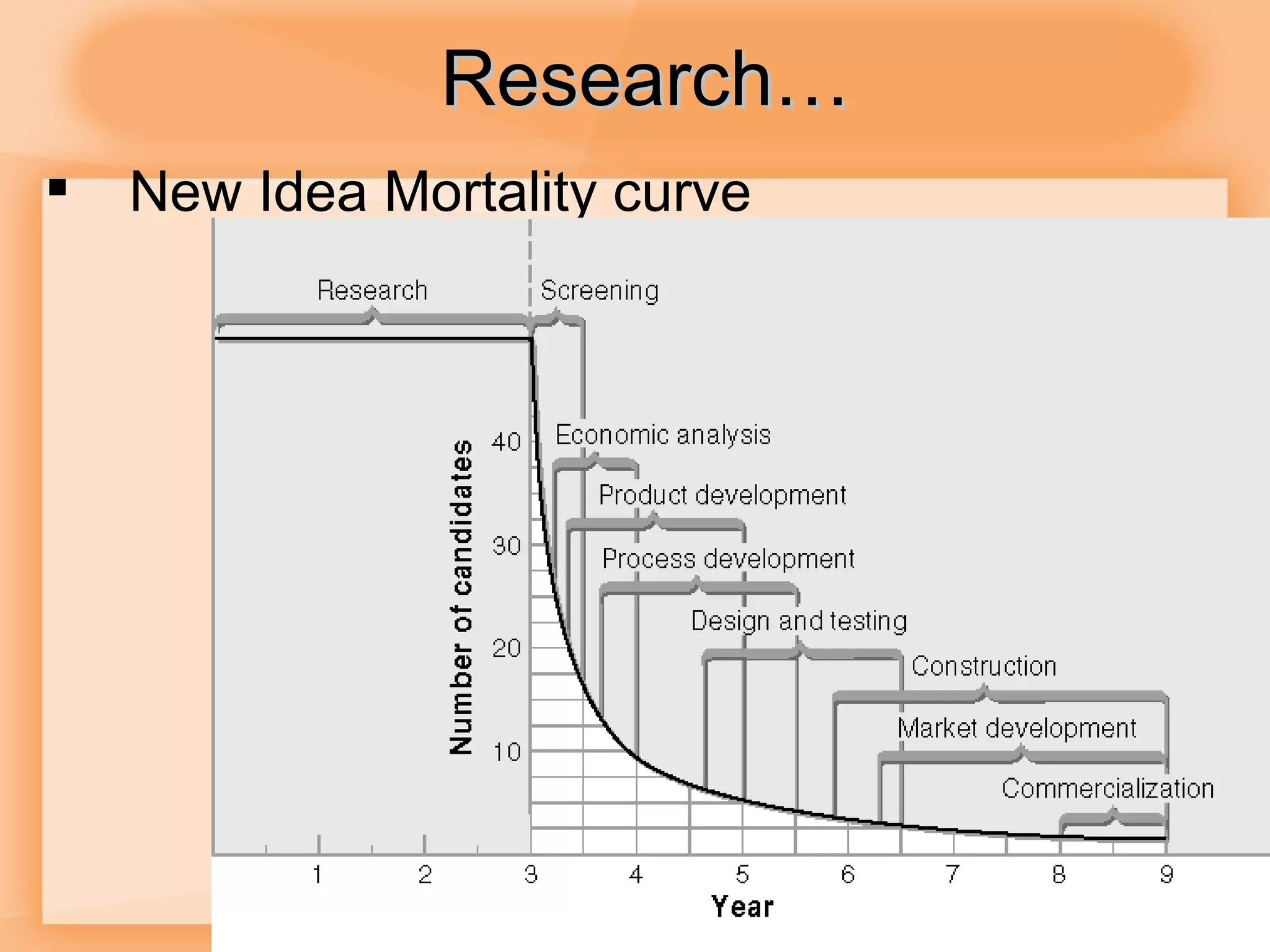
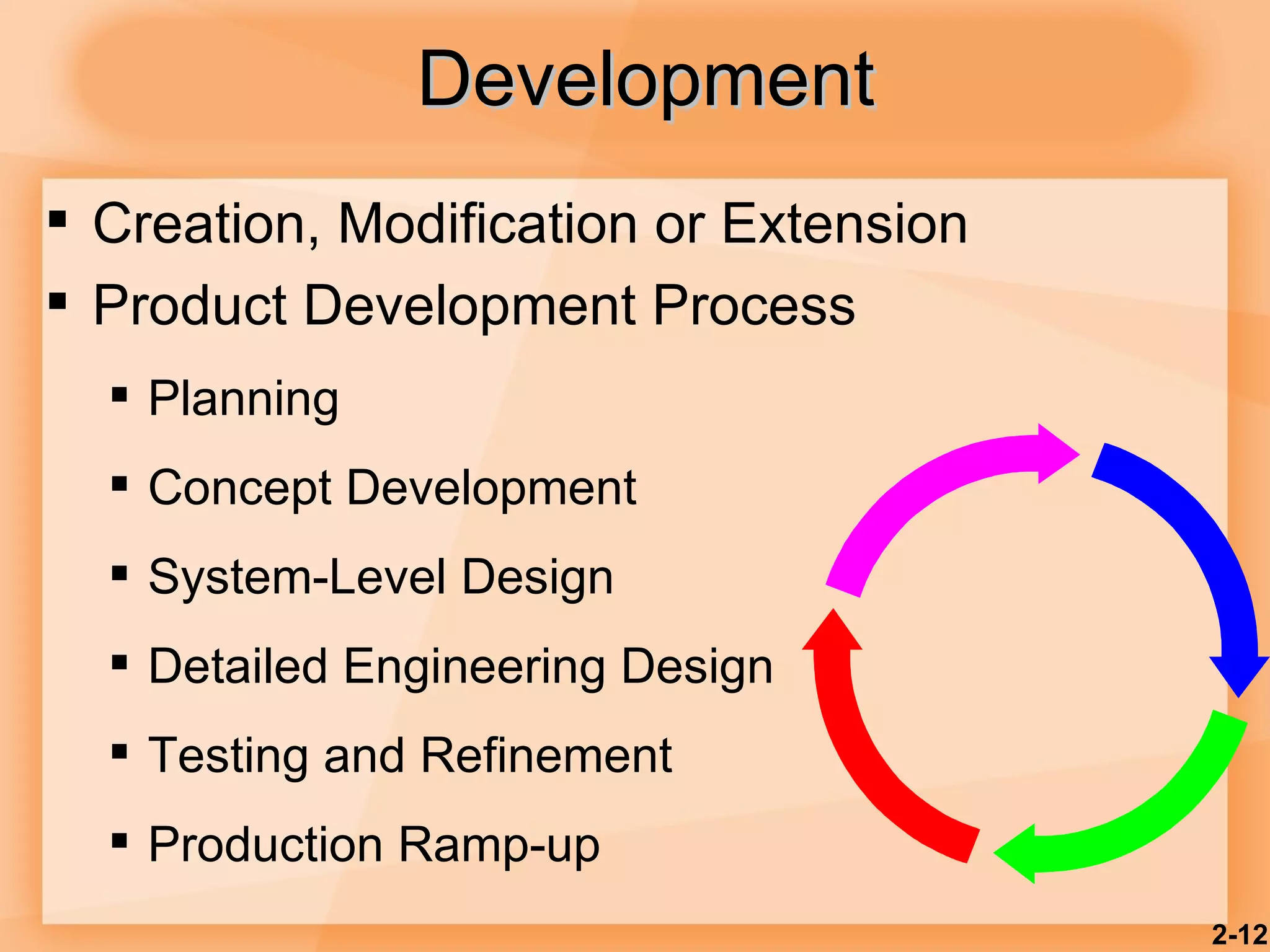
1) The product selection process involves research, development, design, testing and marketing research before a product is launched.
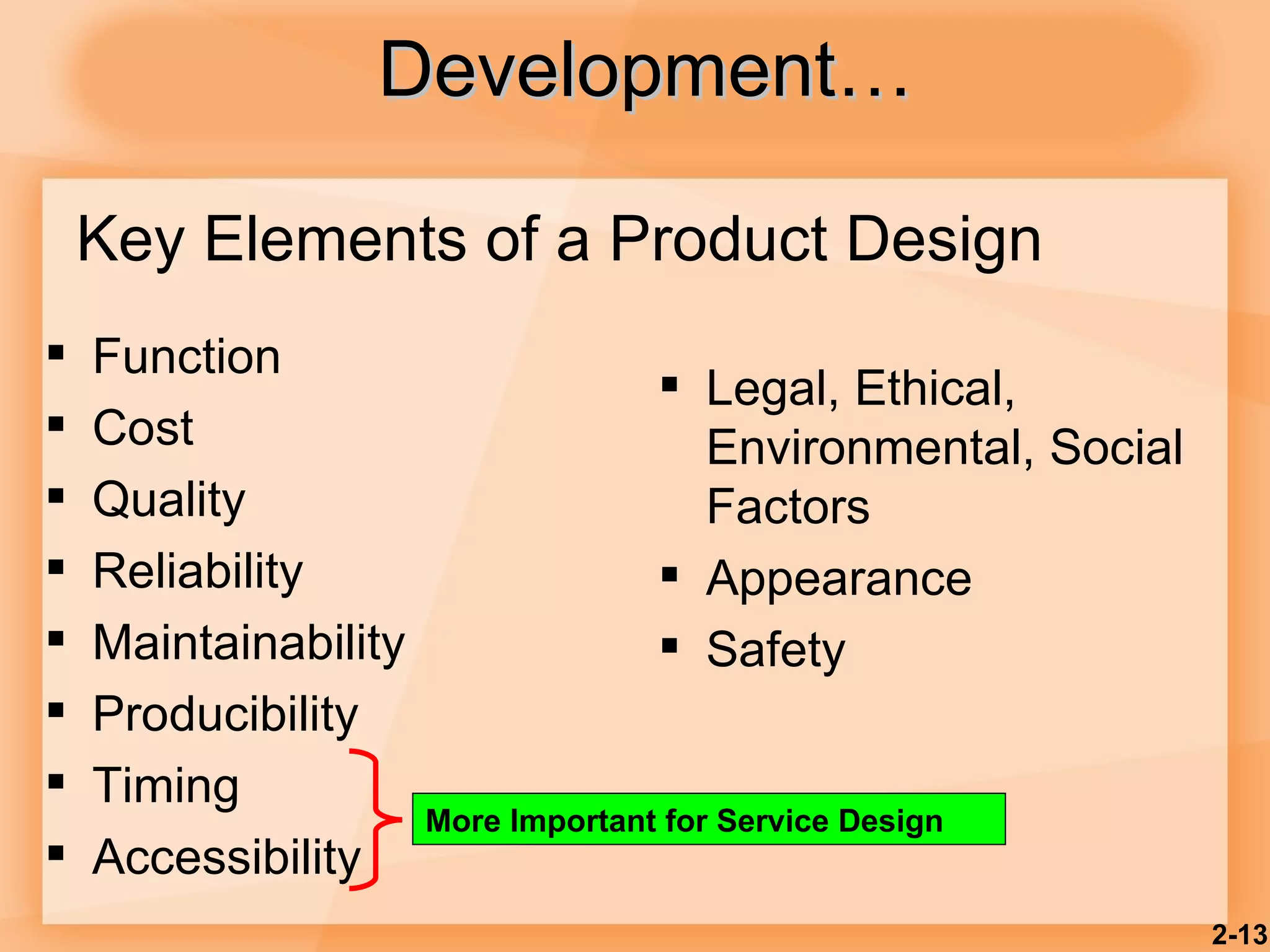
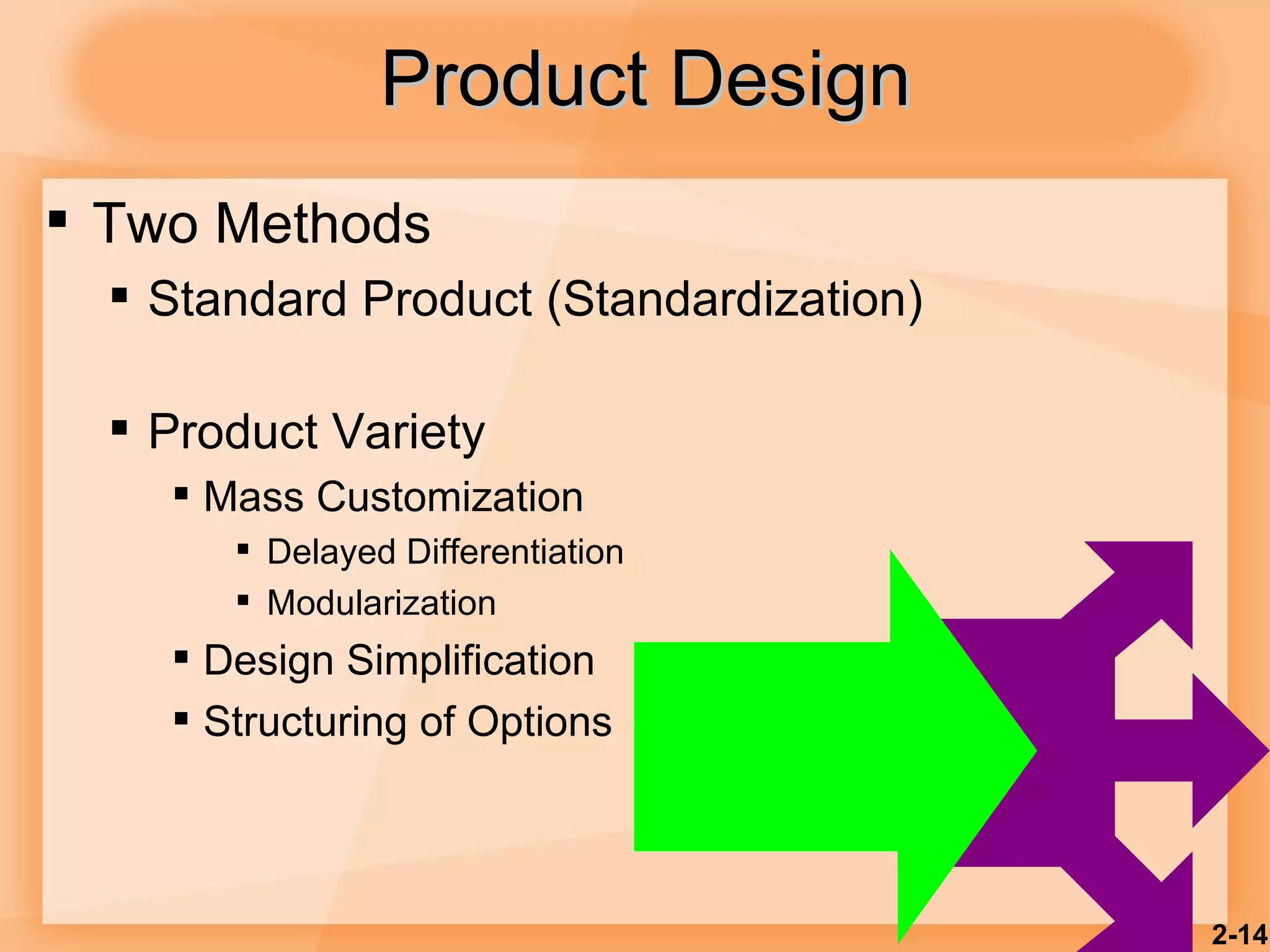
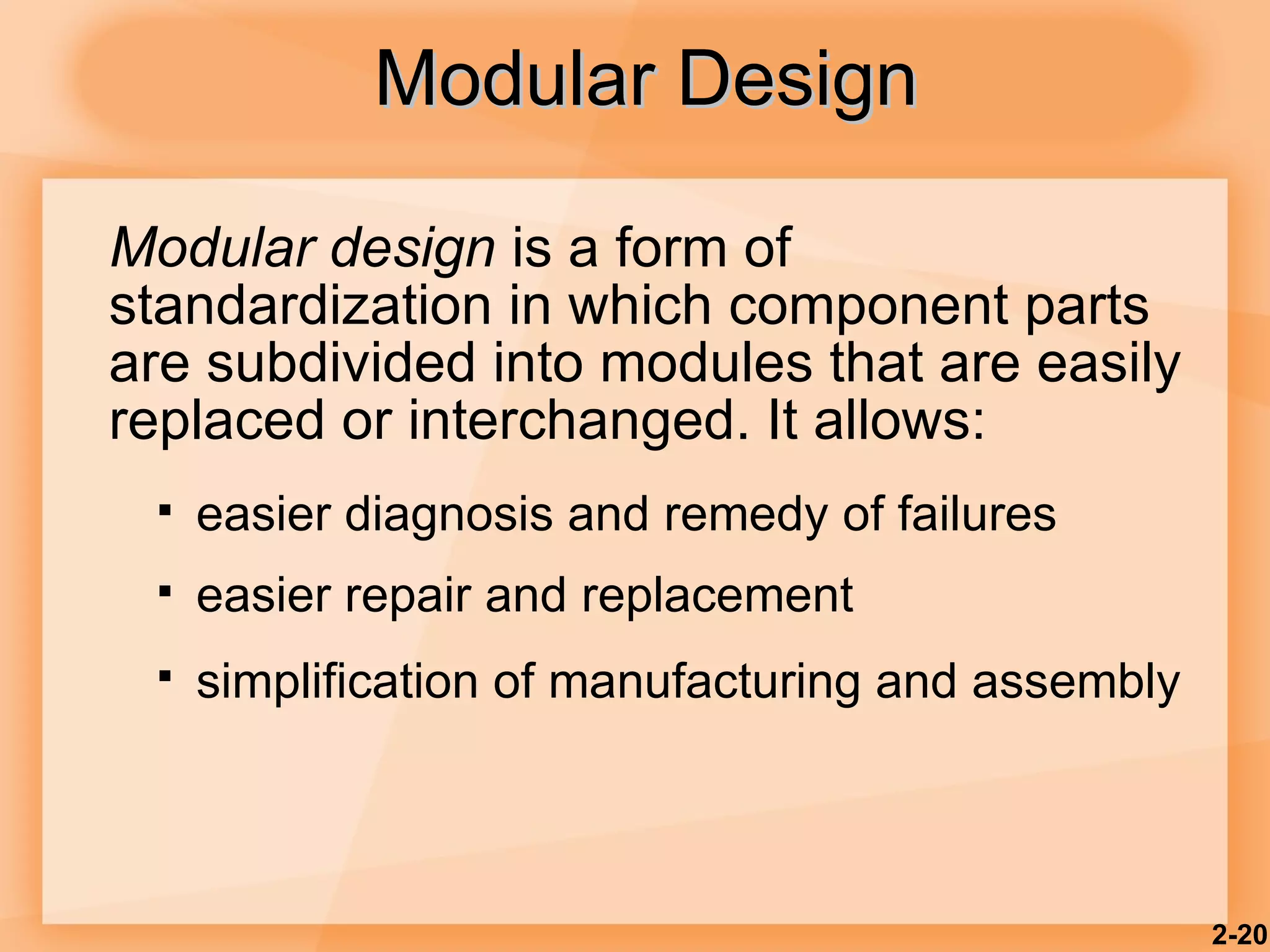
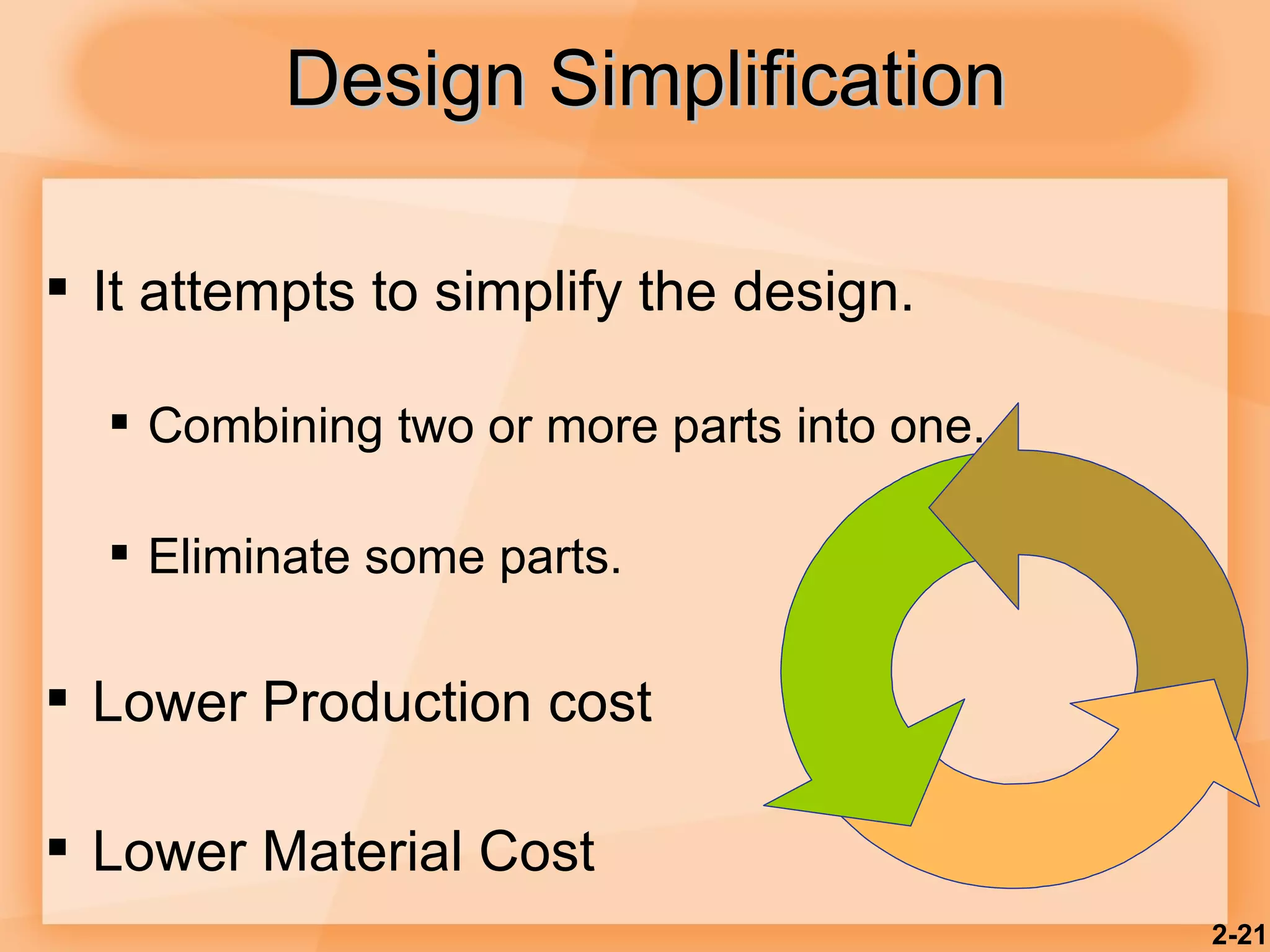
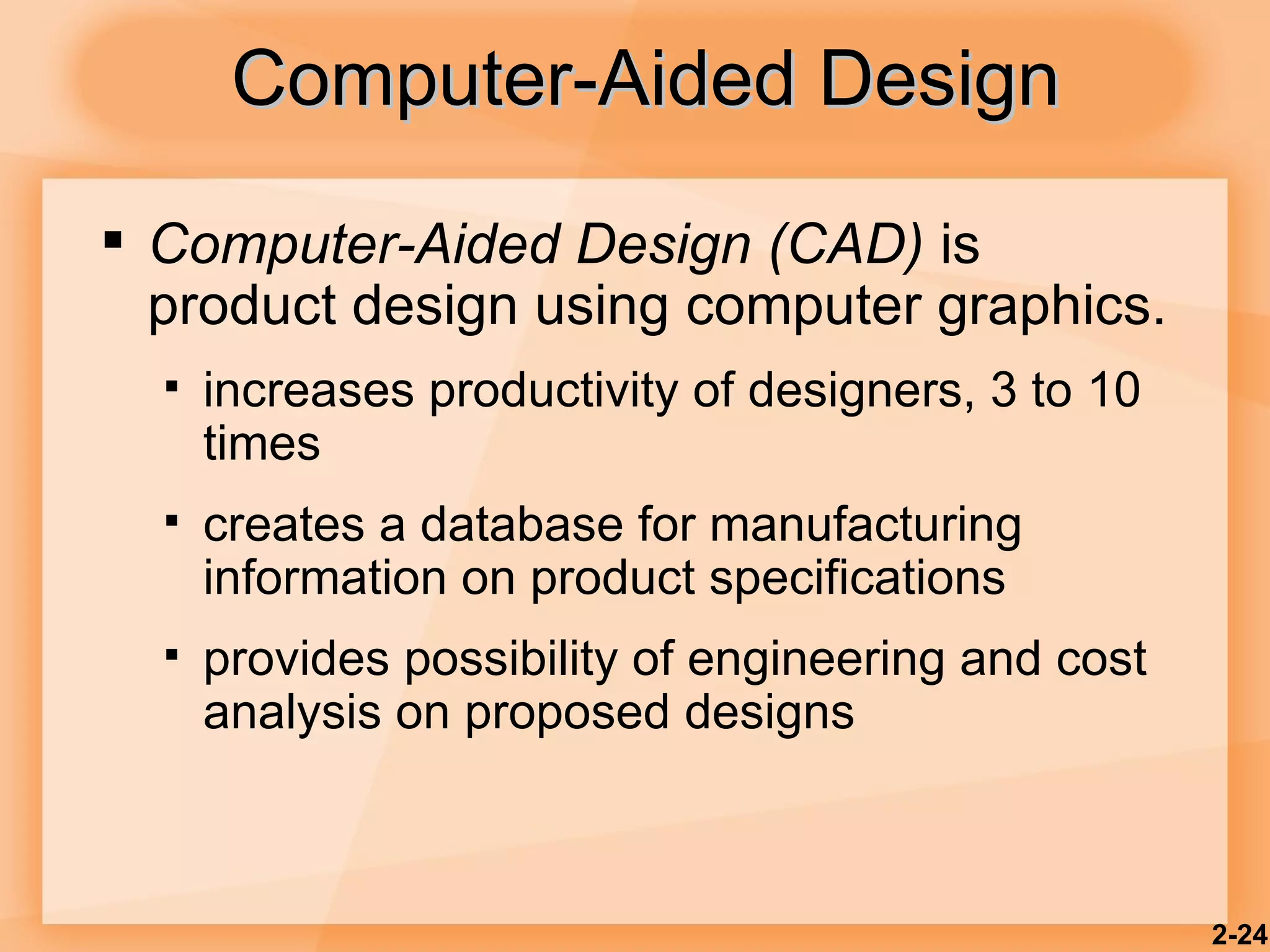
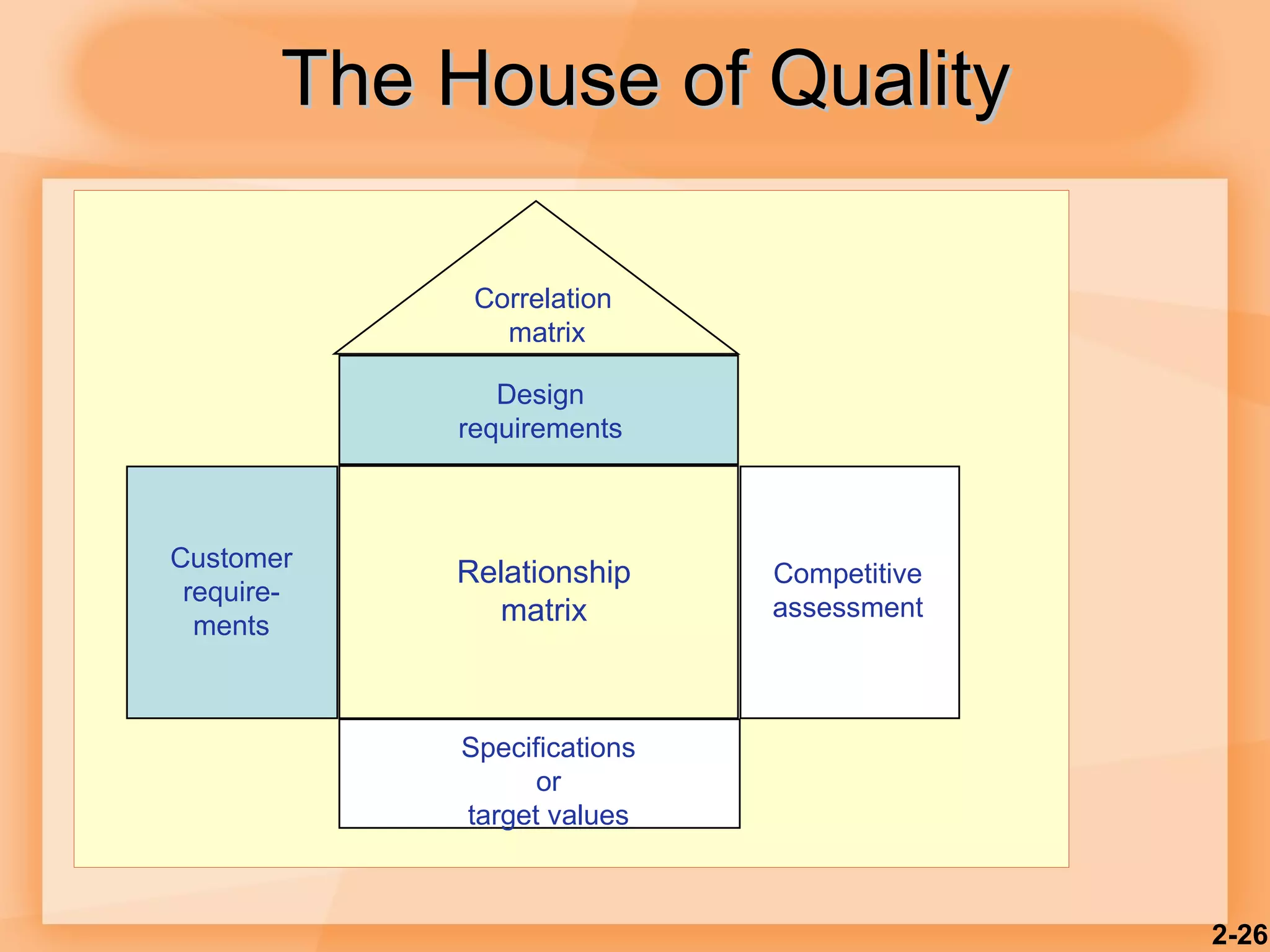
2) Product design should be closely tied to an organization's strategy and focus on customer satisfaction as well as functional, cost, quality and other factors.
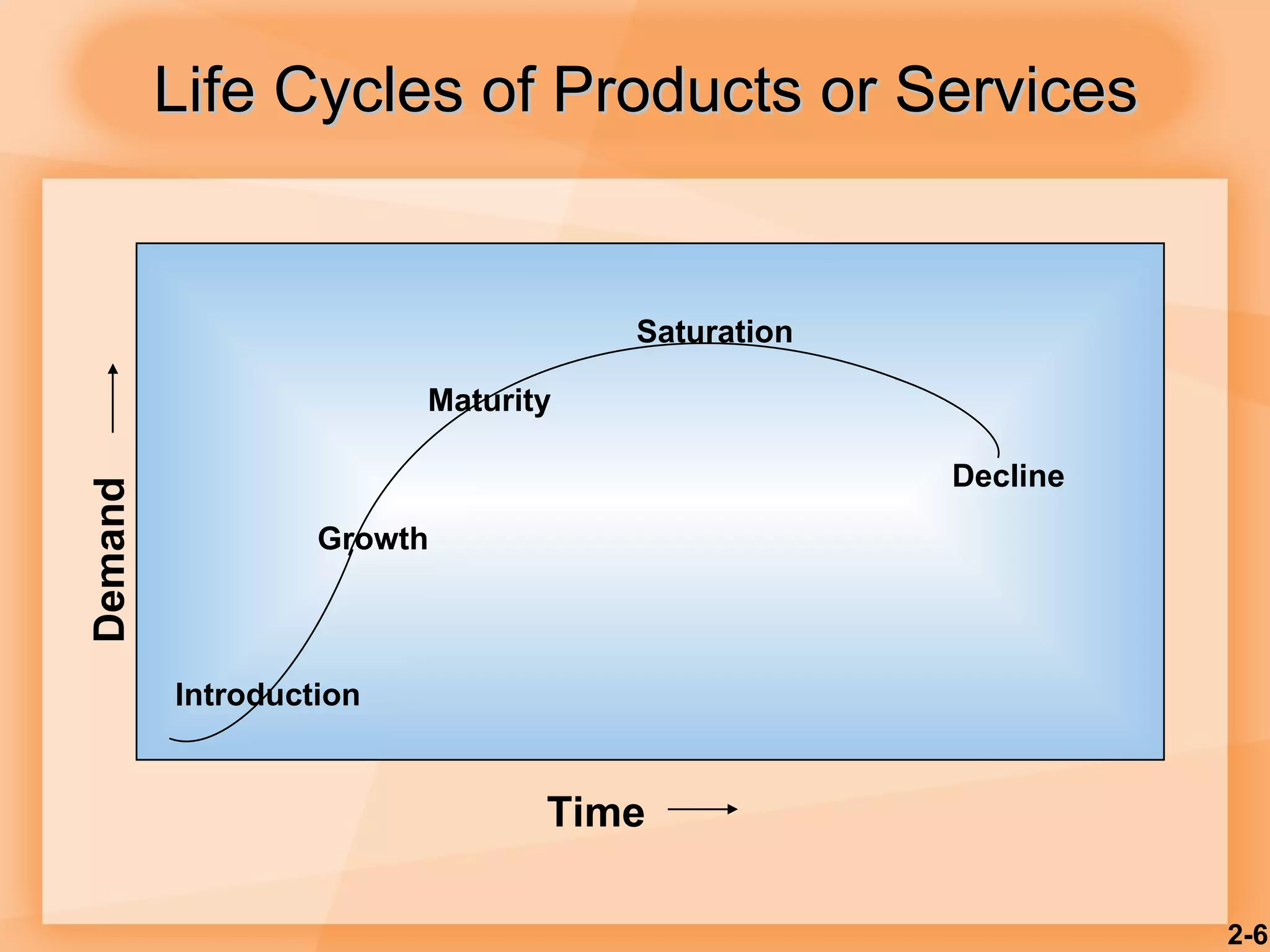
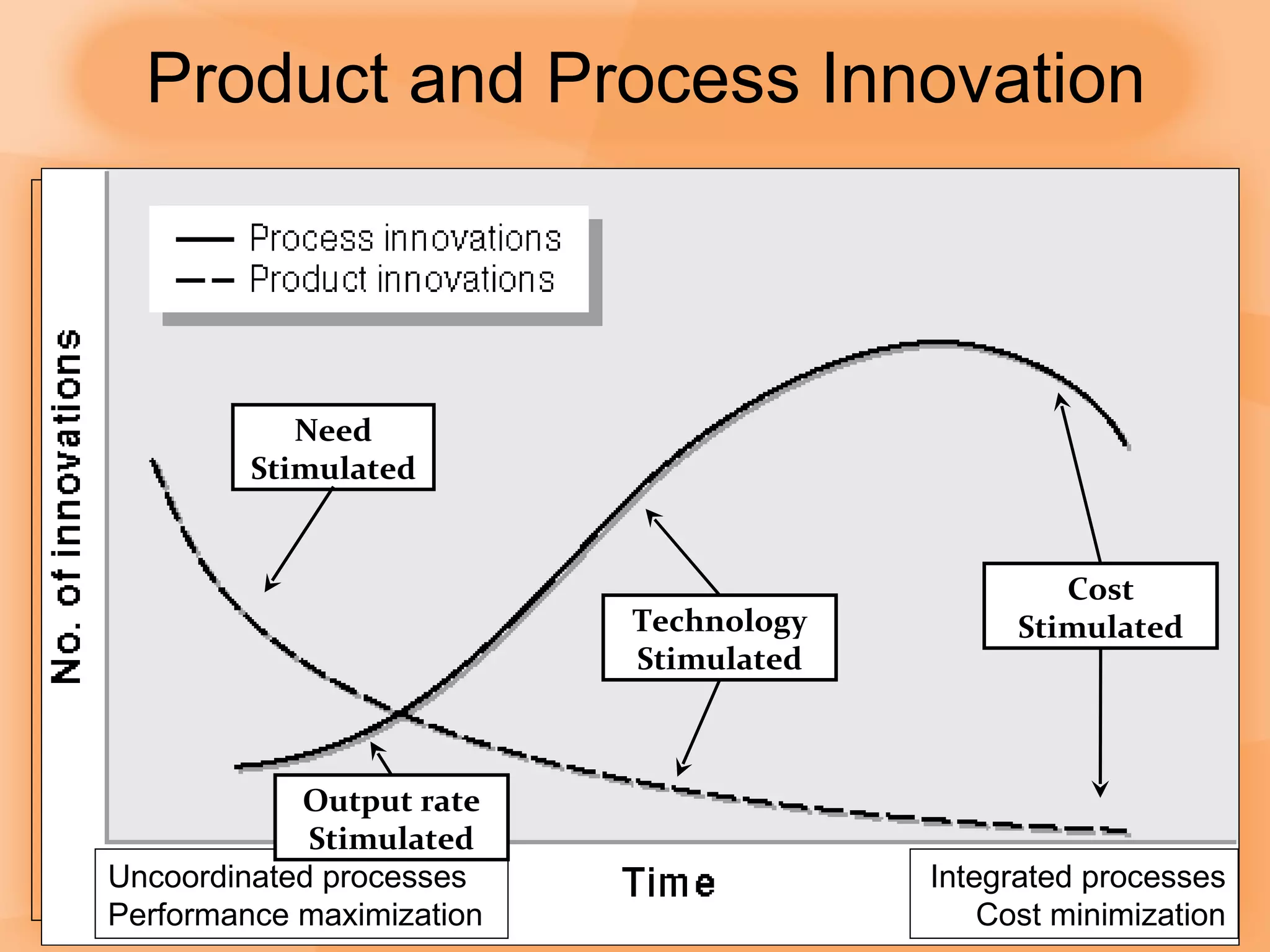
3) Products and services go through life cycles of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline with changing demand over time.