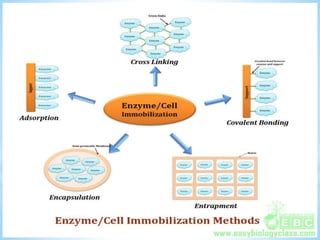
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are proteins and greatly increase the rate of biochemical reactions. They contain an active site that converts substrates to products. Enzymes accelerate reactions by lowering the activation energy required for substrates to reach the transition state. This is achieved through the enzyme-substrate complex. Immobilizing enzymes makes them reusable and more stable while reducing costs. Common immobilization methods include entrapment in a polymer matrix, microencapsulation, adsorption, covalent binding, and cross-linking to a support. Enzyme applications include medical, analytical, manipulative, and industrial uses.