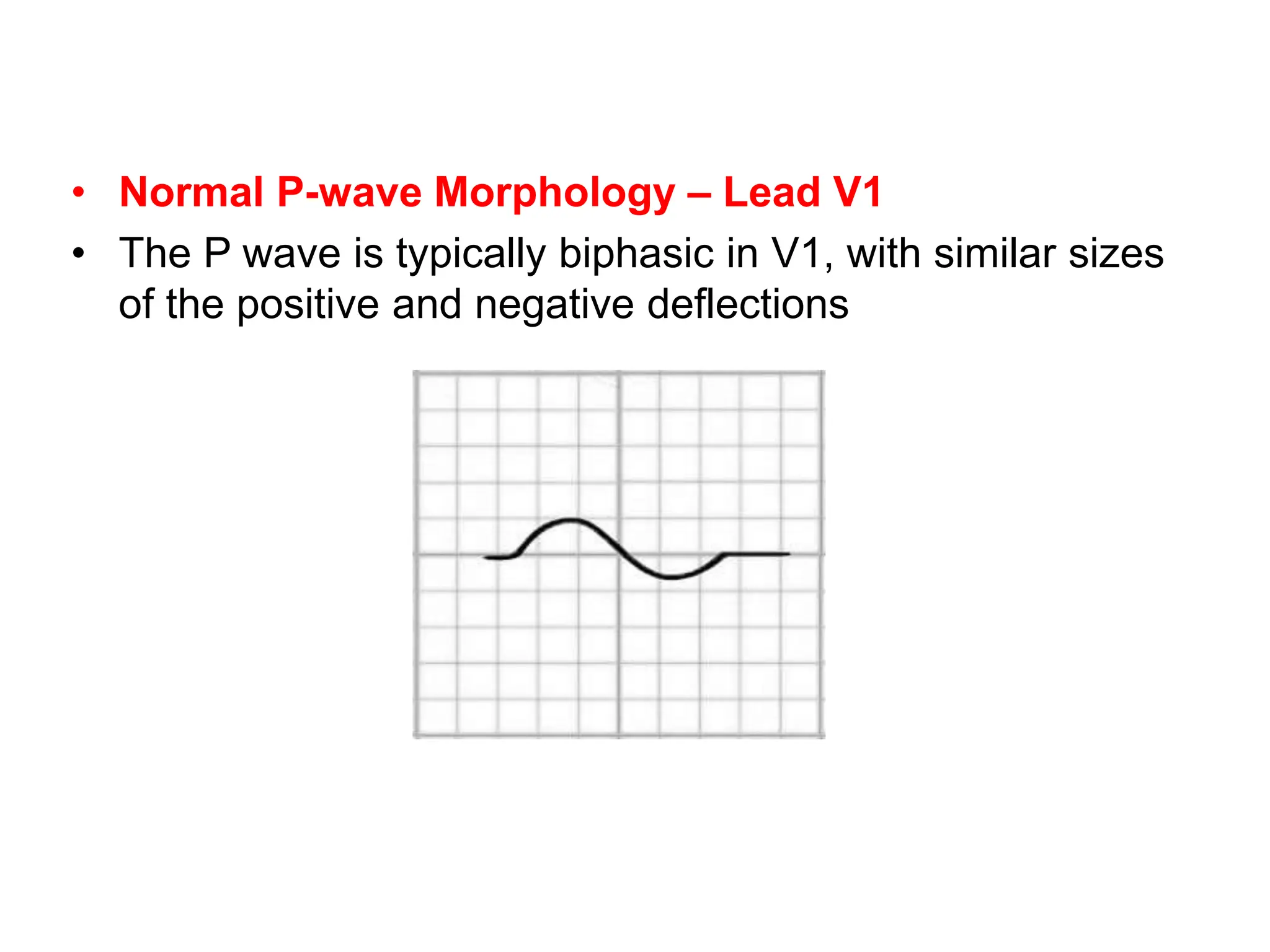
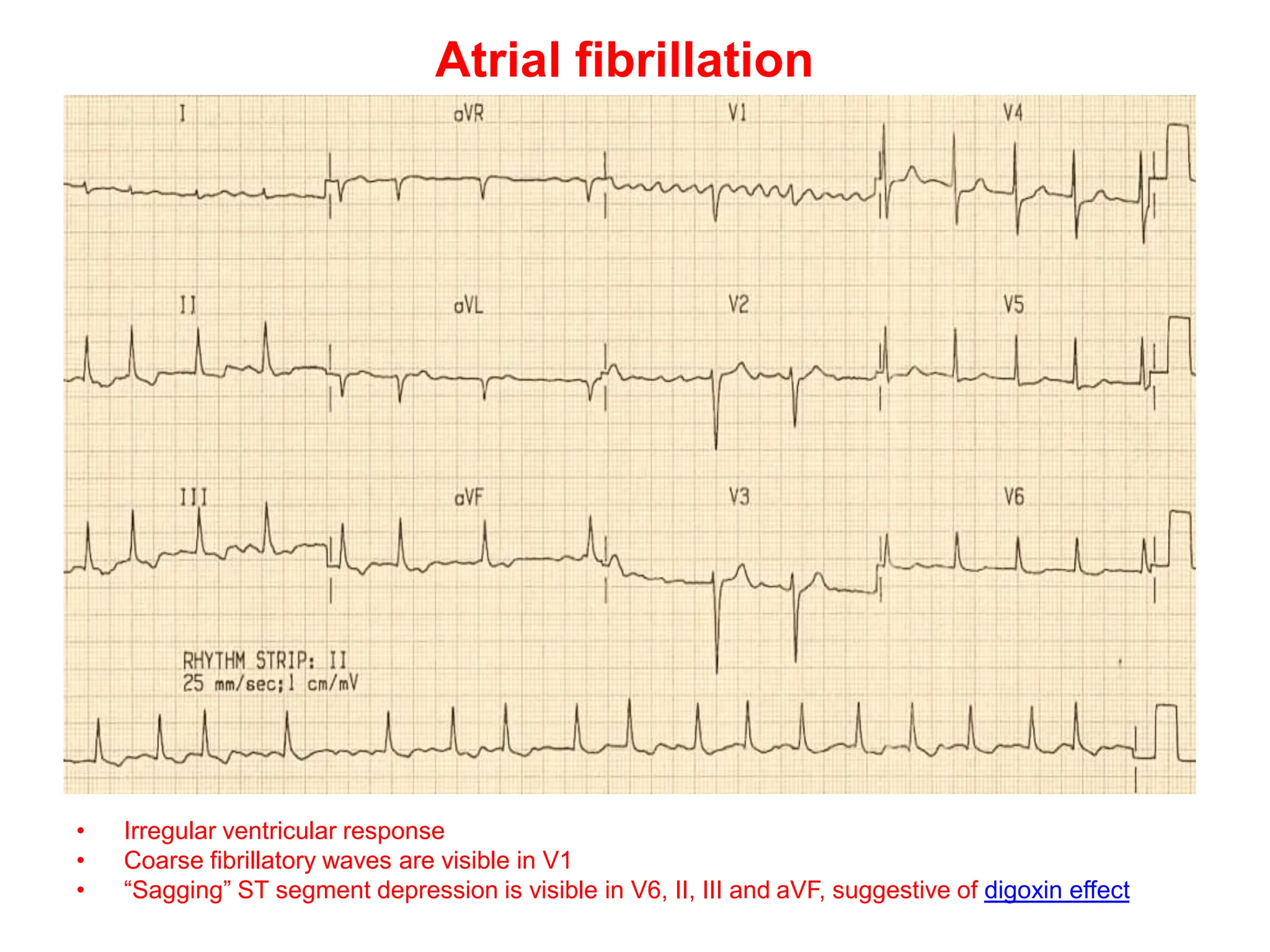
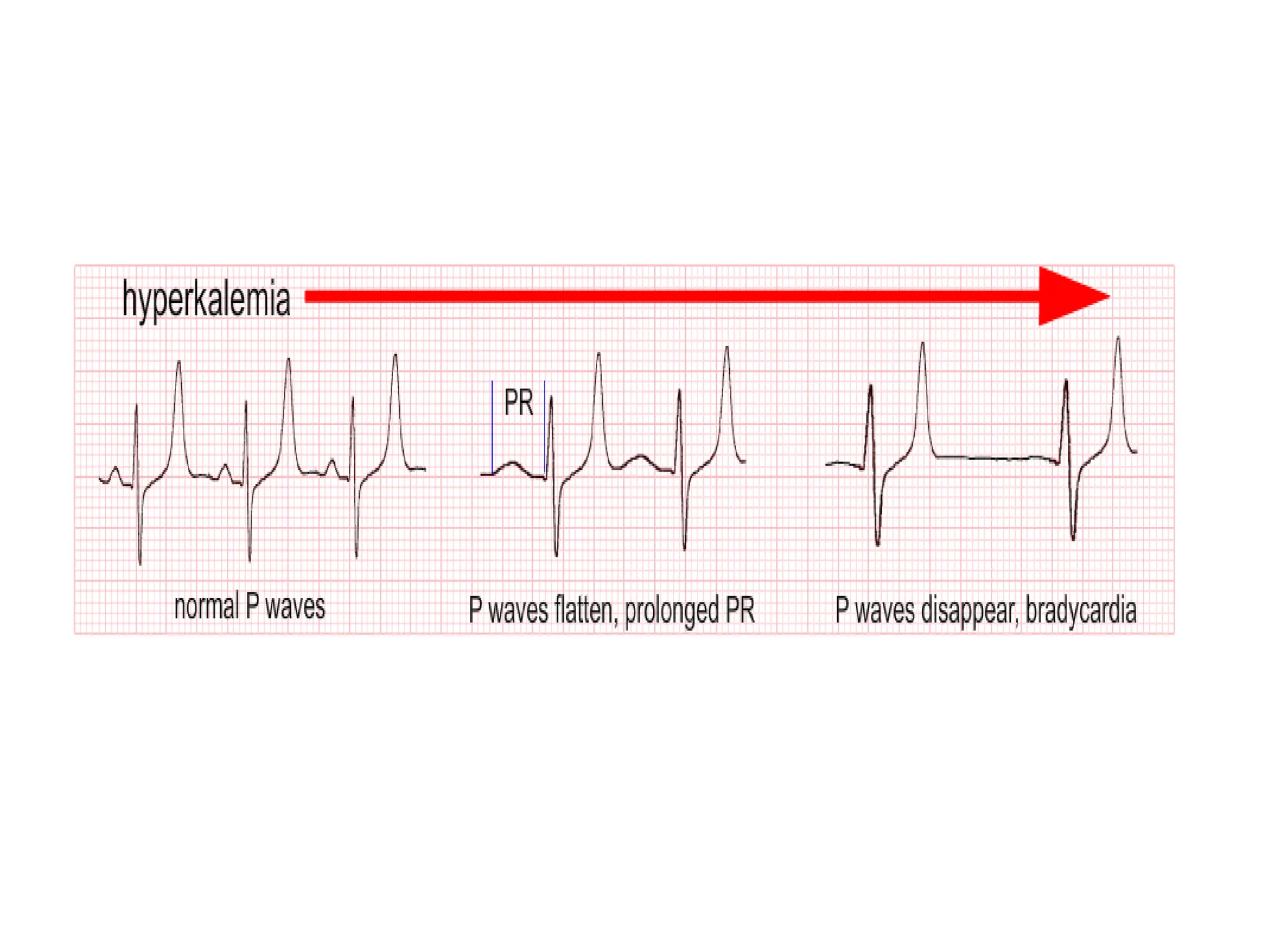
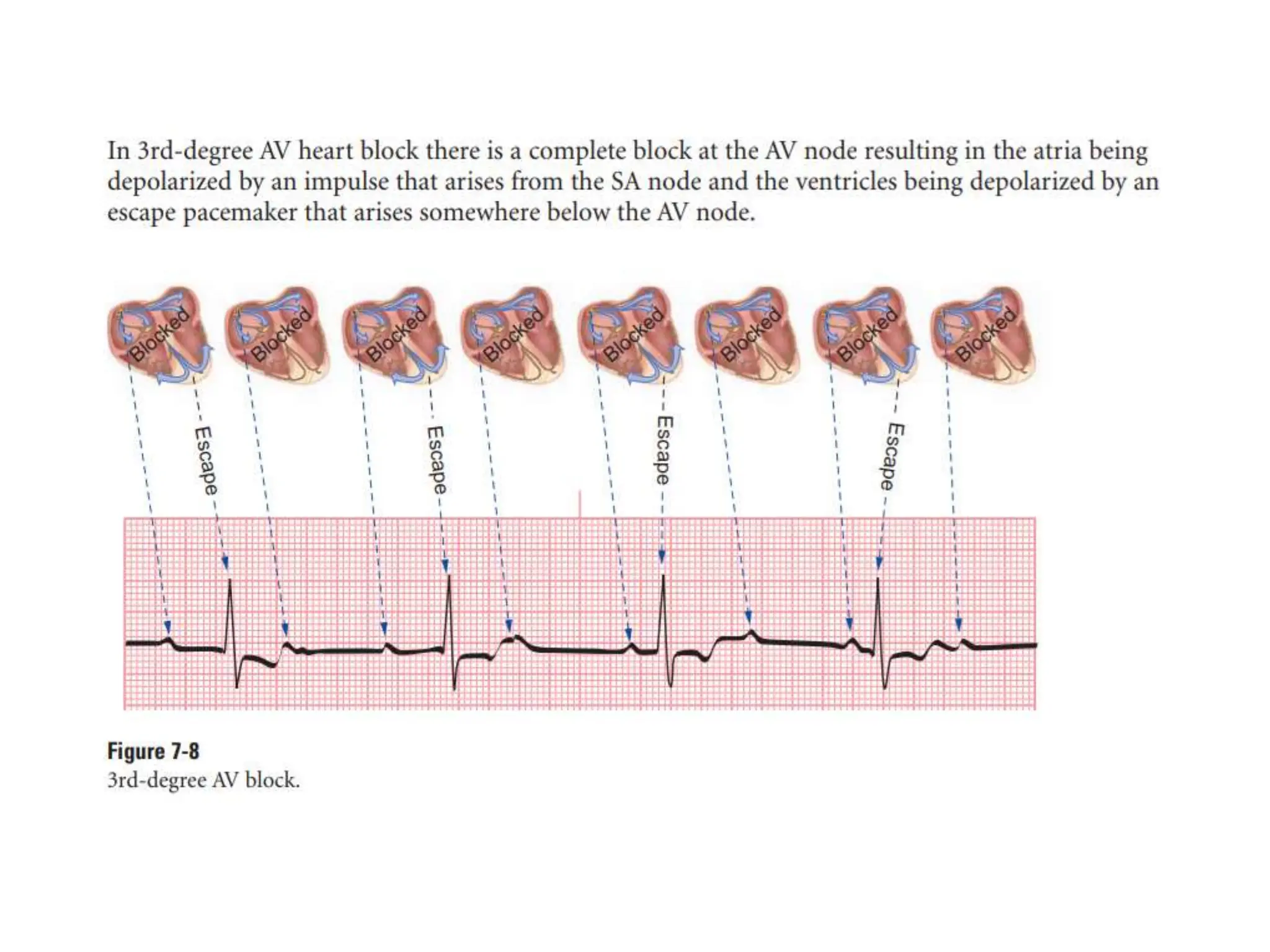
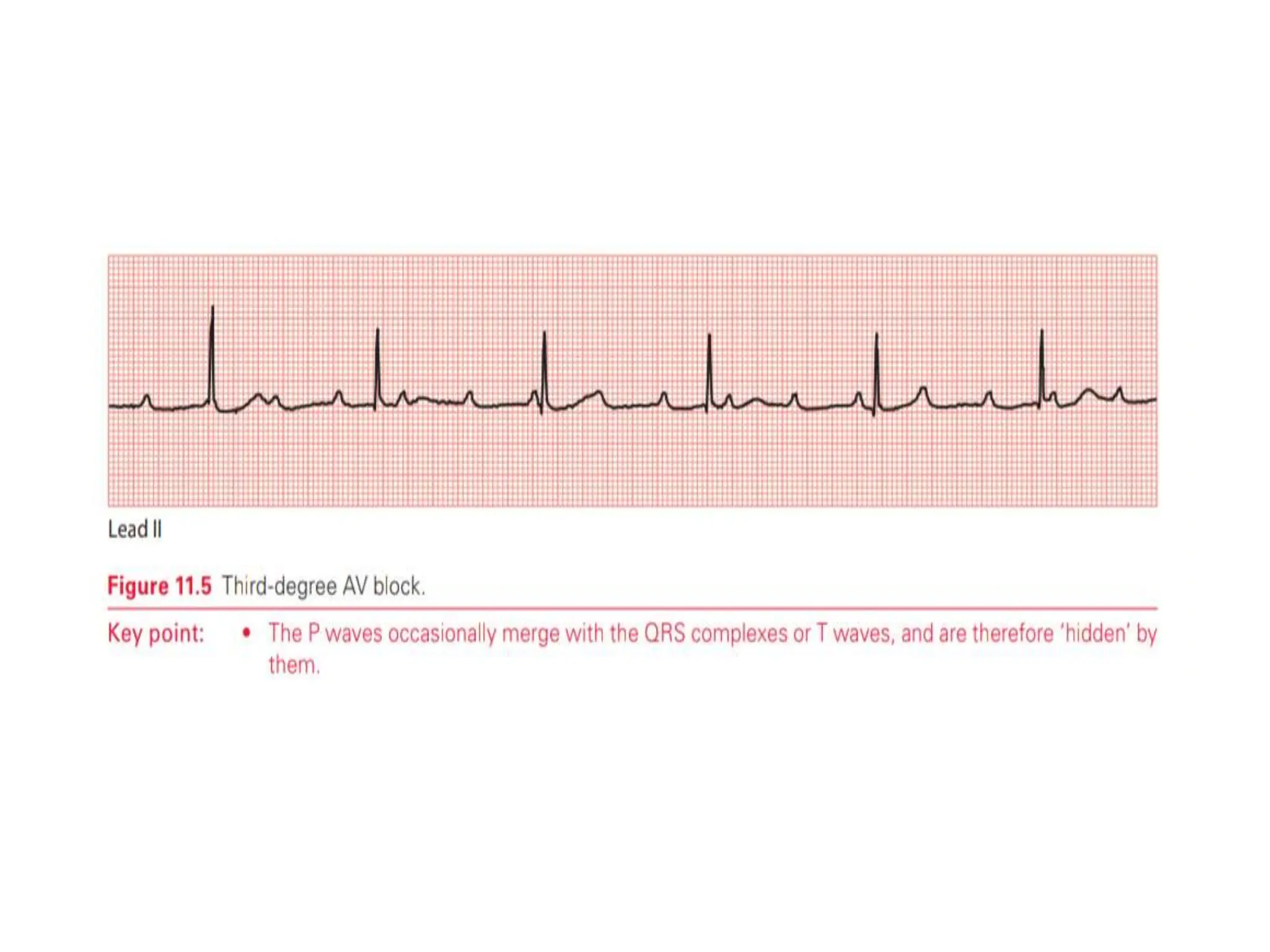
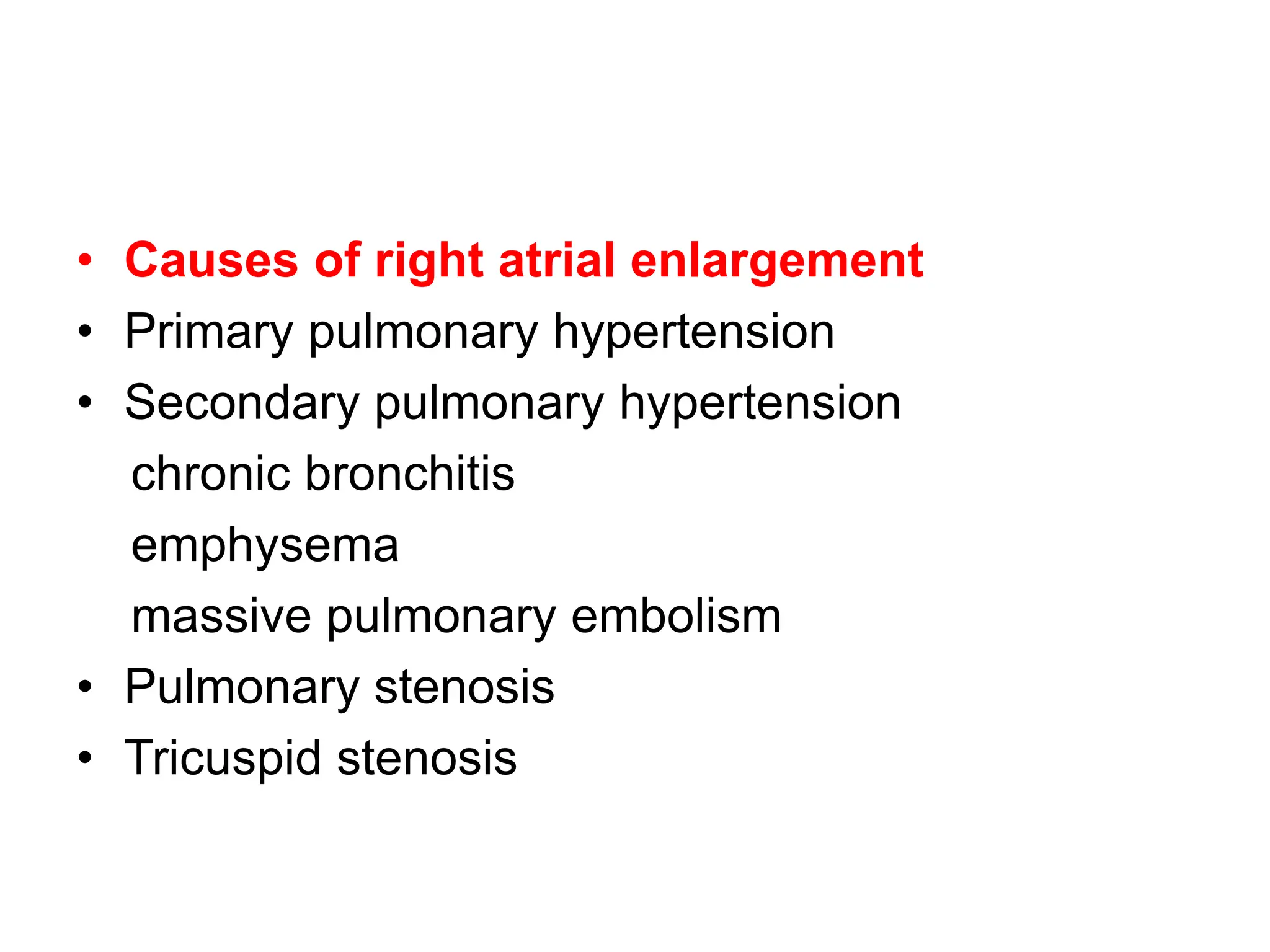
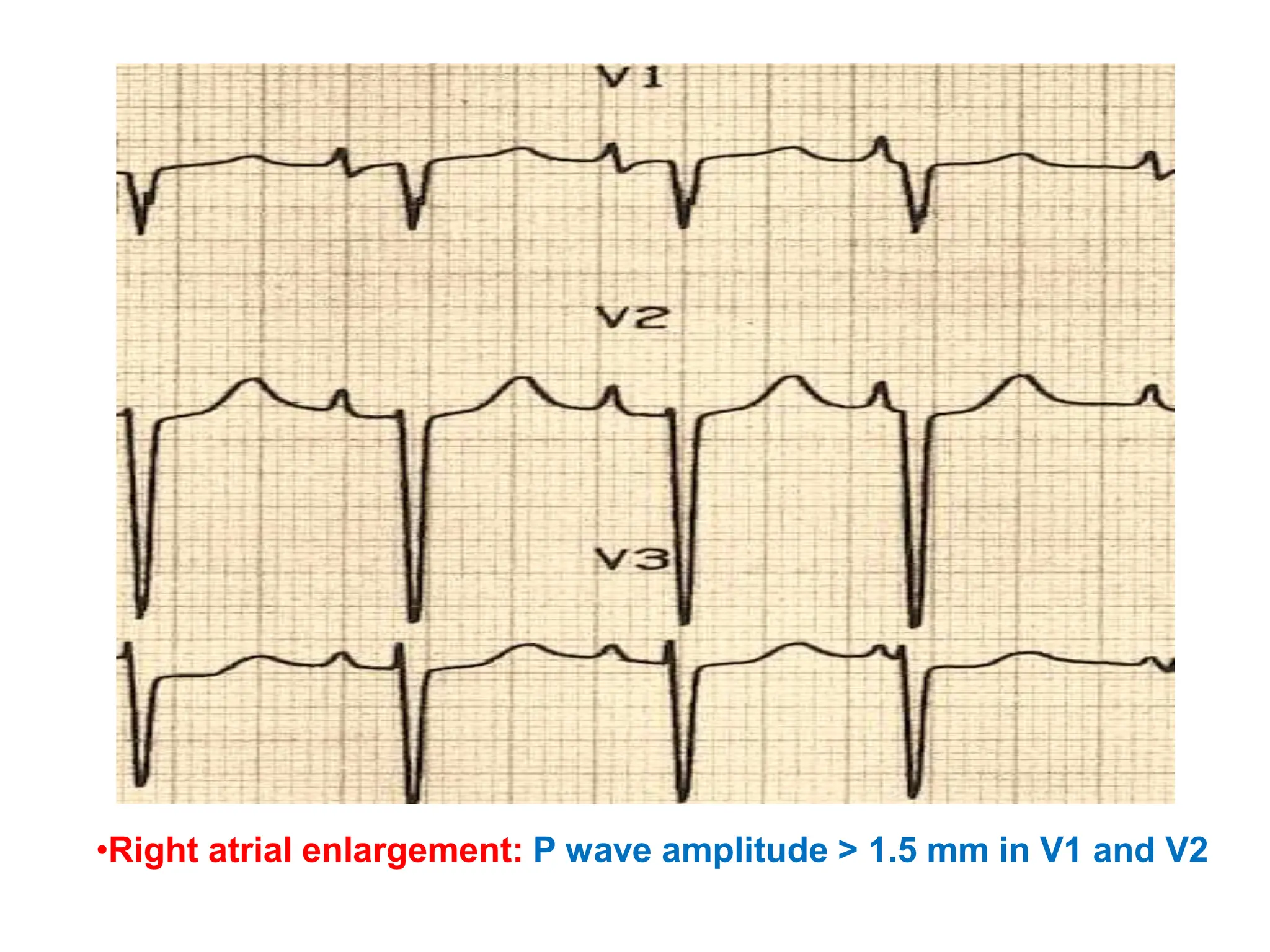
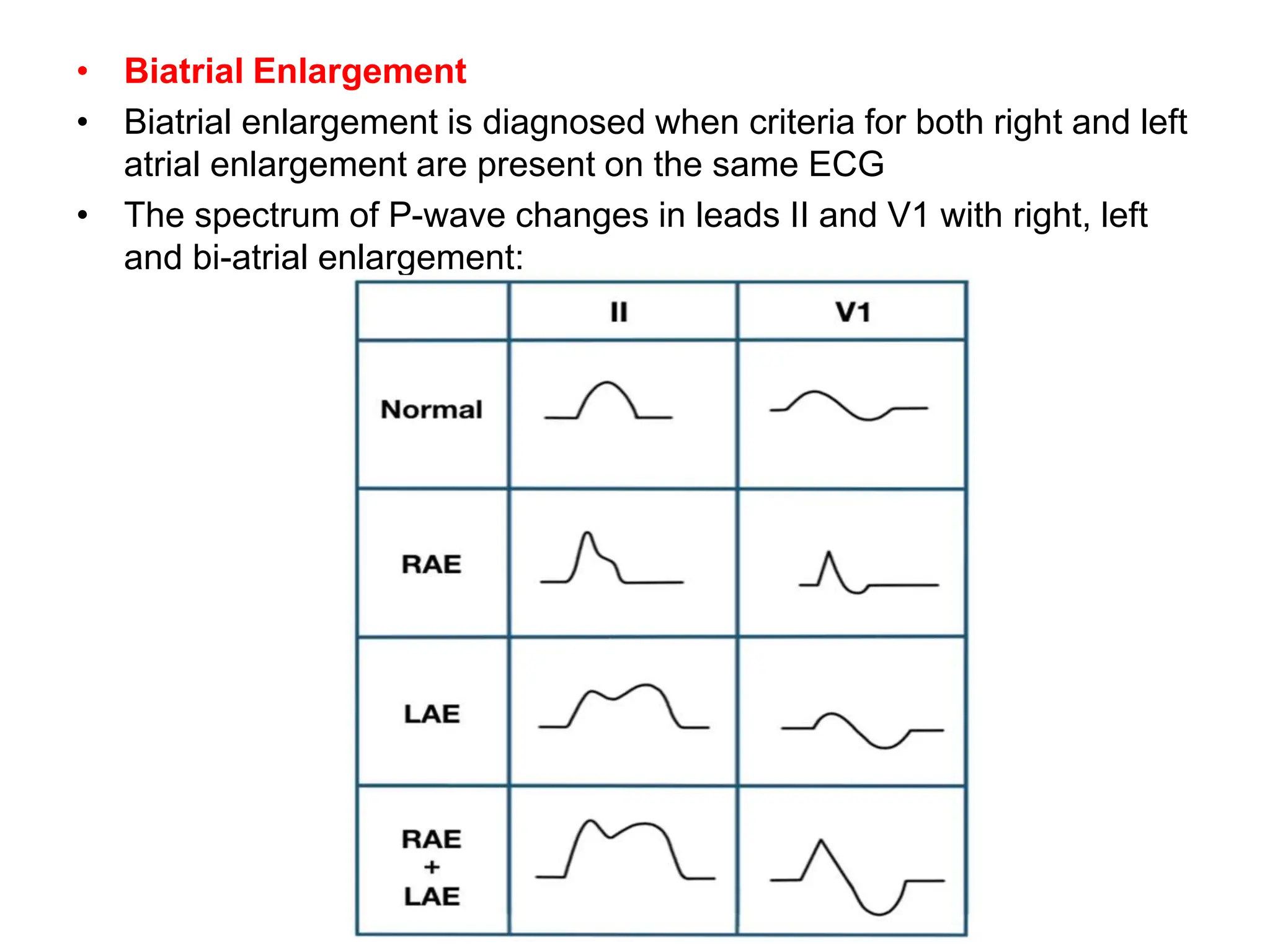
This document discusses the P wave on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It defines the P wave as representing atrial depolarization. It describes the normal characteristics of P waves including morphology, axis, duration and amplitude. It explains how right and left atrial depolarization summate to form the P wave. It discusses various abnormalities of P waves seen in conditions like atrial fibrillation, sinus arrest, right atrial enlargement and left atrial enlargement. It provides criteria for diagnosing enlargement of the right atrium or left atrium based on changes in the P wave.