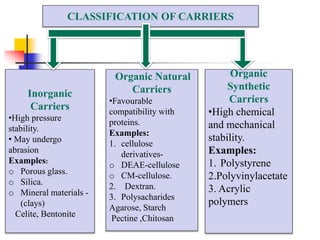
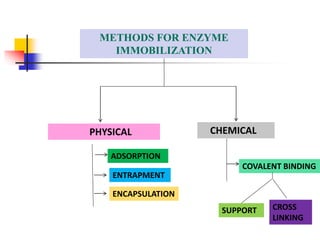
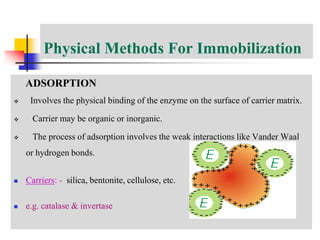
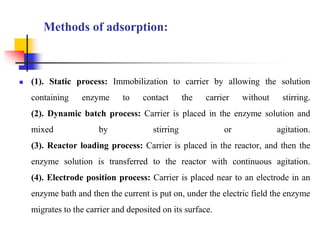
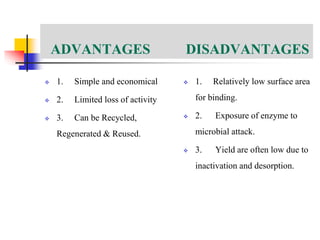
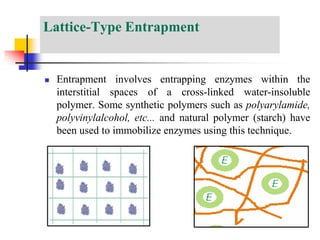
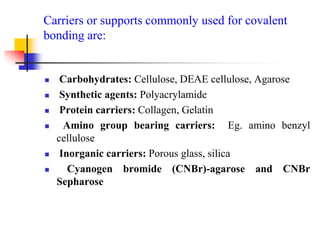
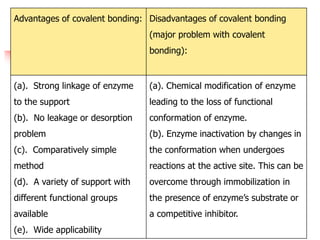
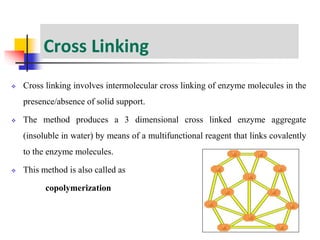
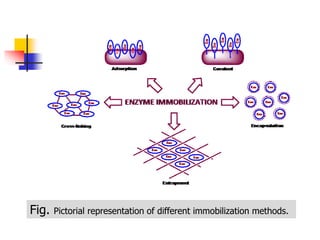
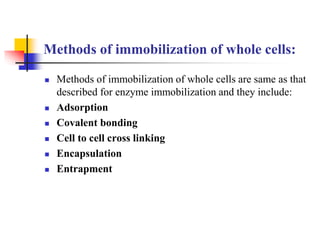
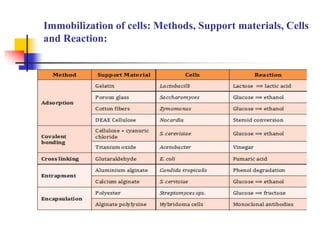
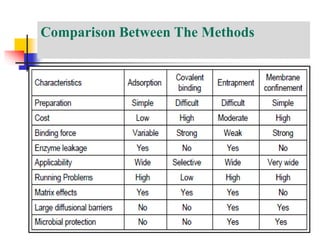
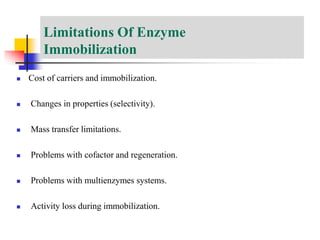
An immobilized enzyme is one that has restricted movement, confined to a solid support to enhance stability and facilitate substrate conversion. Enzyme immobilization offers various benefits, including protection from degradation, reusability, and easy separation from products, through methods such as physical adsorption, entrapment, and covalent binding. Whole cell immobilization is another approach that maintains enzyme activity within their natural environment and is effective for fermentation processes, although it may produce unwanted byproducts.