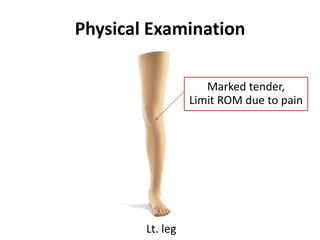
1) The patient is a 5 year 5 month old Thai boy who was brought in after a soccer goal post fell on his left knee. He reported pain, difficulty walking and bending his knee.
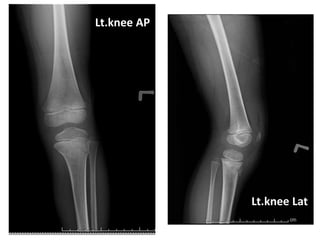
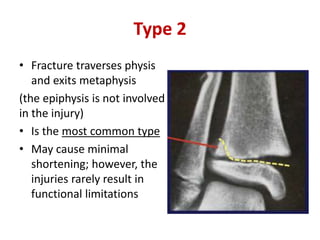
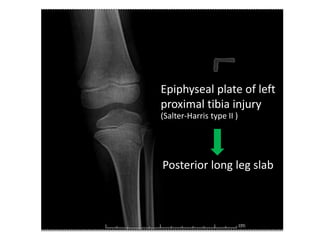
2) Examination found tenderness over the left knee with limited range of motion due to pain. X-rays revealed a Salter-Harris type II injury of the left proximal tibial epiphysis.
3) The diagnosis was an epiphyseal plate injury of the left proximal tibia (Salter-Harris type II). Treatment was with a posterior long leg slab.