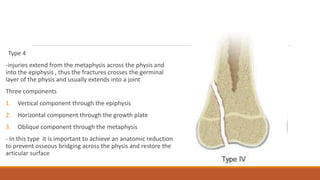
This document discusses epiphyseal (physeal) injuries in children, including:
- The Salter-Harris classification system divides physeal injuries into 5 types based on the location of the fracture through the growth plate. Types I-II are usually treated non-operatively while Types III-IV often require surgery.
- Complications of physeal injuries include growth arrest, which can cause limb length discrepancies or angular deformities. The goals of treatment are anatomic reduction and fixation that avoids further injury to the growth plate.
- Limb length discrepancies are addressed through shoe lifts for small differences or surgical lengthening for larger discrepancies once the child reaches maturity.