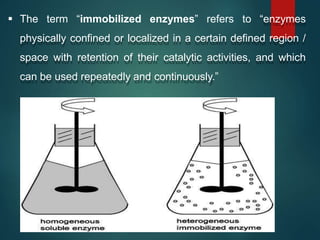
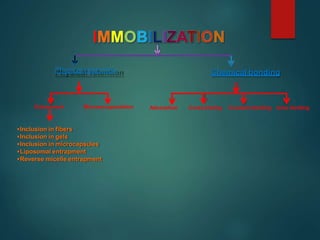
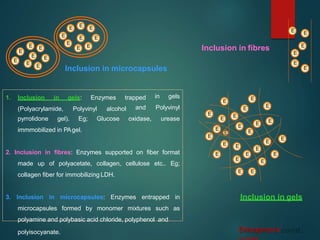
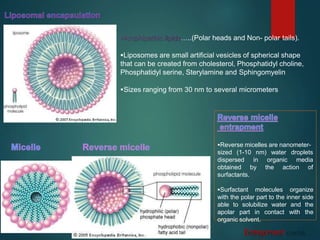
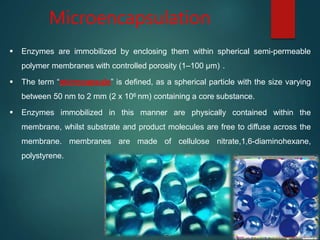
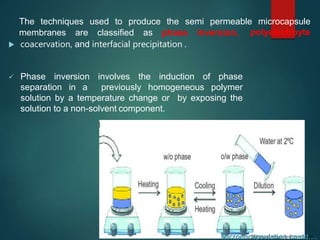
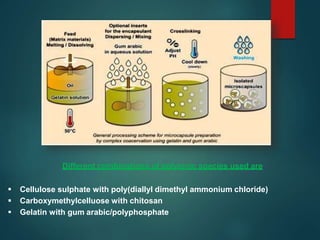
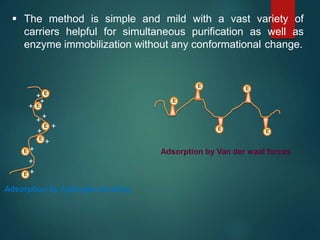
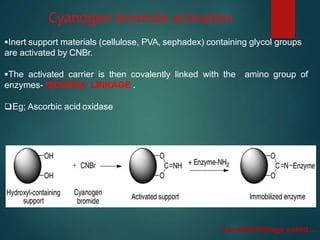
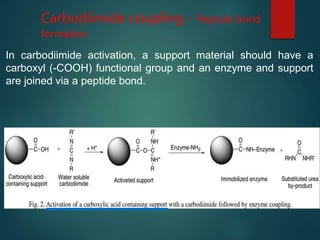
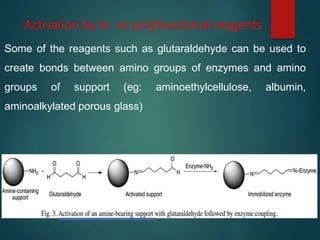
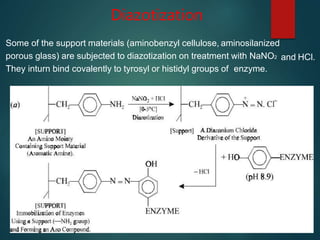
The document discusses enzyme immobilization, which involves confining biocatalysts to enhance their efficiency and reuse in various biochemical processes. It outlines the historical context, advantages, and disadvantages of enzyme immobilization methods, including entrapment, microencapsulation, and carrier binding, highlighting specific applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Additionally, it examines the techniques used for immobilization and the importance of maintaining the enzymes' activity while preventing contamination.