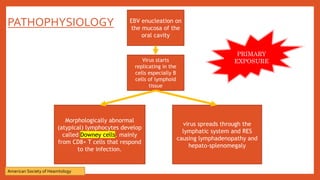
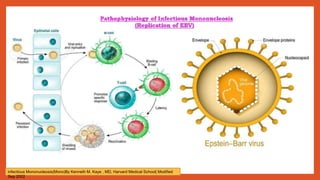
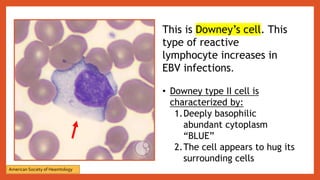
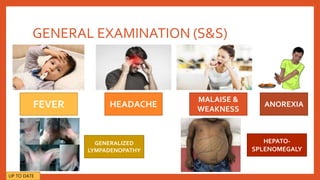
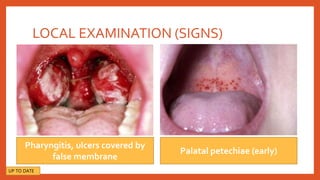
Mononucleosis is caused most commonly by the Epstein-Barr virus. It is characterized by fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. While symptoms usually clear within a few weeks, fatigue can sometimes last for months. Diagnosis involves physical exam findings along with blood tests detecting heterophile antibodies or EBV antibodies. Treatment is supportive with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications for fever and pain. Complications are rare but may include spleen rupture or neurological issues. Prevention involves good hygiene and avoiding sharing foods or drinks with those exhibiting viral symptoms.