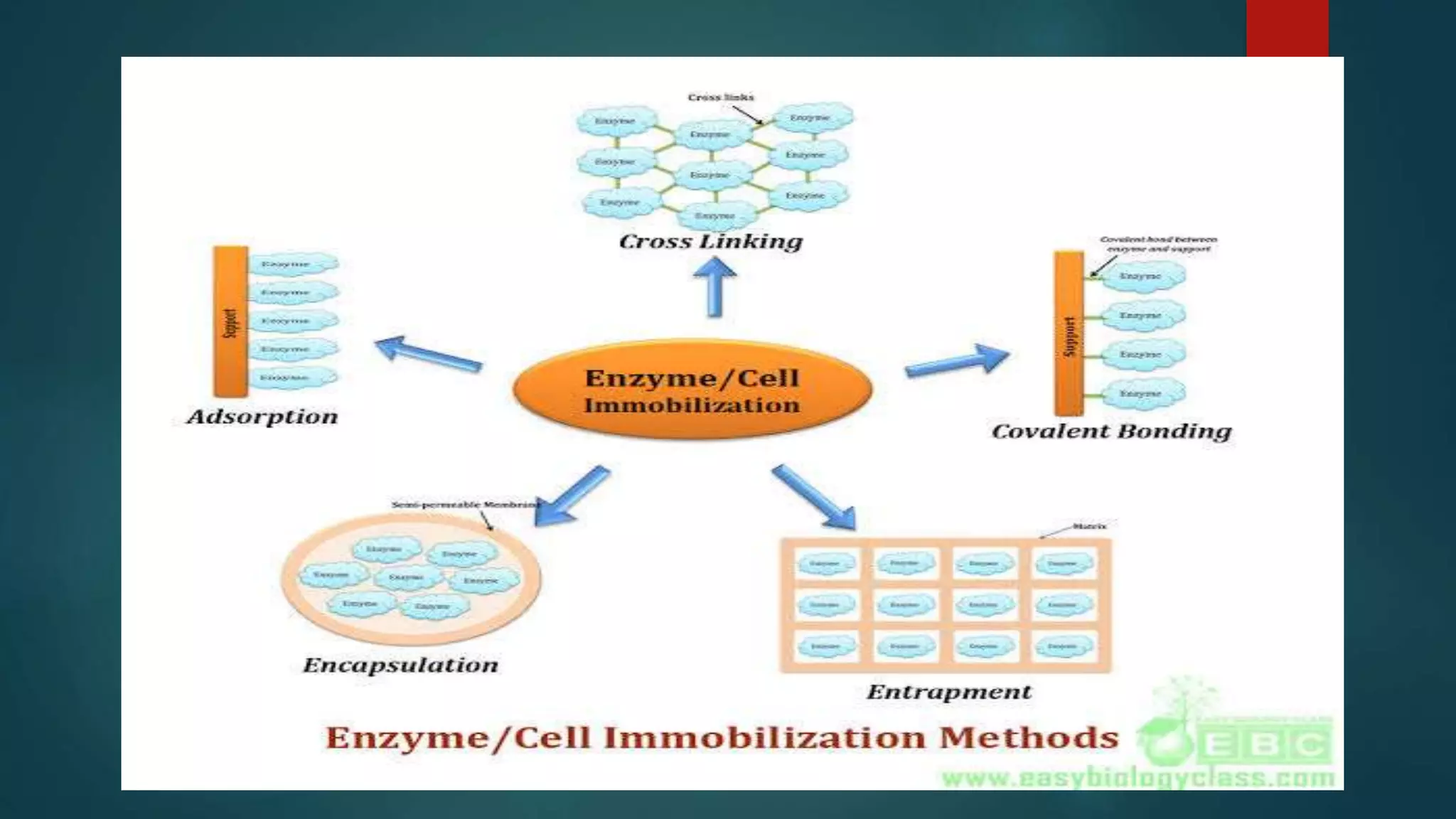
The document discusses various techniques for immobilizing enzymes and cells, detailing methods such as adsorption, covalent binding, cross-linking, entrapment, and encapsulation. It highlights the advantages of enzyme immobilization, such as increased stability and ease of separation from products, along with disadvantages like potential loss of catalytic properties and high costs. Additionally, it describes the implications of immobilizing non-viable cells for industrial applications and the associated benefits and drawbacks.