Embed presentation
Download to read offline

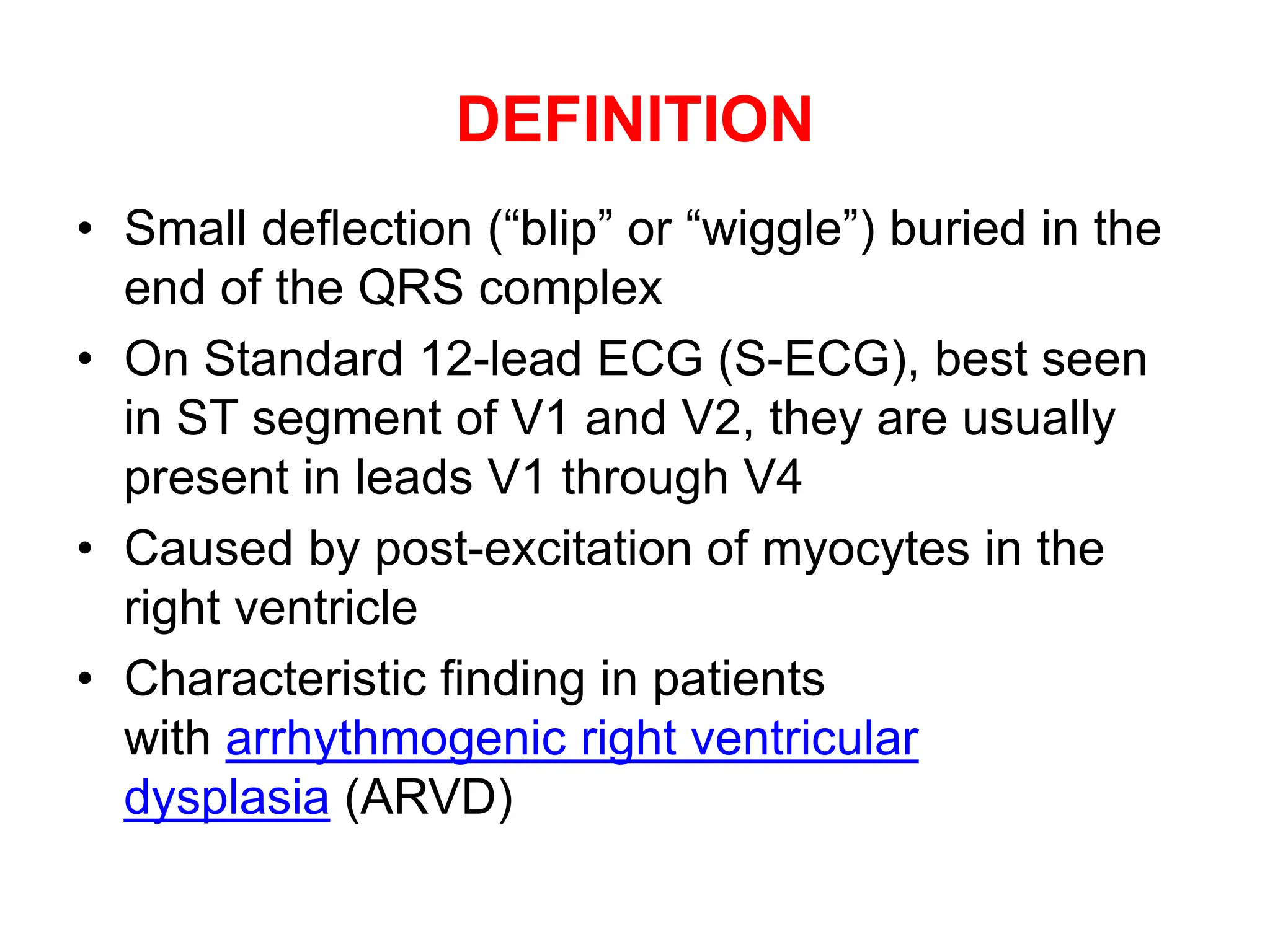
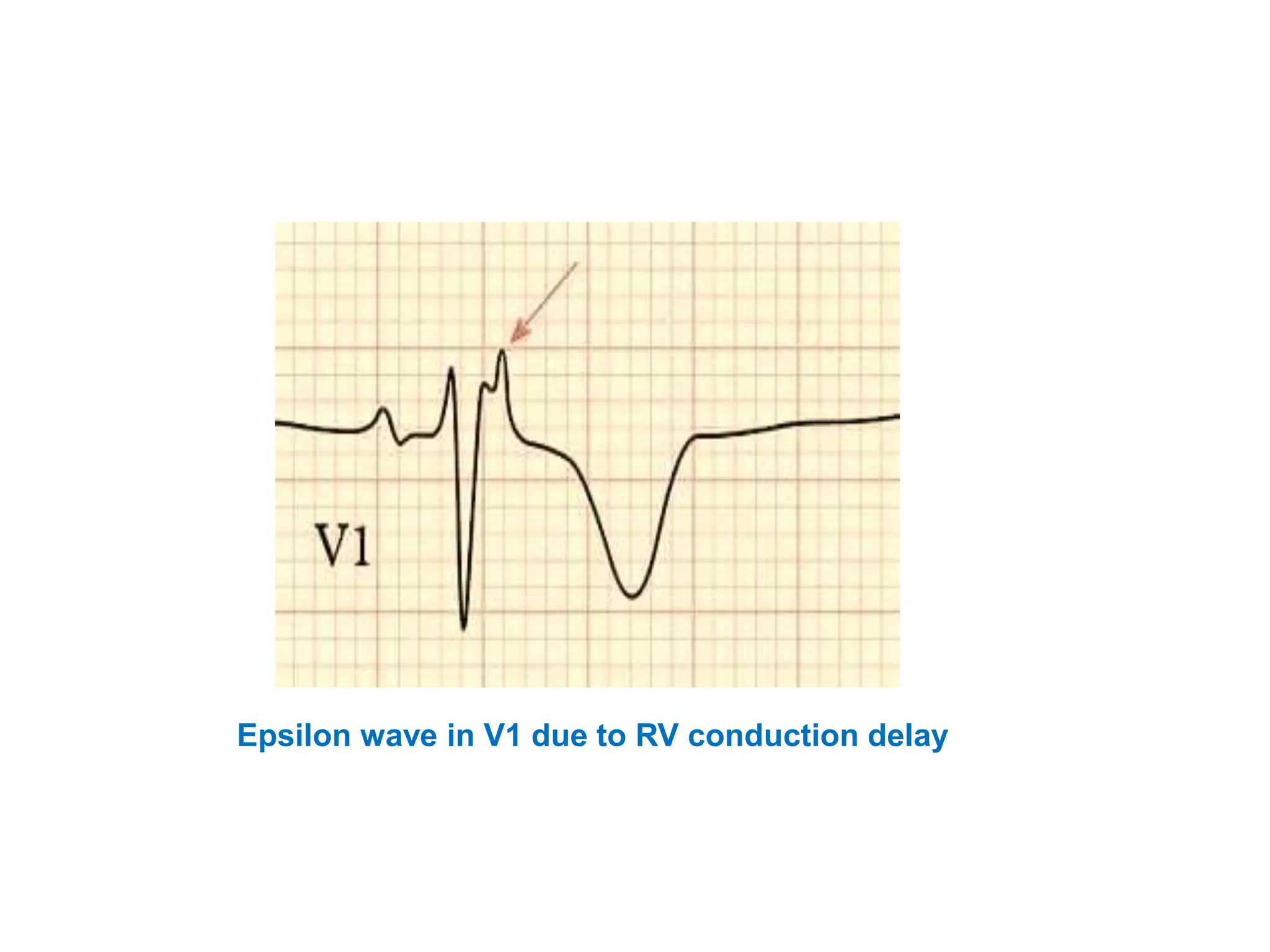

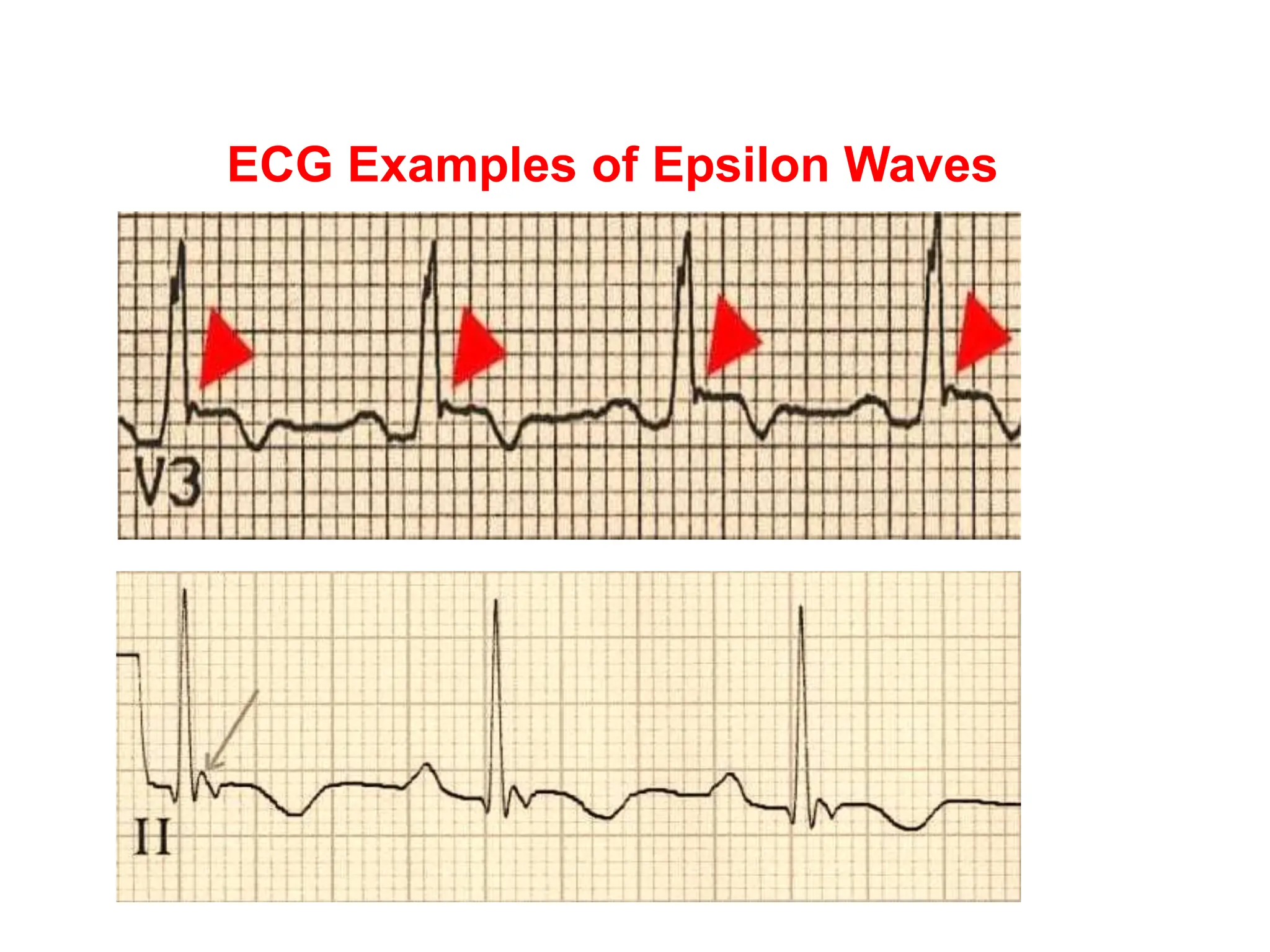
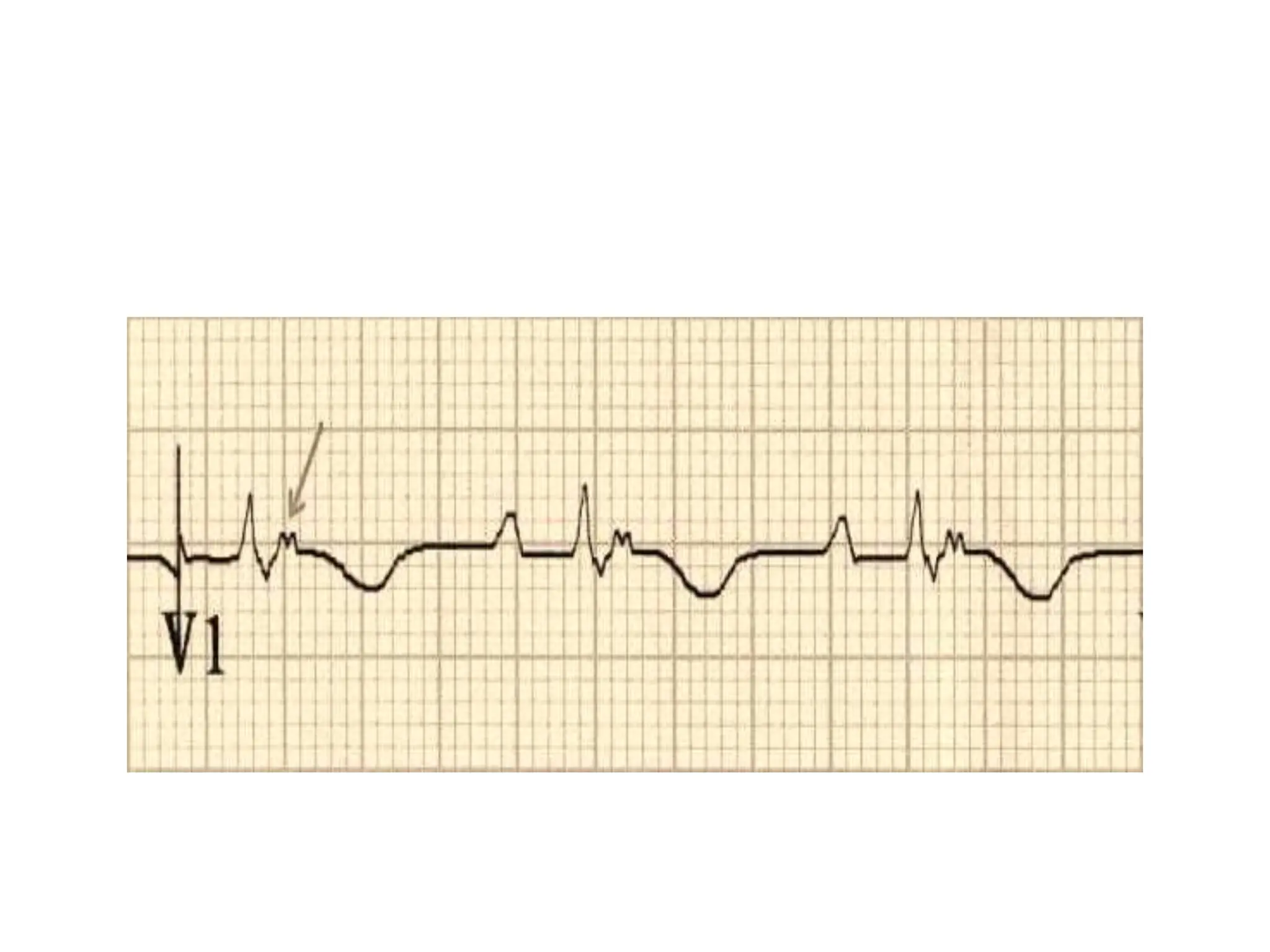

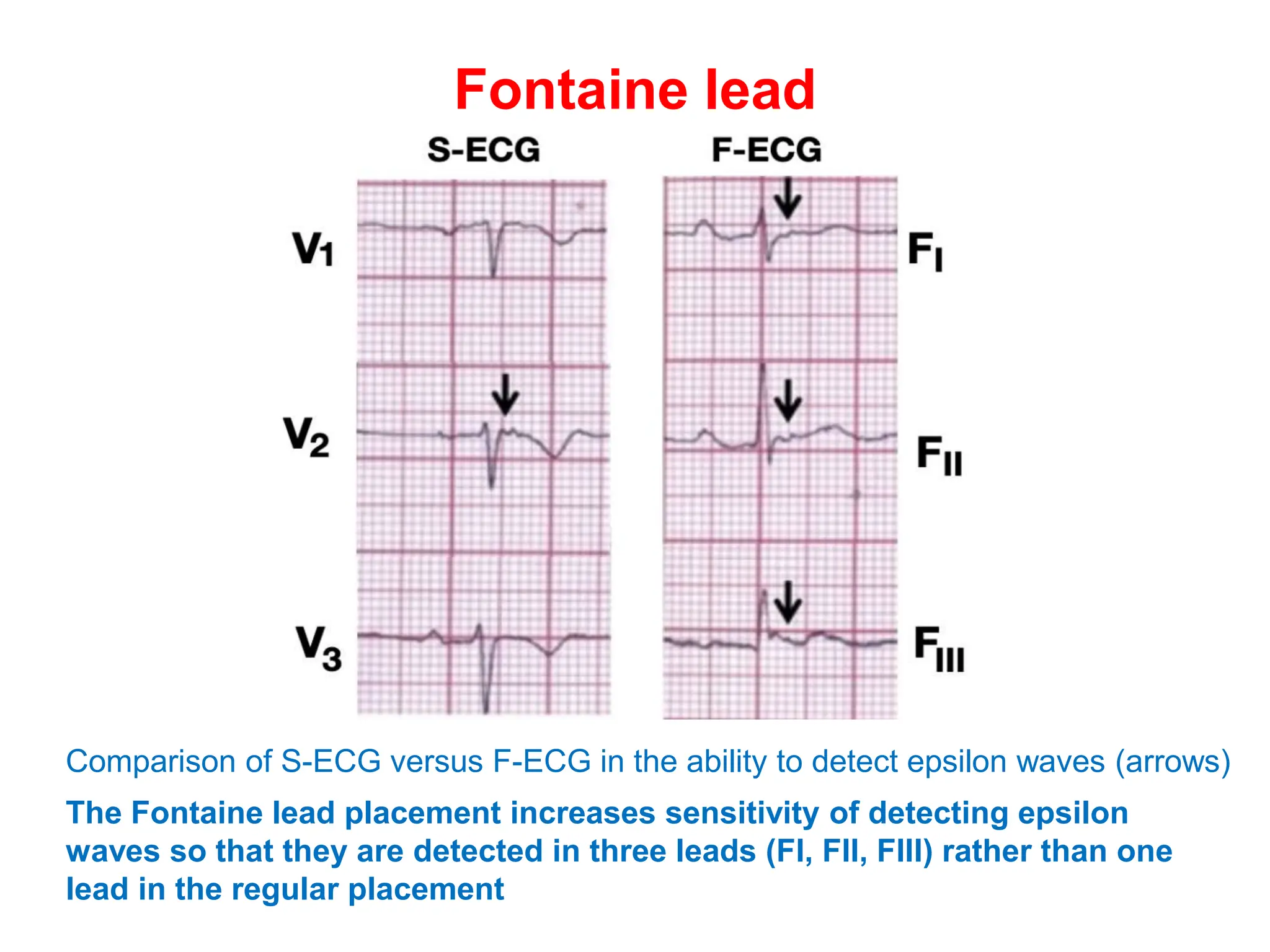
Epsilon waves are small deflections seen in the ST segment of leads V1 through V4 on an ECG. They are caused by delayed excitation of right ventricular myocytes. Epsilon waves are the most specific finding for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), a condition where right ventricular myocytes are replaced by fat. This replacement of myocytes by fat causes conduction delays in the right ventricle, producing the small epsilon wave deflections. Epsilon waves have also been seen in other conditions that cause right ventricular conduction delays or infiltration, such as infarction or sarcoidosis. Placement of Fontaine leads increases the sensitivity of detecting epsilon waves compared to standard ECG lead placement.







