Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

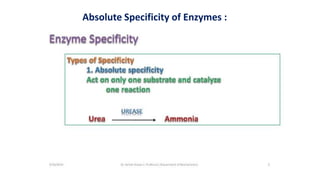
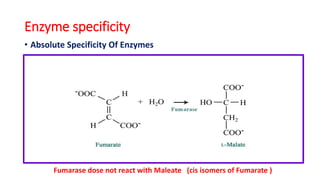
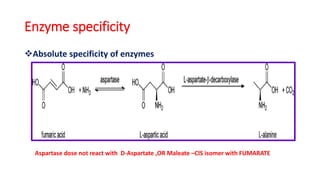
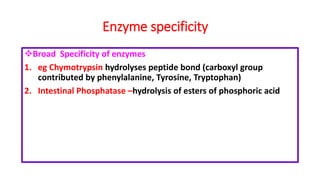
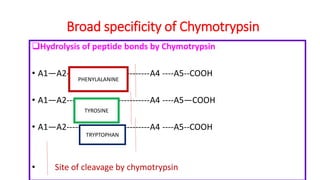
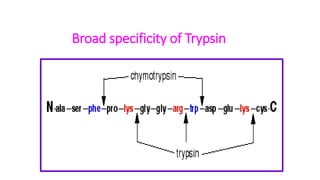
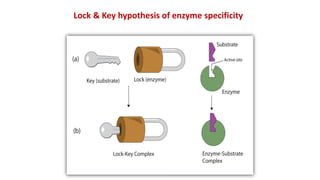
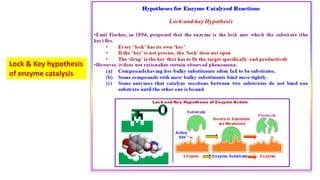
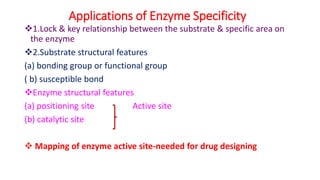
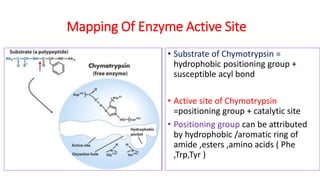

The document discusses enzyme specificity, outlining two types: absolute and broad specificity, with examples including fumarase and chymotrypsin. It explains the lock and key hypothesis in enzyme catalysis and the importance of enzyme active site mapping for drug design. The document emphasizes the functional and structural features of substrates and enzymes that contribute to their specificity.












